2.3.1.2. Database Server
The Database Server houses the files and records of bank
products, services and customers. It shares application processing with the PC
Client Workstations. It performs database searches and retrieves customer
information and/or files. Additionally, the Database Server stores the code
that executes the nightly update processing tasks when instructed by the
Nightly Processing module.
2.3.1.3. PC Client Workstations
The PC Client Workstations are used for shared application
execution with the Database Server and also serves as a display to view the
information and is also a data entry and manipulation point. 120 PCs used by
FINABANK's Management Information System, present the following technical
capacities: 1.80GHZ possessing capacity of CPU, 0.98GB of RAM and 150GB of
Local Disc capacity storing.
2.3.2. Video Surveillance Hardware
FINABANK, considered as a big company, takes seriously the
issue of security. Once you observe carefully into corners of FINABANK's
building, one can difficultly notice that there are small and small cameras
deployed any where capturing images and conveying them through appropriate
cables up to the wide video surveillance screen as well as storing that serous
information in database server for the future use. The following is hardware
used by FINABANK Video Surveillance System:
Table3: Video Surveillance Hardware
|
No
|
Description
|
Quantity
|
Brand name
|
Technical
Capacities
|
|
1
|
Camera
|
15
|
SOME
|
90 days
|
|
2
|
Screen Monitor
|
1
|
IRIS
|
16 channels
|
|
3
|
Cables
|
-
|
CAT6
|
-
|
|
4
|
Disc Video Recorder
|
1
|
IRS
|
90 days
|
Source: Primary Data (2008)
A camera records images, either as a still
photograph or as moving images known as videos or movies. The term comes from
the camera obscura (Latin for "dark chamber"), an early mechanism of
projecting images where an entire room functioned as a real-time imaging
system; the modern camera evolved from the camera obscura.
Cameras may work with the light of the visible spectrum or
with other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. A camera generally
consists of an enclosed hollow with an opening (aperture) at one end for light
to enter, and a recording or viewing surface for capturing the light at the
other end. A majority of cameras have a lens positioned in front
of the camera's opening to gather the incoming light and focus
all or part of the image on the recording surface. The diameter of the aperture
is often controlled by a diaphragm mechanism, but some cameras have a
fixed-size aperture.
Category 6 cable, commonly referred to as
Cat-6, is a cable standard for Gigabit Ethernet and other
network protocols that is backward compatible with the Category 5/5e and
Category 3 cable standards. Compared with Cat-5 and Cat-5e, Cat-6 features more
stringent specifications for crosstalk and system noise. The cable standard
provides performance of up to 250 MHz and is suitable for 10BASE-T, 100BASE-TX
(Fast Ethernet), 1000BASE-T / 1000BASE-TX (Gigabit Ethernet) and 10GBASE-T
(10-Gigabit Ethernet). Category 6 cable has a reduced maximum length when used
for 10GBASE-T; Category 6a cable, or Augmented Category 6, is characterized to
500MHz and has improved alien crosstalk characteristics, allowing 10GBASE-T to
be run for the same distance as previous protocols. Category 6 cable can be
identified by the printing on the side of the cable sheath.
VDR (Video Disk Recorder) is
an open source application for Linux designed to allow any computer to function
as a digital video recorder, in order to record and replay TV programming using
the computer's hard drive. The computer needs to be equipped with a digital TV
tuner card. VDR can also operate as an mp3 player and DVD player using
available plugins
2.3.3. THE Queue Management Hardware
The problem of long lines made up people need to be served by
the bank, was on mind of several managers as well as researchers. Now the queue
Management system is the appropriate response to that particular challenge
faced by FINABANK since long time ago. This equipment is made up following
hardware:
Table 4: Queue Management Hardware
|
No
|
Description
|
Quantity
|
Brand name
|
|
1
|
Queue Management machine
|
5
|
QM
|
|
2
|
Black Screen
|
40
|
QM
|
|
3
|
Cables
|
X
|
CAT6
|
|
4
|
Number caller button
|
40
|
QM
|
|
5
|
Satisfaction test button
|
40
|
QM
|
Source: Primary Data (2008)
The first objective of any queue management system is to
achieve a better quality of service to customers. In its most basic form, a
queue management system will issue a queue ticket to an arriving customer and
later call the ticket when service is available, eliminating the need to stand
in line while waiting. In this way, queue management systems help to provide
comfort as well as fairness to customers, by allowing them to maintain their
position in the queue while they are seated comfortably or engaged in
constructive activity.
The first objective of any queue management system is to
achieve a better quality of service to customers. In its most basic form, a
queue management system will issue a queue ticket to an arriving customer and
later call the ticket when service is available, eliminating the need to stand
in line while waiting. In this way, queue management systems help to provide
comfort as well as fairness to customers, by allowing them to maintain their
position in the queue while they are seated comfortably or engaged in
constructive activity.
2.3.4. Network Communication hardware
FINABANK grows continually and opening branches in different
provinces constitute in this nation. These branches are interconnected dispute
the long distance, through the Network Communication. Helped by Rwanda tell and
MTN Rwanda cell Companies, FINABANK uses following hardware to link various
activities performed by its branches.
