4.2 Conception

Figure 4.3: Tensor Flow logo / Source[4]

Figure 4.4: Tkinter symbol /Source [5]
4.2 Conception
To further give a intuitive on the code implementation we will
use the UML and particularly the class diagram to describe the structure of the
model and the inner interaction between the sub-models.
4.3 The Maps Dataset
the maps data set contain two folders for the training and
valuation data, the dataset for the pix2pix model is a couple of the source
image(satellite image) and the target image(map image) 4.5 , in the
implementation of the code we first unpack the data set then load it ,we feed
the satellite image to the generator to transfer it to a map image,then we feed
the generated image along with the original sattelite image to the
discriminator ,then we feed a real data couple to train the discriminator ,for
further explanation look at the previous chapter. here are some example of the
used samples 4.5
29
4.4 Generator Implementation
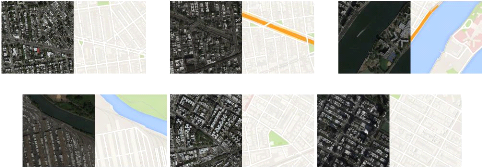
(a) example 1 (b) example 2 (c) example 3
(d) example 4 (e) example 5 (f) example 6
Figure
4.5: Examples from the data set
4.4 Generator Implementation
Listing 4.1: encoder_block
1 def define_encoder_block(layer_in, n_filters,
batchnorm=True):
2 init = RandomNormal(stddev=0.02)
3 g = Conv2D(n_filters, (4,4), strides=(2,2),
padding='same',kernel_initializer=init
)(layer_in)
4 if batchnorm:
5 g = BatchNormalization()(g, training=True)
6 g = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2)(g)
7 return g
Listing 4.2: decoder_block
1 def decoder_block(layer_in, skip_in, n_filters,
dropout=True):
2 init = RandomNormal(stddev=0.02)
3 g = Conv2DTranspose(n_filters, (4,4), strides=(2,2),
padding='same',
kernel_initializer=init)(layer_in)
4 g = BatchNormalization()(g, training=True)
5 if dropout:
6 g = Dropout(0.5)(g, training=True)
7 g = Concatenate()([g, skip_in])
8 g = Activation('relu')(g)
9 return g
Listing 4.3: generator
1 def define_generator(image_shape=(256,256,3)):
2 init = RandomNormal(stddev=0.02)
3 # image input
4 in_image = Input(shape=image_shape)
30
4.5 Discriminator Implementation
5 # encoder model: C64-C128-56-C512-C512-C512-C512-C512
6 e1 = define_encoder_block(in_image, 64, batchnorm=False)
7 e2 = define_encoder_block(e1, 128)
8 e3 = define_encoder_block(e2, 256)
9 e4 = define_encoder_block(e3, 512)
10 e5 = define_encoder_block(e4, 512)
11 e6 = define_encoder_block(e5, 512)
12 e7 = define_encoder_block(e6, 512)
13 # bottleneck, no batch norm and relu
14 b = Conv2D(512, (4,4), strides=(2,2), padding='same',
kernel_initializer=init)(e7)
15 b = Activation('relu')(b)
16 # decoder model:
CD512-CD1024-CD1024-C1024-C1024-C512-56-C128
17 d1 = decoder_block(b, e7, 512)
18 d2 = decoder_block(d1, e6, 512)
19 d3 = decoder_block(d2, e5, 512)
20 d4 = decoder_block(d3, e4, 512, dropout=False)
21 d5 = decoder_block(d4, e3, 256, dropout=False)
22 d6 = decoder_block(d5, e2, 128, dropout=False)
23 d7 = decoder_block(d6, e1, 64, dropout=False)
24 # output
25 g = Conv2DTranspose(3, (4,4), strides=(2,2),
padding='same', kernel_initializer=
init)(d7)
26 out_image = Activation('tanh')(g)
27 # define model
28 model = Model(in_image, out_image)
29 return model
| 


