2.3.4.9. Dobryakov et al. (2008)
Gas outlet
Inert gas inlet
Capillary tube
In order to investigate infinite dilution activity coefficient
of alcohols in three different ionic liquids, Dobryakov et al. (2008)
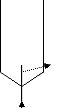
constructed a 5 cm3 dilutor cell which was filled with 3
cm3 of solvent during experiments. Their still which is shown in
figure 2-10 used a single capillary tube plumbed in at the bottom as a
dispersion device. Measurements were done with inert flow rates between 8 and
20 cm3. min-1.
Figure 2-10: Dilutor cell designed by Dobryakov
et al. (2008). 2.3.4.10. Kutsuna and Hori (2008)
Drawing inspiration from previous work by Lei et al (2007a)
and Shunthirasingham et al. (2007), which established that the IGSM led to
inaccurate Henry`s law constants in case of semi-volatile and surface active
solutes, particularly when small gas bubbles such as those with < 1 mm in
radius were used, Kutsuna and Hori (2008) proposed the design shown in figure
2-11 and photograph 2-1. They determined Henry`s law constants of
perfluorooctanic acid (PFOA) in aqueous sodium chloride and sulfuric acid
mixtures. To deal with semi-volatile and surface active solutes, their design
incorporated a helical plate that increased the residence time. In addition,
the dispersion device allows the formation of larger bubbles. Kutsuna and Hori
performed experiments with 300 cm3 of solvent in the dilutor cell,
achieving a residence time of 15 seconds and using bubbles larger than 3 mm in
radius and an inert gas flow rated as high as 80 cm3.
min-1. Photograph 2-1 shows bubbles rising up along the underside of
the glass helix from the bottom to the top of the solution placed in the
cell.
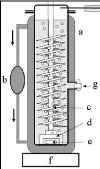
Figure 2-11: The dilutor cell designed by
Kutsuna and Hori (2008).
a- Jacketed Duran glass column; b-
Temperature-controlled water circulator; c- Gas-
introduction tube with a
glass helix; d- Polytetrafluoroethylene support; e- Magnetic bar;
F-
magnetic stirrer; g- Sampling port for injection.

Photograph 2-1: The helical plate used in the
dilutor cell designed by Kutsuna and Hori (2008).
Chapter 3: Theoretical considerations
| 