Table 5: Communication Hardware
|
No
|
Description
|
Quantity
|
Brand name
|
|
1
|
Routers
|
6
|
SISCO
|
|
2
|
Switchers
|
14
|
SISCO
|
|
3
|
Cables
|
-
|
CAT6
|
Source: Primary Data (2008)
A router is an equipment of a network interconnection enables to
determine the path of data by joining packages within two or more
networks.30
A switch is an electronic equipment help to connect more segments
to one network.
Access Control System in FINABANK is composed mainly by two kinds
of hardware: One Card reader Machine and six accesses scanner machines.
2.3.5. Fire Safety Hardware
Among many serous risks that can affect the bank, we can
highlight fire. The fire safety system is not only the voluptuous choice of
FINABANK by it is also the recommendation from the insurer. To handle this
problem, FINABANK does its best to protect its assets, data and people by
combining following hardware:
30 STEWART, T. «3M Fights Back,»
Fortunes, February5, 2006, p. 99
Table 6: Fire safety equipments
|
No
|
Description
|
Quantity
|
Brand name
|
|
1
|
Fire extinguishes
|
30
|
SAVAL GP9
|
|
2
|
Smoke Detector
|
80
|
MANVIER
|
|
3
|
Fire alarm Controller
|
6
|
MANVIER MF9304
|
|
4
|
Speakers
|
20
|
Sonny
|
Source: Primary Data
The Fire Safety System of FINABANK uses three types of
hardware:
Fire extinguishes: used to attack fire when occurs.
Smoke Detector: helps to notice in advance the fire by
distinguishing smoke. Fire alarm: helps to inform others on the mater.
Speaker: From which alarm worn people upon incident
2.4. THE «SOFTWARE» COMPONENT OF THE FINABANK'S
INFORMATION SYSTEM
To play a useful role in the firm's information technology
infrastructure, computer hardware requires computer software. As it has been
defined by KENETH C. LAUDON in his book named Management Information Systems,
the computer software is a detailed instruction that control the operation of
computer system. 31
31 LAUDON, K. and LAUDON, J.P. «Management
Information Systems: Organization and Technology,» Prentice-Hall of
India: New Delhi, 1999, p.89
Selecting appropriate software for organization is a key
management decision.
As a reference to the first chapter, FINABANK has also two kinds
of software: Application and operating software:
2.4.1. The FINABANK's System Software
Are called System Software (as well explained in the literature
review), ones coordinate other software in a computer, put in relation the
hardware and application software and perform several tasks like DVD playing,
keeping and manage files, etc. Within this context, FINABANK has the following
operating system software.
2.4.1.1. Windows XP Professional
The Windows XP used by FINABANK is Reliable, robust operating
system for powerful PCs with versions for both home and corporate users.
Features support of the internet, multimedia, and the group collaboration,
along with powerful net working, security, and corporate management
capacities.
2.4.1.2. Windows Saver
The Windows Saver supports multitasking, multiprocessing,
intensive networking, and internet services for corporate computing.
2.4.1.3. UNIX
The UNIX Used by FINABANK for powerful PCs, workstation and
servers. Supports multitasking, multiprocessing, intensive networking. It is
portable to different models of computer hardware.
2.4.2. FINABANK's Application Software
Application soft wares are software conceived to perform a given
and specific task. Software of this kind held by FINABANK are the following:
2.4.2.1. Equinox Banking Software
Activities of FINABANK are linked, complete each other and
this happens through the software named «EQUINOX» includes at least
main activities performed by the bank. Here is EQUINOX main interface:
Figure 9: Equinox Banking System's
interface

Source: FINABANK, back office processing, 2009, p.1
Changes in the current business climate around the world place
pressure on industry and commerce. Cyclical boom, bust economic conditions and
the rising global economy place demands on banks and all commercial ventures to
increase productivity, cut costs and be flexible. All of the above are on the
base of shifting from MICROBANKER to EQUINOX Banking System.
FINABANK uses Equinox Banking System to perform and deriver
services to customers. This software has replaced MICROBANKER in 2008 because
it is more advantageous than the last one. EQUINOX is considered as a friendly
user based on its graphical user interface whereas MICROBANKER was a command
line.
2.4.2.2. MICROBANKER
MICROBANKER was the bank system used by FINABANK until 2008,
to handle all business problems in the banking industry, but it has been
replaced by EQUINOX Banking System because it was no longer compatible with the
volume of the bank activities. This application was able to receive a limited
number of users at a once while the number of employees in need was growing as
the business grows. In addition, This system was a command line, what was
somehow complicated to some users, but is very different from EQUINOX Banking
System, currently in use, has a friendly interface, what to say, instead of
commanding the system what to do, it gives to the user various options and
he/she selects the best one.
2.4.2.3. SWIFT System
This software is used by FINABANK to send and receive transfers
between banks either locally or internationally.
2.4.2.4. MEGA System
They use MEGA System to handle problems related to checks, and to
prepare the clearing list to NBR.
