3. QKD protocols
QKD in short mean Quantum Key Distribution was
invented by Bernett and Brassard in 1984,
this innovation was recognized as a main key-technology for our century. There
are many questions which are still asked like you can see in the publication of
[SRS12]. QKD use same classical notions learnt from public-key cryptosystem
such as management of keys and their creation, the activation, assignment,
building (to identities), escrow, as well revocation and destruction. The
experiment of QKD did with people and organisation, like work of Tanaka et
al. in 2008. It shows that the randomness for QKD keys still a vital
security of subsequent applications based on these keys. Till now, this field
has many questions which brings innovations in security science. In this
section, we will try to focus our mind in QKD protocols, give details relate to
the basis of each protocols. As we showed it previously, such technic requires
a knowledge in quantum mechanic, particularly in light.
3.1 QKD with classical notion
That QKD is a new tool in the toolbox of cryptographers, does
not excludes classical notion for security concepts as defined in other
section. To share data, informations or messages using QKD, we need to use
cipher; most of the times the QKD network uses One-time-Pade1
cipher. For interaction between different parties, we may need to establish
three mains phases to secure communication; this is deeply explained in the
litterature of [SML10]
1. Key agreement : This phase is about the agreement of sharing
private key between parties
2. Authentification : Second phase is to be sure that the
message received comes from a particular party to avoid the attack of
man-in-the middle2
3. Key usage : Once the key security is etablished, it can be
used for encryption, further authentification or other cryptographic
proposes
Every day cryptography is improving. People come up with new
tools; after discovering a problem in one cryptosystem, they want to improve
that and the cryptography system base on public-key, which is more
used in the community, are retooled with new and standards algorithms over the
coming years. That give a big opportunity to incorporate QKD as a new tool
offering fundamentally new security features. QKD is based in quantum mechanics
notion, it provides two kinds of protocols which use Heisenberg Uncertainty
Principal and quantum Entanglement.
3.2 Main operation of key exchange technic of QKD
Based on Vernam code, this cipher required the use of key
which provide only authorized parties suppose to know and the key are renewed
this is an idea of the rapport of [KDB+]. All QKD have two phases
1One-time-pade is a crypto-system where the key is
used once for sharing data
2Man-in-the middle : Its the attack of Eavesdropper
when she is placed in the middle of the channel and when the transmission of
message come, she will take it decrypt and send it to Bob without Bob knowing
that the message was decrypted and when Bob will reply to Alice she will do the
same
Section 3.2. Main operation of key exchange technic of QKD Page
15
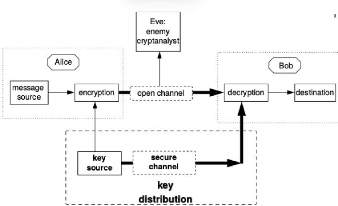
Figure 3.1: Key distribution in conventional cryptography
1. Firstly, Alice will send to Bob a signals 3 to
measure.
2. Secondly, Alice and Bob will deliver to check the result of
measure4
For this two phases, QKD use two channels one for quantum
signal build with optical fiber and the classical channel for classical
communication which is public. The above figure explain the principe of
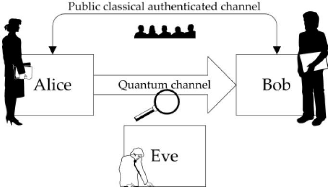
Figure 3.2: Principe of QKD
QKD. In the next point, we will talk about which kind of QKD
can be found in practice. There exist two kinds of QKD based in quantum
mechanics notions which are HUP5 and the Entanglement.
3The signals that we are talking is quantum (other
talk instead of quantum they use soap bubble) 4To check the result
of measurement, they use the classical way
5Heisenberg Uncertainty principle
Section 3.3. Assumption and protocol Page 16
| 


