I. Theoretical Approach of the Foreign Cross-Listing
I.1. Preamble
Definition of the foreign cross-listing:
In this research, a company is considered as foreign
cross-listed, if and only if its own shares are officially listed on one
or several foreign stock exchanges, in addition to the stock exchange
of its incorporation country.
By the term officially listed, we consider cross-listing
initiated on the behalf of the company.
Nowadays, foreign cross-listing may complete the hierarchy of
financing sources, the Pecking Order Theory developed by S. Myers and N. Majluf
in 1984.
#1: Successive Process of Global Financingl
Domestic Capital
Market Operations
International
Bond Issue
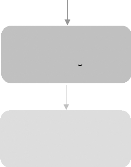
Foreign Equity
Issue
Foreign Equity
Listing
1
R. Nyvltova, 2006, "The Effects of Cross-Border Listings on the
Development of Emerging Markets: the Case of Czech Republic0
Holders
Stock Exchange
Barcllys ADR 1::
NYSE
AXA
ADR 1:1 11
Tel 'talia
ADR
1:10110
Sanof I ADR 2:1
Depositary Receipts System
Trust
arcla Barclays
tock
Stock
Tel Italie
tock
Stock
Sanof I
tock Stock
AXA
toc Stock
Bank
I.2. Different Methods of Foreign Cross-Listing
In addition to the simple and direct listing through shares,
the financial engineering for corporate finance has developed complementary
ways to perform a foreign cross-listing.
I.2.a. Depositary Receipts (DRs)
Depositary receipts (DRs) are an indirect mean to list foreign
shares. DRs are tradable certificates issued by a "sponsoring bank" (or
"depositary bank"), representing the ownership of stocks in the capital of a
foreign company and compliant with the local financial markets laws. This
product replicates an underlying stock of a company, which is in fact held by a
trust vehicle in a foreign bank. A DR may represent a fraction of a stock, a
single stock, or several stocks. For instance, foreign companies aiming at a
listing in the United States or the United Kingdom may respectively use
"American Depositary Receipts" or "Global Depositary Receipts". In a lesser
extent, there are also "European Depositary Receipts", "International
Depositary Receipts" in Brussels, "Dutch Depositary Receipts" in Amsterdam,
"Swedish Depositary Receipts", "Singapore Depositary Receipts" and so on.
The sponsoring bank provides all the services regarding the
registration, the agency services, the broker trading, the conversion of
dividends into the DR holder's currency, and so on. As a consequence of the
utilisation of a trust vehicle, DR holders are not considered as shareholders
of the company and do not have voting rights; but they may instruct the DR
depositary bank how to vote the stocks underlying their DRs.
There are four types of DR (I, II, III, unsponsored), each one
corresponding to different classes. A sponsored level I DR trades
over-the-counter (OTC) and implies the minimal requirements for companies (e.g.
neither obligation to publish quarterly/annual reports nor to meet the U.S.
GAAP). Level II DR (no capital is issued), is different from level III DR (new
capital is issued), but both have the highest disclosure and fulfilling
requirements. At these two levels, companies with DRs listed in the United
States must annually fill forms (registration statements and financial
statements) for the American S.E.C. and fully meet U.S. GAAP.
Most of time, DRs are issued according to the will of a
company to be listed on a specific market with the aim to become accessible to
new investors and thus to attract additional pool of capital. However, a bank
may also issue unsponsored DRs, that is to say not realized on the behalf of
the company but of an investor. Nowadays, there are no formal requirements to
seek companies' authorisation to issue unsponsored DRs, since such operation is
completely passive, i.e. presents no risks, no future implications, no costs
for the company.
Today DR is the most used method for a listing abroad, in
particular in the United States and in the United Kingdom. According to the
Bank of New York, issues of DRs exceed US$50.0bn in 2007 vs. US$44.5bn in 2006,
which had already set a record high2. Most of DRs issued in 2007 had
been realized on the Nyse, Nasdaq, Nyse Alternext (former Amex) and L.S.E; with
two third of issuers originating from the BRIC countries (Brazil, Russia,
India, China).
| 