2.4.2.5. CRI System
They use CRI System to create, analyze and submits a report,
related to Risk and Arrears Centralization, to NBR.
BNR System Software is a proper version to create and submit
reports, but as these reports are so official and has to be well done; other
software has putted in place as the draft to perform these reports. The
following are interfaces of CRI software related to report to be done:
Figure 10: New credit declaration interface from CRI
system:
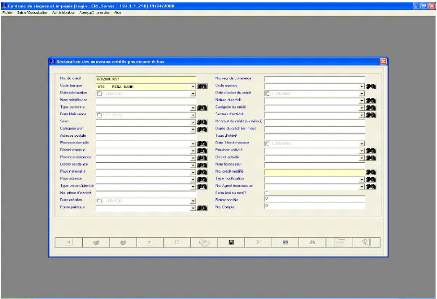
Source: FINABANK, back office processing, 2009
After daftly processing this declaration of new credit the
statistician transfers the report created from CRI system into BNR system which
has the following interface:
Figure 11: New credit declaration interface from BNR
system software
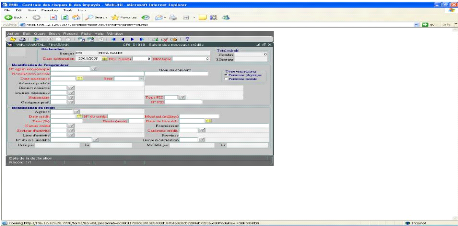
Source: FINABANK, back office processing,
2009
Figure 12: Risk situation interface from CRI system
Software:
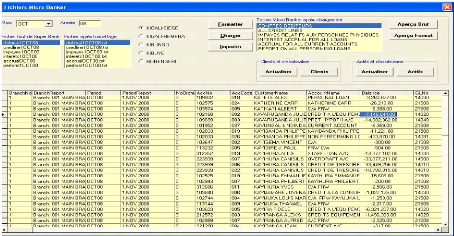
Source: FINABANK, back office processing, 2009
After getting the required information through different ways of
CRI system, it has to be converted into following BNR System's interface:
Figure 13: Risk situation interface from BNR System
software
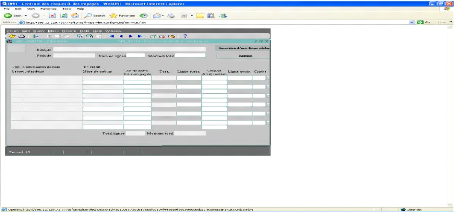
Source: FINABANK, back office processing, 2009
The interface bellow enables the statistician to perform the
situation of credit arrears in BNR system:
Figure 14: Credit arrears report from BNR System
software
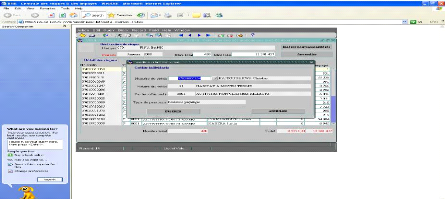

Source: FINABANK, back office processing, 2009
2.4.2.7. LEASEPAC
FINABANK uses LEASEPAC software to establish and manage leasing
facilities.
It is the SME bank with the advertisement sport: «Your
partner in growth and development,» FINABANK makes growing and developed
businesses by providing to them lease loans. To provide loan is one thing and
to manage it is another one, which is some how more complicated. To handle
this, FINABANK has appropriate and qualified software called
«LEASEPAC.» The following is its main interface:
Figure15: Leasepac system software
Source: FINABANK, back office processing manual, 2009
This software (LEASEPAC) contributes on FINABANK's performance
in the way that allows the user to collect any desired information from the
applicant himself and his business as well as to manage the loan. By example
the following is the interface helps the user to collect the information
related to the applicant:
Figure 16: Applicant information interface from LEASEPAC
software
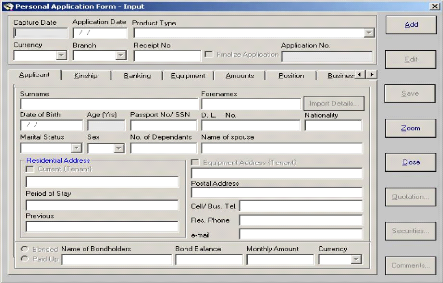
Source: FINABANK, back office processing manual, 2009
2.4.2.8. BNR System
FINABANK uses BNR System to perform, in an appropriate way,
monetary reports to NBR.
NBR has in its responsibilities, to keep stable the Rwandan
currency. So, each and every financial institution, including banks, has to
report, weekly and monthly, to Rwandan Central Bank (NBR). It's in this regard
that National Bank of Rwanda has provided particular software to bank for good
preparing these reports. The following is the main interface of that kind of
software:
Figure 17: Debit interface of BNR System
Software
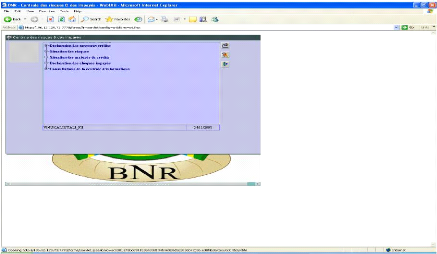
Source: Primary data
(2008)
2.4.2.9. ASETWARE
They use ASETWARE to manage adequately bank assets.
