V.3.2 Estimation
Les estimées xne(k) peuvent être
obtenues de manière récursive en utilisant les mesures pour
améliorer les variables prédîtes
xnp(k). La correction aux
prédictions est proportionnelle aux résidus des mesures :
x n e ( k + 1) = x nP
(k + 1) + K( k + 1) [ z( k + 1)
- H . x nP( k + 1) ] (V.32)
K(k+1) est la matrice de gain de Kalman
[ z ( k + 1) - H .x n P
(k + 1)] est le vecteur d'innovation, et
|
H
|
?li[
|
x n(k ),k ]
|
(V.33)
|
|
?xn
|
Pour le choix de la matrice de Kalman K(k+1), nous devons
définir les erreurs d'estimation ee et de prédiction
ep respectivement :
e e ( k + 1) = x
e ( k + 1) - x n ( k + 1)
(V.34)
e P ( k+ 1)= x
np ( k + 1) - xn( k + 1)
(V.35)
Ses matrices de covariance associées sont :
P P ( k + 1) = E [ e
P ( k + 1) . e P ( k + 1)
T ] (V.36)
P e ( k + 1) = E[ e
e ( k + 1) . e e ( k +
1)T ] (V.37)
Donc, la matrice de covariance de I'erreur d'estimation
Pe, devient :
P k [ ] [ ] T T
+ = -
I K k H P k I K k H K k R K k (V.38)
e ( 1) ( 1) . ( 1) ( 1)
+ + - + + +
( 1) . . ( 1)
+
P
ou R est la covariance de I'erreur de mesure, définie par
(V.26).
Il est possible de choisir la matrice de gain K(k+1) de
manière a minimiser les variances des erreurs d'estimation des
éléments du vecteur d'état qui est estimé. Dans ce
cas la K(k+1) est appelée matrice de gain de Kalman. Alors
?trace { P( k + 1) } = 0
? K ( k +1
(V.39)
)
nous obtenons ainsi la matrice de gain de Kalman :
T T
[ ]1
-
K k P k H HP k H R
( 1) ( 1) . . ( 1) .
+ = + + + (V.40)
P P
Avec cette expression, nous avons la matrice de covariance de
l'erreur d'estimation :
P k
( 1 ) [ ( 1 ) ] . ( 1 )
+ = -
I K k H P k
+ + (V.41)
e P
Le calcul de K(k+ I) et de Pe (k + I ) a besoin de la
matrice de covariance Pp(k+1), donc :
P k
( 1) ( ) . ( ) . ( ) ( )
+ = F k P k F k Q k
T + (V.42)
P e
Où :
|
? f
|
{ x k u k k
( ) , ( ), } {
? f x k u k k
( ) , ( ) , }
n n
|
? S ? S
1 2
1 0
= x k
( )
ne ? 0 0 1
F k
( )
? x k
n ( )
x k n ( )
1
?
?
?
?
? ]
(V.43)
{ x k u k k }
n ( ) , ( ) ,
? f
AD k
( )
0
et Q(k) est la covariance de l'erreur du modèle,
défini par (V.23) et calculée de la manière suivante :
tk + 1
Q k
( ) = ? ö ( 1 , ) ( ) ( 1 , )
tk + ô ô ö
Q T tk + ô d ô (V.44)
tk
ou Ô( t k +1.,ô ) est la matrice de
transition associé a F(T ,xn(z )) pour z E [k,k + I ]
. Ensuite, Q(k) est calculée par
intégration trapézoïdal :
Q k
( ) ( 1, ) . . ( 1, )
= ö +
[ k k Q k k Q
T + ] T 2 e
. (V.45
0 ö + 0
V.3.3 Calcul de F(k) et H(k) ? h x k
k
[ ] r 1 0 0 0 0
n ( ),
H = = (V.46)
?L ?]
? x 0 1 0 0 0
n
? AD k
( ) F k F k
1 ( ) ( ) 1
5
? ?
F k F k
6 Ò
? 2 ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) Ò
3 7
? F k F k
F k
( ) = ? ? (V.47)
F k F k
( ) ( )
? 4 8 Ò
? 0 1 1 Ò
?? ??
? ?
où :
|
? di ds
F k
1 ( ) =
? S 1
|
? di qs
, F k
2 ( ) =
? S 1
|
? di dr
, F k
3 ( ) =
? S 1
|
? di qr
, F k
4 ( ) =
? S 1
|
, (V.48)
|
? di ds
F k
5 ( ) =
? S 2
? di qs
, F k
6 ( ) =
? S 2
? di dr
, 7 ( ) =
F k
? S 2
? di qr
(V.49)
, F k
8 ( ) =
?S2
|
Valeurs initiales de :
- Vecteur d'état xn0=xn(t0)
- Matrices de covariance Q=Q0
R=R0
P0=P(t0)
Prediction du vecteur d'état x np (
k + 1) = f[x ne( k ), u
( k ), k ]
|
?f(xn
Linéarisation du mdèle augmenté F (
k) =[AD(k)
0 ? n ?S2
1
Calcul de la matrice de covariance p ( k 1)
F ( k ) p ( k ) F ( k )
T Q ( k )
+ = +
p e
d'état
Calcul de la matrice de gain de Kalman [
T ]1
-
K k
( 1) ( 1) .
+ = P k H HP k H R
T
+ . ( 1) .
+ +
P P
Estimation xn e ( k + 1) =
xn P ( k + 1) + K ( k + 1) [
z ( k + 1) - H . xn P (
k + 1) ] du vecteur d'état
Calcul de la matrice de covariance ( 1 ) [ ( 1 ) ] . ( 1 )
P k + = -
I K k H P k
+ +
e P
De l'erreur d'estimation
Retour à la prédiction
xne(k)=xne(k+1)
Pe(k) = Pe(k+1) k=k+1
I
i


( ), u ( k ), k)k
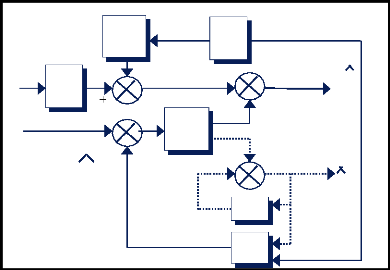
u(k)
1)
AD
1
-
q
+
+
X(k+1)
BD
+
+
K(k+1)
+
-
+
Z(k+1)
e(k+1)
AD
H
k)
X(k+1)
Tableau (V.1) : Algorithme du filtre de Kalman Etendu
| 


