1.2. MEANING AND ROLE OF MIS IN THE ORGANIZATION
«Management Information Systems,» as the stamina of
our study, could be number one to be clarified but before one can explain it,
the terms systems, information, and management must briefly be defined.
Thus,13
Figure 1: MIS Terminology

M-I-S
Source: MURDICK, G, (2006-26)
Management
Information
Systems
1.2.1. Management
Management has been defined in a variety of ways, but for our
purposes it comprises the process or activities that describe what managers do
in the operation of their organization: plan, organize, initiate, and control
operations. One plans by setting strategies and goals and selecting the best
course of action to achieve the plan. He/she organizes the tasks necessary for
the operational plan, set these tasks up into homogeneous groups, and assigns
authority delegation.
Management is usually defined as planning, organizing,
directing, and controlling the
business operation. This definition, which
evolved from the work of HENRI FAYOL in the
early 1900s, defines what a
manager does, but it is probably more appropriate to define
13 2nd
MURDICK G., JOEL E. ROSS and JAMES R. «Information
Systems for Modern Management,» Edition, McGraw
Hill 2006,p.26
what management is rather than what management does.
Management is the process of allocating an organization's inputs, including
human and economic resources, by planning, organizing, directing, and
controlling for the purpose of producing goods or services desired by customers
so that organizational objectives are accomplished. If management has knowledge
of the planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of the business, its
decisions can be made on the basis of facts, and decisions are more accurate
and timely as a result.
They control the performance of the work by setting
performance standards and avoiding deviation from standards.
Because decision making is such a fundamental prerequisite to
each of the foregoing process, the job of Management Information Systems
becomes that of facilitating decisions necessary for planning, organizing, and
controlling the work and functions of the business.
1.2.2. Information
Information consists of data that have been retrieved,
processed or other ways used for informative or inference purposes, argument,
or as a basis for forecasting or decision making. An example here would also be
any one of the supporting documents already mentioned, but in this case data
could be used by internal auditor, or internal management service department of
an external auditor, or internal management for profit planning and control or
for other decision-making purposes.14
14 BAXTER, ANDREW, «Smart Response to a
Changing Market», Financial Times, March 1, 1995, p. 13.
1.2.2.1. Dimensions of Information
As a knowledge worker this issue of information value is an
important one. Because he/she works with and produces information as a product,
information is one of his/her most valuable resources. So, how to determine the
value of information? What makes certain information highly valuable and other
information completely worthless? Unfortunately, it's impossible to put an
exact dollar figure on the value of information. But what one can do, is
defining his needs according to three dimensions of information-time, content,
and form presented as follows15:
Figure 2: Dimension of Information
Source: LAUDON, K. (1999, pp.67)
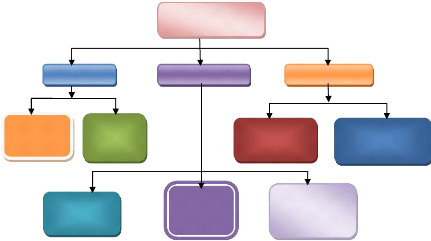
Timeliness
(When)
Time (When)
(free errors)
Accuracy
(up-to-date)
Currency
Content (What)
Relevance
Dimensions of
Information
(Useful)
(more details)
Detail
(Detailed relatively)
Completeness
Form (How)
(appropriate form)
Presentation
15 LAUDON, K. and LAUDON, J.P. «Management
Information Systems,» Prentice-Hall of India: New Delhi, 1999,
pp.67
- The Time Dimension of Information
Whether you're providing your customers with information about
products and services or using information to make a decision, the time
dimension of information is critical. The time dimension of information deals
with the «when» of information aspect. Time characteristics of
information include:
Timeliness: Information when you need it
Currency: Information that is up to date
Timeliness means having Information when you need it. If you
don't have the right information at the right time, it's almost impossible to
make the right decision.
Currency means having the most recent or up-to-date
information. In today's fast-paced business environment, yesterday's
information is often obsolete and of no use to a knowledge worker.
- The Content Dimension of Information
«Content» is often considered as the most critical
dimension of information. It deals with the «what» aspect of
information, and its characteristics include
Accuracy: Information free of errors
Relevance: Information useful to what you're
trying to do
Completeness: Information that completely
details what you want to know. - The Form Dimension of
Information
The last dimension of information is the «form», which
deals with the «how» aspect of information. Form of information
include
Detail: Information detailed to the appropriate
level
Presentation: The information that is provided
in the most appropriate form-narrative, graphics, color, print, video, sound,
and so on.
1.2.3. Systems
A system can be defined as a set of elements joined together,
interrelated, for a common objective. A subsystem is a part of a large system
with which we are concerned. All systems are part of large systems. For our
purposes the organization is the system, and the parts (divisions, departments,
functions, units, etc.) are the sub systems.
The systems concept of MIS is therefore one of optimizing the
output of organization by connecting the operating subsystems through the
medium of information exchanges.16
| 