2.4.2.10. Internet Explorer
They use Internet explorer to find and to display information
and web site in order to communicate, publish, and advertise what they do as
well as to update the knowledge of personnel.
2.4.2.11. Microsoft Office 2003 and 2007
- Microsoft Office Excel
FINABANK performs calculations, analyzes information, and
visualizes data in spreadsheets by using Microsoft Office Excel.
- Microsoft Office Outlook
They send and receive e-mail; manage your schedule, contacts, and
tasks; and record their activities by using Microsoft Office Outlook.
- Office PowerPoint
They create and edit presentations for side shows, meeting, and
web pages by using Microsoft Office PowerPoint.
- Microsoft Office Words
They create and edit professional looking documents such as
letter, papers, reports, and booklets by using Microsoft Office Words.
2.5. THE «DATA» COMPONENT OF THE FINABANK'S
INFORMATION SYSTEM
2.5.1. Introduction
DATA are any raw facts or observations that describe a
particular phenomenon. For example, the cash in hand, the cost of transport of
personnel, and a picture captured all are data.32
In business, for instance, the cost of merchandise may be
information to buyer, but it may represent only data to an accountant who is
responsible for determining the value of current inventory levels. The current
value of inventory for that merchandise is the information the accountant
derives from the two pieces of data and it will be useful to take decision when
selling.
Within FINABANK, data are raw facts or observations that
describe money deposed or withdrawn, given as loan, gotten as loan repayment to
or from customers, disbursed as salary to employees or as the cost of bank's
assets.
32 ROBINS, G., «Data warehousing: Retailers on
the cutting Edge,» STORES, September 1995, pp.19, 24-28
These facts are key resources to FINABANK, because our economy
tends to base on the knowledge and information as it has described by our
general introduction.
2.5.2. The Database and Database Management System (DMS)
in FINABANK
In FINABANK, databases and database management systems provide
the foundation of organizing, managing, and working with the information. In a
database and database management system environment, the database contains the
information, and the database management system is the collection of software
tools that supports management of a database and performance of the bank.
Employees of FINABANK throughout the organization's knowledge workers or IT
specialists, interact with a database by using a database management system
software tools.
2.5.3. FINABANK Data Processing
Data processing can be speeded up by several processors to work
simultaneously on the same task.
As it is appearing on following figure, FINABANK uses
simultaneously parallel processing (online processing) and serial processing
(batch processing) in data processing. In parallel processing, multiple
processing units (CPUs) break down a problem into smaller part and work on it
simultaneously. Getting a group of processors to attack the same problem at
once requires both rethinking the problems and special software that can divide
problems among different processors in the most efficient way possible,
providing the needed data, and reassembling the many subtasks to reach an
appropriate solution.
Massively parallel computers have huge networks of processor
chips interwoven in
complex and flexible ways to attack large computing
problems. As opposed to parallel
processing, in Sequential or batch
processing, where small numbers of powerful but
expensive specialized chips are linked together, massively
parallel machines link hundreds or oven thousands of inexpensive, commonly used
chips to break problems into many small pieces and solve them.
Figure 18: Sequential and parallel process
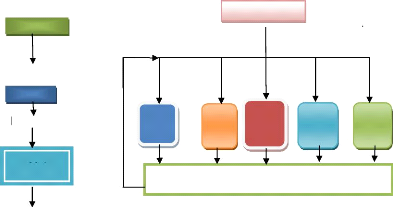
CPU
CPU
CPU
CPU
CPU
Task3
Task5
Task4
Task1
Task
RESULT
PROGRAM
CPU
Result
PROGRAM
PROGRAM
Task2
CPU

Result Source: Primary Data (2008)
2.5.4. FINABANK's Data Storing
The capabilities of computer systems depend not only on the
speed and capacity of the CPU but also on the speed, capacity, and design of
storage, input and output technology.33
The following figure gives an image of how FINABANK stores data
at the same time using it in what they call Storage Area Network:
33 NOVACK, J., «The Data Miners,»
Forbes, February 12, 1996, pp.96-97
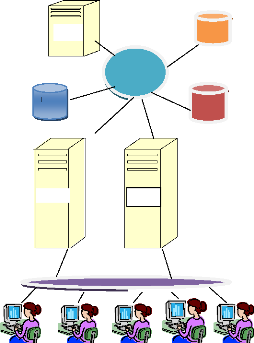
SERVER
RAID RAID
TAPE
LIBRARY
SAN
SERVER
RAID
Figure 19: A Storage Area Network (SAN).
