Introduction
h Representational Learning
h Generative Models Taxonomy
h Generative Adversarial Networks
h GAN Training
h Applications of GANs h Conclusion
2.1 Representation Learning
In representation learning, data is sent into the machine,
and it learns the representation on its own. It is a way of determining a data
representation of the features, the distance function, and the similarity
function that determines how the predictive model will perform. Representation
learning works by reducing high-dimensional data to low-dimensional data,
making it easier to discover patterns and anomalies while also providing a
better understanding of the data's overall behaviour.

Representation learning is a class of machine learning
approaches that allow a system to discover the representations required for
feature detection or classification from raw data. The requirement for manual
feature engineering is reduced by allowing a machine to learn the features and
apply them to a given activity.[1]
Definition 2.1
?
2.1.0.1 Supervised Representational Learning
Supervised Dictionary Learning
2.2 What is generative Modelling
Multi-Layer Perceptron Neural Networks
2.1.0.2 Unsupervised Representational Learning
Learning Representation from unlabeled data is referred to as
unsupervised feature learning. Unsupervised Representation learning frequently
seeks to uncover low-dimensional features that encapsulate some structure
beneath the high-dimensional input data.
2.2 What is generative Modelling
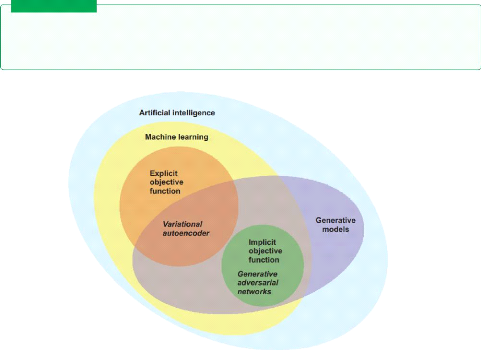
By definition generative modeling is an unsupervised
learning task in machine learning that involves automatically discovering and
learning the representations or patterns in input data in such a way that the
model can be used to generate new examples. [6]
Definition 2.2
?
15
Figure 2.1: generative modeling in the
landscape of artificial intelligence / Source[1]
Example 2.1 let's say we want to create
realistic looking images of cats, first we will need a dataset containing
images of cats ,we call it training data ,we use it to teach our model the
rules that govern the appearance of a cat ,the target will be for our model to
generate a realistic samples that has never existed before yet still looks
real.
· Note The generative model must be
probabilistic rather than deterministic ,it can't be simply a fixed calculation
like taking the average of all the pixels in the dataset,doing this will
produce a deterministic
16
2.2 What is generative Modelling
model which means it's gonna produce the same output
every time,the model must have an element of randomness (not generating the
same image).
2.2.1 Generative Models
Generative models are deep learning networks with the task of
generating data. All these models represent probability distributions over
multiple variables in some manner. The distributions that the generative model
generates are high-dimensional. For example, in the classical deep learning
methodology like classification and regression, we model a one-dimensional
output, whereas in generative modelling we model high-dimensional output.
We describe some of the traditional generative networks:
| 


