2.2. Other specific political risks and
impacts
2.2.1 Inflation rate and political
crisis
The following figure compares the inflation rate between UEMOA
(Union Monetaire West Africaine), and WAMZ (West Africa Monetary Zone). All
eight member states of UEMOA share the same currency, CFA, while each member of
WAMZ (Ghana, Guinea, Nigeria, Liberia, Sierra Leone) has it own currency.
The finding is that the inflation rate of WAMZ is far above that
of UEMOA from 2001 to 2003.
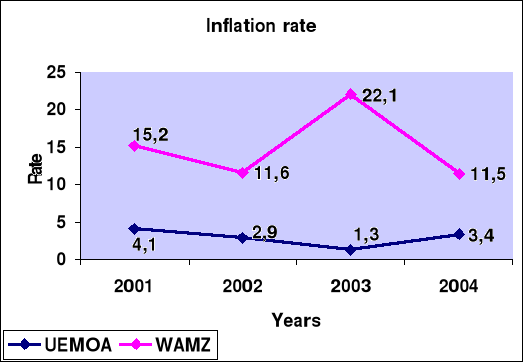
During this period, each group was facing tough political
situation. Sierra Leone and Cote d'Ivoire have been at wars. Though civil war
has been prevailing in each group, UEMOA kept a low inflation rate. We assume
that, this low rate is due to the relative stable currency, CFA. Regional
monetary grouping is a factor that favor better exchange rate in transactions.
European Union is another good example. Therefore, in international marketing
operations, a marketer should look for currency stability, and choose to work
with such monetary grouping countries, even though some political risks may
exist. West Africa nations, through ECOWAS are now planning to make one major
currency by putting UEMOA and WAMZ together.
2.2.2 Import and Export in UEMOA zone
during political conflicts
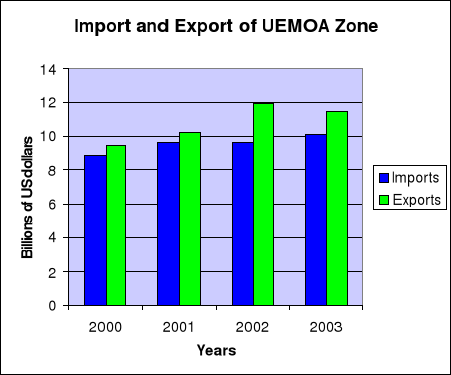
The following figure shows that from 2000 to 2003, EUMOA total
exports exceeded imports. During that period, Cote d'Ivoire the largest economy
of the group, 40% of total share, has been at civil war. Though in conflicting
situation, UEMOA did not face any trade deficit. Production might be disrupted
but products can cross borders and be sold in neighboring countries. This
resulted in increase trade in other UEMOA countries and contributes to keep the
overall exports higher. An international marketer that really knows the terrain
where is making business, could always find opportunities when political risks
erupt.
2.2.3 Employment distribution in UEMOA zone during political
conflicts
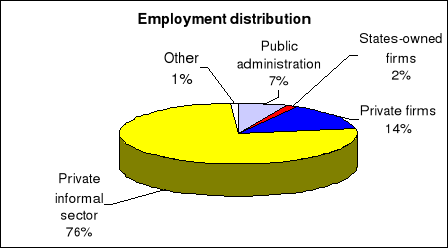
We have selected employment status in UEMOA countries capital
cities, in 2001-2002. Figure 4 is an illustration.
Private informal sector owns 76% of the employments, private
firms supply jobs up to 14%, public administration is responsible of 7% of jobs
rate against 2% for states-owned firms and 1% for other, mainly association
sector.
Informal private sector is a specific work area in developing.
It comprises of individual not officially register as corporate, but who work
as such. Some work like, carpentry, shoes repairing fabric, hair cut
shops...etc, are concerned. As shown in the figure, it represents a huge
segment of market, which any international marketer should take into account if
his firm activities should encompass those sectors. Because he will have to
share customers with those individuals, plan should be carefully tailored.
People working in the informal private sector are easy to delocalize to work
for a national or multinationals, since their working conditions are too hard
and gains too small.
The formal private sector covers only 14% of employment. This
means that opportunities still exist, and one should foster private
investments, mainly in other non agricultural industries like communication,
mining, electricity, electronic, and so forth. Increasing investment is a way
to reduce the redundancy high rate (11.4%) in UEMOA Zone.
States-owned firms represent only 2%, this is an indicator of
privatization that is going on in every country in Africa.
| 