User1 User2 User3 User4 User5
Source: Primary data (2008)
The SAN of FINABANK consists of a server, storage devices and
is used strictly for storage. The SAN stores data on many different types of
storage devices, proving data to the users in the bank. The SAN supports
communication between any server and the storage unit as well as between
different storage devices in the network.34
34 2nd
HAAG, S. «Management Information Systems for the
Information Age,» Edition, McGraw Hill/Irwin, Boston,
2000, p173
2.6. THE «PROCEDURES» COMPONENT OF FINABANK'S
INFORMATION SYSTEM
In field of MIS, FINABANK undertakes several procedures to
meet its objectives both effectively and efficiently. Among these procedures we
are going to analyze, in this section, four most important of them which are:
account opening procedure, employee recruitment procedure, credit analysis
procedure and the fire safety procedure.
2.6.1. Account opening procedure
To create an account into FINABANK, the following procedures have
first to be undertaken:
For a corporate business wants open an account requirements
are: A notified copy of the startup contract, the trade license or the RDB
permission, on photo and specimen of each of company representatives.
When the client to be served is an individual, he/she is asked
to bring the copy of his/her ID card, one photo and fill the application form.
For these two categories of client, to open their accounts it's made for free
of charge.
2.6.2. Employee recruitment procedure
Prior the right employee arrive in the right place, the following
procedure in FINABANK must be respected:
The department, in need of an employee, makes a requisition to
the Human Resource Management Department, and this one recruits a desired one
through new times, IMVAHO news paper or specialized institutions. The
department prepare and give practically and theoretically an exam to
candidates. The candidate succeeded the both tests (written and interview) is
hired by the department in charge of recruiting and hiring (HR), the new
employee get a concise training in relation with the job he/she is going to
perform. After the training, the new employee sign a temporary
contract (3 to 6 months), if well finished, a definitive contract is signed
between the bank and its employee.
2.6.3. Credit Analysis Procedure
Figure 20: Credit analysis procedure
|
|
Business Banking / SME / Consumer Banking
|
|
Credit Control
|
|
|
Client
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Application letter Recommandation bases on : Credit analysis
bases on
level of risk quantitative issues and
Business Banking SME

Head of Credit Risk Managing Director Board of Directors
Credit
Administration and legal sub
department

: Approval: if x < 10,000,000 Verify the legal conformity
Verification of legal
Approval: if x < 100,000,000 Two parts sign the contract
conformity
Approval: if x >=100,000,000
. tangible facts
Credit Control
Recovery Department
: Establishment of credit Recovery dills with all customer and
reimbursement
monitoring for class 4, 5 and 6 of clients
Source: FINABANK, credit policy and procedure manual, May
10th, 2009
2.6.4. Fire safety procedure
To minimize damages that can be caused by fire in FINABANK,
here's the fire safety procedure to undertake whenever fire occurs in the
bank:
1. Press fire alarm
2. Shout «Fire» «Fire»
3. Call 999 and inform the fire brigade giving precise location
of building, including floor and/or room in which fire has been observed.
4. If possible attack the fire extinguishing appliance avoiding
risk to life.
5. Evacuate the building immediately without stopping to collect
any belongings.
6. Do not use lifts.
7. Use all designated fire exits and stairs to evacuate.
8. Proceed quickly to the nearest designated assembly points.
9. Do not re-inter the building until fire services have
declared the premises safe.
2.6. THE «PEOPLE» COMPONENT OF FINABANK'S
INFORMATION SYSTEM 2.6.1. Introduction
We were discussing hardware, software, data and procedures;
all of this was to give us a broad overview of the nature of MIS components
within FINABANK. Let's now turn our attention to the most important resource in
the business, especially for Management Information Systems-people as the
knowledge worker. 35
Recall that, as a knowledge worker, FINABANK's employees work
with and through
produces information as a product. And it really doesn't
matter if they use a high-powered
35 MARTIN, J. «Are You as Good as You Think
You Are?» Fortune, September 30, 1996, pp.142
workstation or calculator; they are still a knowledge worker,
responsible for processing information that their business (FINABANK) want to
survive.
To succeed, as a knowledge worker in today's information-based
business environment, FINABANK do its best to make its personnel understanding
the true nature of information, what means to be an information-literate
knowledge worker, and to assume the ethical responsibilities of working with
information.
2.6.2. Being an Information-Literate Knowledge
Worker
An information-literature knowledge worker must define what
kind of information is needed, knows how and where to obtain that information,
understands the meaning of the information once received, and can act
appropriately, based on the information, to help the organization achieve the
competitive advantages.36
Knowing the appropriate time, content, and form dimensions of
information needs is a major step toward becoming an information-literate
knowledge worker in FINABANK. But it doesn't stop there-knowing what they need
is only part of the information equation. They also do their best to know such
things as how and where to obtain that information and what the information
means once you receive it.
IT tools are great for helping FINABANK'S employees through
the problem-solving or advantage-realizing process. In fact, many IT-based
systems are designed specifically to help them solve a problem or take
advantage of an opportunity.
36 2nd
HAAG, S. «Management Information Systems for the
Information Age,» Edition, McGraw-Hill, Boston, 2000,
p187
2.6.3. Being a Motivated Employee 2.6.3.1.
Definition
Twyla Dell writes of motivating employees, "The heart of
motivation is to give people what
they really want most from work. The more
you are able to provide what they want, the
more you should expect what you
really want, namely: productivity, quality, and service."
