1.2.3 English with Specific Topics
It is uniquely concerned with anticipated future English need.
For example, scientists requiring English for postgraduate reading studies,
attending conferences or working in foreign institutions (Carter,1983) .
English for Social Studies.
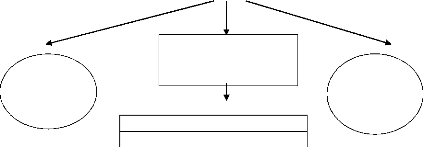
English as a Restricted Language.
English for Business and Economics.
English for Science and Technology.
English for Academic and Occupational Purposes.
English with Specific Topics
ESP
Diagram1: Types of ESP ( David Carter , 1983 )
.
1.3 English for Business and Economy
Business English is a part of ESP that is used by non-native
speakers for the goal of communicating business with English speaking
countries. According to Rita Johan (2014) «business English is the
English language that is related to international trade». For her,
«business English is a part of ESP and can be considered a specialism
within English language learning and teaching» (P.01).
1.4 The Characteristics of an ESP Course
David Carter (1983) states that there are three features common
to ESP courses:
1.4.1 Authenticity: That is to say, the teaching materials
used by the teachers should Be
9
The Review of Literature
authentic because they have a positive effect on learners'
motivation as they enable them to interact with the real language and content
rather than the form. In fact, learners feel that they are learning the target
language as it is used outside the classroom.
1.4.2 Purpose-related orientation
It refers to the stimulation of communicative tasks required
by the target situation. Orientation lesson must be according to needs and
wants of the learners.
1.4.3 Self-direction
It means that ESP is concerned with turning learners into
users for self direction, and the teacher should encourage the learners to have
a certain degree of autonomy or freedom to decide when , what and how they will
study .
1.5 The role of ESP practitioners
The teacher in ESP is different from that of general English
(GE) teachers. In fact, there are important practical ways in which the work of
the GE teacher and the ESP teacher differ. An ESP teacher must play many roles.
He may be asked to design courses, to set learning objectives, to establish
learning environment in the classroom, and to evaluate learners' progress.
Sierocka (2008) claims that the ESP teacher has got more roles to play besides
the role of a «teacher». Dudley-Evans and ST John (1998) define five
key roles for the teacher in ESP
1.5.1 As a teacher
It is true that the ESP teacher and the GE teacher share
common roles, for example teaching the English Language. However, the
differences lie in the objectives behind teaching In ESP a teacher does not
mean only being a language provider, but also a needs analyst. (Harmer,2001).
That is to say, he/she has to understand the learners' needs in order to
10
The Review of Literature
understand their knowledge of the content so as to bring the
appropriate materials required by the group of learners in class (Bojovic
2006). For instance, if the teachers know that the learners needs more practice
in the writing skill, they will bring materials that would help them to improve
that skill.
| 


