III. Model specification of
willingness to pay
To measure WTP, this paper uses the contingent valuation
method consisting of directly asking respondents the amount they are disposed
to pay for a potential scenario of improving local leadership aiming for
instance at fighting against its disappearance or to anticipate its damageable
parts. It is an enquiry-based method frequently used to measure the monetary
value on non-market environmental good and services (Djemaci, 2010). Here, the
method is set on a referendum enquiry.
The method «contingent valuation» requires that
replies recorded follow a bidding scenarios process. Proposed scenarios are
possible but not certain to occur since they vary from an individual to
another. Contingent valuation entails a change in the notable's utility that
can be monetary valued and obtained by the maximum amount that a respondent
accepts to forgo for achieving a given good. Le Gall-Ely (2010) views CVM as a
surveying method helping to capture some psychological price. In such a case,
deems Le Gall-Ely (2010), biases are higher resulting from an overestimation of
WTP. However, previous scholars suggest that questions referring to starting
price have yielded more considerable results than open-ended questions
(Donaldson et al., 1997) cited by Dror, Radermacher and Koren et al. (2006).
«Take-it-or-leave-it» method is basically viewed as a dichotomous
trade-off on suggested amounts. In fact, Dong et al. (2004) deemed that
variance in responses results from some extent from the selection by
respondents. The biding game consisting of presenting several prices varying
from relatively higher to lower prices and the respondent choses if he is ready
to pay a given set biding price, a process realized on all alternatives until
the respondent accepts the bid.
Moreover, the interval regression method was applied to assess
WTP in various WTP assessment studies. In that boat it is used to estimate
hypothetical values of the real goods or/and services (Lang, 2010). The method
as developed by Hanemann is advised when the correlation coefficient exceeds
0,7 (Alberini, 1995) instead of the bivariate probit model initially
established to measure WTP. It is set on the response between the first and the
second bid (Corso et al., 2013; Labii, 2015).
As dummy questions are asked in the survey, it is suggested an
amount to an individual. If the individual accepts to disburse under that
price, a higher amount is directly advanced for his trade-off. On the other
hand, if he rejected the first bid, then a lower amount is immediately proposed
under his trade-off.
Furthermore, based on how the model was specified by Corso et
al. (2013) when assessing the benefits of preventing child maltreatment death
in Ecuadorian population and, also, its adoption by Labii (2015);the current
research model evolves as follows:
The WTP value,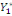 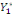 of of   individual is translated by the model individual is translated by the model 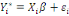 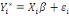 where where 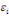 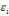 is a random disturbing term and normally distributed with a mean zero
(hypothetical) and is a random disturbing term and normally distributed with a mean zero
(hypothetical) and 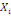 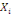 corresponds to individual respondent characteristics. As corresponds to individual respondent characteristics. As 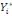 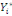 is not direclty observed, the respondent's WTP interval location lies
between both bounds is not direclty observed, the respondent's WTP interval location lies
between both bounds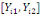 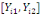 . Then, the corresponding likelihood contribution becomes: . Then, the corresponding likelihood contribution becomes:
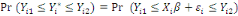 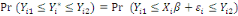 (1) (1)
When an upper bound is unknown, that is the right-censored
data is unknown; the likelihood affected is
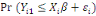 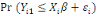 (2) (2)
Whereas when a lower bound (left-censored), a lower bound is
set at zero and the likelihood contribution is:
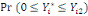 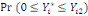 (3) (3)
From there is taken out a summarizing situation of all
possibilities to be registered over the bids. Four patterns are classified from
the dichotomous trade-off: «Yes» to both the first and the second
question (Y, Y), «Yes» to the first question and «No» to
the second proposing a higher amount(Y,N); «No» to the first and
«Yes» to the second (N,Y), in case the lower value, and
«No» to both values (N,N).
Scenarios imply the following likelihood distribution
according to measuring WTP. But before proceeding, let's assume an individual
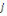 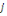 to whom is fist propose an amount to whom is fist propose an amount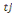 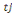 . If admitted, a higher amount . If admitted, a higher amount 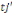 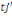 is again proposed. In contrast, if the first was not accepted, a lower
amount is again proposed. In contrast, if the first was not accepted, a lower
amount 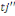 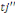 is then advanced. is then advanced.
Ø When both answers are positive, that is to say that
the individual  's willingness to payis higher than 's willingness to payis higher than 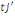 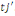 Differently said, the superior bound is unknown; data are
right-censured and the likelihood ( Differently said, the superior bound is unknown; data are
right-censured and the likelihood (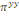 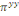 ) noticed that their WTP to be located in the interval is ) noticed that their WTP to be located in the interval is
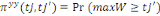
Ø If then the first answer is positive and the second
negative (accounting for the upper bound), willingness to pay is located
between the lower bound 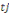 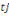 and the upper bound. And the associated likelihood is given by and the upper bound. And the associated likelihood is given by 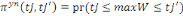 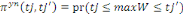
Ø Therewith, if the first answer is no and the second
no to both bids, one's willingness to pay is under 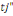 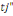 and the likelihood to and the likelihood to 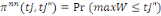 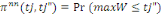
Ø At last, when the individual   answers no to the first and yes to the second, it means his maximum WTP
is located between answers no to the first and yes to the second, it means his maximum WTP
is located between   and and 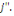 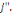 In the context, the likelihood of locating WTP in the interval is given
by In the context, the likelihood of locating WTP in the interval is given
by 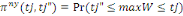 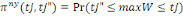 . .
| 