37
2.6.3. 2. How Maslow's Needs Hierarchy helps to motivate
FINABANK's personnel
As MASLOW's theory is true, there are some very important
leadership implications to enhance workplace motivation. The Human Resource
Department profits from these staff motivation opportunities to motivate each
employee through FINABANK style of management as follow:
· Physiological Motivation: FINABANK provides ample breaks
for lunch and recuperation and pay salaries that allow workers to buy life's
essentials.
· Safety Needs: FINABANK provides a working environment
which is safe, relative job security, and freedom from threats.
· Social Needs: FINABANK generates a feeling of acceptance,
belonging, and community by reinforcing team dynamics.
· Esteem Motivators: FINABANK recognizes achievements,
assigns important
projects, and provides status to make employees feel
valued and appreciated.
· Self-Actualization: FINABANK offers challenging and
meaningful work assignments
which enable innovation, creativity, and
progress according to long-term goals.
37 ZEIGER, D. «Smart Card Technology to Get
Boost,» The Denver Post, October, 2006, p.23
2.6.4. FINABANK Employee Situation within five
years
The following figure presents how much FINABANK has increasingly
recruited employees as far as the company itself became bigger compared to the
previous periods:
Figure 21: Employee mouvement situation into
FINABANK
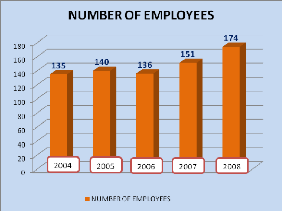
Source: Pimary Data (2004-2008)
From the above figure, FINABANK every and each year increase
its employees for the seek of increasing also its income: in 2004 it had 135
employees, 140 employees in 2005 means an increase of 37% and 136 employees in
2006 means a decrease of 2.9%, this reduction has been justified by the
implementation of the FINABANK police related to cost control from that period.
In 2007 as well as 2008 employees have increased respectively up to 151 and 174
employees. FINABANK chooses increasing continually based on the principal of
economies of scales.
2.7. CHAPTER 2-SUB CONCLUSION
In general, hardware is composed by any physical material that
enables the bank to collect, process, storing and communicating information.
Among this hardware, PCs Work Stations are very crucial for
FINABANK's IT infrastructures to perform banking activities.
To provide a good service to its clients, we sow that
FINABANK has 120 PCs (brand name: HP and DELL) fill the following technical
capacities: The speed of processing (micro-processor): 1.80GHZ, 0.98GB of RAM
and 150GB of Local Disc capacity storing and referring to classical measurement
conditions, as we sow them in previous chapter, one can easier notice that all
these machines meet the normal technical prescription as indicated by
specialists. In addition to these 120 PCs Work Stations, FINABANK uses also 54
laptops with HP AND DELL as brand name, technical capacities: 2.00 GHZ, 5200MB
of RAM and 120GB Disc storing capacity. These laptops perform the same activity
as PCs but there are used by Account Relation Managers (ARM) and other workers
who do not have a fixed work place based on their job.
All of these machines are connected, using CAT6 cables, to
fileserver as well as to database server and all together make a good network
which helps FINABANK to handle quickly and massively a lot of problems so as to
provide a desirable services to its clients.
As this principal hardware, PC Work Stations, used by FINABANK
march three basic technical conditions of the hardware, as FINABANK uses
several applications and operating software in collection, processing as well
as in exploratory of data; as it has curried out a set of procedures to speedup
bank's operations and his sufficient, motivated and qualified employees
enabling FINABANK achieving its objectives. All of these issues help the
researcher proved the first hypothesis. .
CHAPTER 3: BENEFITS OF MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS
(MIS) TO
FINABANK BETTER BANKING SERVICES
3.1. INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents qualitatively and quantitatively how
significantly components of Management Information Systems (MIS) have
contributed directly or indirectly to FINABANK's better banking services within
2004-2008 timeframe.
3.2. BENEFITS OF «HARDWARE» TO FINA BETTER
BANKING SERVICES
The present section analyses and presents different benefits of
«hardware» held by FINABANK, as presented into second chapter, and
gives their contribution to its better banking services.
3.2.1. Benefits of the Equinox Banking
Hardware
Equinox Banking Hardware helps FINABANK:
· control costs and remain competitive in the ever-
changing global economy.
· store data centrally, but share processing between users
so that they can run many applications and process work simultaneously.
· collect, process, store and convey quickly and massively
the information
· The PC Client Workstations are used by FINABANK for
sharing application execution with the Database Server and also serves as a
display to view the information and is also a data entry and manipulation
point
· The Database Server enables the bank to house files and
record of bank products, services and customers
· The File Server helps FINABANK housing the applications
and handles network administration.
3.2.2. Benefits of the Video Surveillance
Hardware
Bank is an institution plays a role of financial
intermediation what means that it mainly manages other's precious properties
(cash), this issue leads FINABANK to sign some contracts with security
companies (KK security and Intersec security Companies) to secure the bank and
its employees at work place in behalf of the bank itself.
Apart from these contracts, FINABANK has what called
«Video Surveillance System» composed by 15 cameras deployed
clandestinely elsewhere, helps the bank to capture many videos from different
strategic points like strong room, tellers' room, IT room and all corners of
the bank, present them on wide frat screen monitor and saved on the Disc Video
Recorder.
This kind of hardware helps FINABANK to control the movement
and acts of employees, clients and others moving in and around the bank, so as
to detect in advance undesirable activities into the bank.
Briefly, this hardware collects, presents and stores facts done
by employees, clients or non authorized people without being away that they are
watch.
3.2.3. Benefits of the Queue Management
Hardware
Prior the installation of this hardware, FINABANK was always
suffering from non finishing files of clients wished either to depose or to
withdraw their cash. By this equipment each client, depending to what need from
bank and time of arriving, gets from machine a voucher number, takes a seat
till others came before, will be served and his number will display on black
screen located at the top of teller's window.
Up to now, this equipment came to handle 90% of the problem
as declared by FINABANK Kigali Branch Manager. In addition to this, the same
system is able to measure clients' satisfaction. How? Each client served
presses a button of «satisfied» or «not satisfied» and
these statistics helps FINABANK to know how good clients appreciate their
services.
3.2.4. Benefits of the Network Communication
hardware
As FINABANK operates in different regions wants to link its
activities, so to provide a good services to its client. That can't realize in
absence of Network Communication hardware. In addition to this, there are some
financial products that could never exist if FINABANK could not have a good
network system, from this we can say: FINA money transfer, FINA direct, etc.
3.2.5. Benefits of the Access Control
Hardware
Before the installation of this hardware, the movement of
people in the organization was somehow disorganized. However could inter
anywhere, what was unfair and could cause the insecurity to the bank. But now
the current situation is quite different: Each employee inters where is
authorized, other place he/she can't because everyone has a coded access card
enabling her/him to inter the place authorized to her/him.
In addition to that, prior this system, employees were
obliged to fill the name, time of arriving and sign in the attendance book and
could happen that the employee sign and after two hours he/she goes wherever he
wants out of the work. But now, the card reader machine helps the human
resources manager, to know that a given employee comes to the job when, he/she
quite the work place when, even these unnecessary movements of employees within
organization are also recorded, so if necessary the causer can explain.
Finally, this kind of hardware was becoming useful to FINABANK
in terms of securing the bank against bandits or other unfair to the
organization.
3.2.6. Benefits of the Fire Safety Hardware
Fire is the most dangerous threats to banks even to all
organizations. In order to protect itself against, FINABANK uses the fire
safety equipment. The last one is able to detect using «smoke
detectors» easily the smoke, regardless what causes, and the «fire
alarms» worn trough «speakers» immediately that there is the
fire. The alarm is installed so during
the night, even workers whenever they inter the bank using
their usual coded access cards not during the work time, means for their own
purposes, it immediately recognize them as robbers and warns. In other words,
it is one of the security facilitators.
In addition, the system is installed as, people from Fire
extinguishers recognize automatically the threat happening in the bank and
intervene at right time.
Briefly, the «hardware» has contributed positively to
the better banking services of FINABANK within the range of 2004 to 2008 as
proved by the upcoming figure.
3.2.7. Impact of IT infrastructure to the FINABANK's
performance
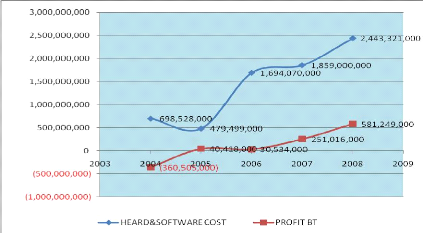
Figure 22: Impact of IT infrastructures to FINA
performance
Source: FINABANK, Financial Statement, 2004-2008
From the above figure stated thet FINABANK sa, in one side,
has spent less maney for aquiring the technological infrastructures in 2005
(479,499,000Rwf) compared to ones disboursed in previous year (698,528,000Rwf)
what signifies a decrease of -31.36%.
The year 2006 justifies how good FINABANK sa has recognized
the role of IT whithin the bank's operations because it has spents a huge
amount of money to purchase a modern and qualified IT infrastructures
(1,694,070,000Rwf), an increase of 253.30% compared to the values of the year
2005.
The value of the FINABANK's IT infrastructure did nover stoped
to increase since there because it reached the value of 1,859,000,000Rwf and
2,443,321,000Rwf, an increase of 9.74% and 36.43% respectively for years 2007
and 2008.
Other side, FINABANK has gained positively in 2005
(40,418,000Rwf) compared to year 2004 where it loosed (360,505,000Rwf) but the
following year (2006) its profit has decreased to 30,534,000Rwf and it has
recorded an increase in profit of 251,016,000Rwf, 581,249,000Rwf respectively
for years 2007 and 2008 what determines an increase of 722.09% and 131.56%
respectively.
FINABANK has recorded a high difference in profit between
2006 and 2007, as it comes to be presented, from 30,534,000Rwf to
251,016,000Rwf; because in 2005 and 2006 had to cover first the big losses
registered in previous years.
Statistically, FINABANK sa spends roughly 1,434,883,600Rwf
every year for acquiring MIS infrastructures, the highest amount of money spent
for the same reason is 2,443,321,000Rwf and the lowest cost on the same issue
is 479,499,000Rwf; all of this is located in the interval of year 2004 and
2008. Considering all the above presented, there is a significant and positive
correlation of 0.816472353 between the cost of hardware and software
infrastructures and the profit registered by FINABANK sa.
3.3. BENEFITS OF «SOFTWARE» FOR FINA BETTER
BANKING SERVICES
This section present various benefits of «software»
and their contributions to FINA better banking services. As EQUINOX Banking
System is considered as the pillar of the inter banking system, let's take it,
so to present benefits of «software,» as one of MIS component, to the
better banking services of FINABANK:
3.3.1. Benefits of the EQUINOX Banking
Software
Equinox Banking Software is taken as the backbone of FINABANK's
operations that largely handles the maximum of problems related to banking
activity using its following models:
3.3.1.1. Benefits of the System Administration
Model
The Administrative Model provides integrated controls and
parameters for the Bank, General Ledger, Relationship Management, Security,
Deposit and Loan Products, Safe Deposit Box, Teller, Rates, Charges and a
variety of other administrative functions. This module defines the bank,
branches, products and how they are set up and processed. For example, the
General Ledger Master Chart of Accounts is created and defined in this
module.
3.3.1.2. Benefits of the Account Processing
Model
After the products have been defined and decided how they
will be processed, this module allows the bank to set up and maintain customer
accounts and process monetary and non-monetary transactions. For
example, credits and debits to General Ledger accounts can be
performed online through this module.
3.3.1.3. Benefits of the Nightly Processing
Model
This module runs the program that updates the database each
day. It processes all batch transactions, accrues and pays interest, assesses
service charges, produces reports, notices, checks, transfers funds and updates
customer files and records. This module is where the bank defines and schedules
the custom reports. For example, the bank defines the level
and detail it wants to show on the Statement of Condition and Income and
Expense Report and the General Ledger accounts to be reflected in these
reports.
3.3.1.4. Benefits of the Teller Processing
Model
This module memo posts deposits, withdrawals, payments and
miscellaneous transactions on the system to accurately reflect account activity
through the teller line throughout the day.
3.3.1.5. Benefits of the ATM Processing
Model
This module allows the bank to setup and maintain its card
and transaction processing for ATM and POS. It also allows the bank to setup
and maintain customer ATM accounts, cards and relationship accounts. This
function can also be performed in the Account Processing module.
Globally, the benefits of the software come in the form of
technical improvements in FINABANK's IT Department -- deploying branches
faster, cheaper, and better. However, what is most interesting is that these
technical improvements are large enough to have an impact well beyond the
borders of the IT department and offering strategic competitive benefits to the
way that FINABANK conducts its business.
The following Technical benefits have been gained from
«software,» the component of the FINABANK's Information System:
· reduction in the average time to create and deploy a new
branch
· reduction in the average technical effort to deploy and
maintain a branch, and therefore reduction in the average technical cost per
branch
· increase in the total number of branches that can be
effectively deployed and managed
These technical benefits translated into a very powerful set of
FINABANK strategic business benefits:
· reduced time-to-market and time-to-revenue for new
branch
· improved competitive financial product value
· higher the FINABANK profit margins by helping its
employees work more efficiently
· improved ability to hit market windows
· better product quality and improved FINABANK reputation
for quality
· improved scalability of business model in terms of branch
and markets
· increased agility to expand into new markets
· reduced risk in branch deployments
· cutting costs by automating routine tasks
· improving customer service levels, perhaps by using ATM
that customers can access some financial services- eg allowing customers to
withdraw money without needing to contact any member of staff directly
3.5. BENEFITS OF «DATA» FOR FINA BETTER BANKING
SERVICES
For large commercial organizations, data security is not only
a corporation option, it's the law. Losing sensitive data by way of natural
disasters or physical robbery can have severe consequences on FINABANK,
possibly demolishing entire organization.
FINABANK's Intellectual property such as its employee and client
information,
product descriptions and business outline all qualify as
priceless information. These critical details are somehow secured at all times
to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of FINABANK. This information is
the core of FINABANK and without it, it can't operate. If a criminal is able to
access this data, there is no limit to the damage they can inflict.
FINABANK recognizes that its data is vulnerable and can be
compromised in the following ways:
Virtual attack - This could be an industry
rival that learns to bypass security and gains access to competitive data. It
could also be a malicious attack that purposely corrupts data.
Physical attack - Perhaps a disgruntled employee
is seeking ways to damage the company by stealing files or purposely destroying
data.
For these problems, FINABANK implements multiple forms of
security by using hardware solutions such as routers and firewalls. These
devices protect essential data by keeping external threats out of the network.
Unfortunately, intruders employ numerous attacks, specifically targeted at that
information but FINABANK does all its best, so attackers couldn't find a way to
penetrate its first line of defense.
| 


