4.2.4.1. Socio-Demographic
Characteristics of Households
The total sample comprised of 221 respondents who were
household heads. The social demographic features of households are as shown in
(Table 7). The majority of the respondents were male (86.9%) while females
constituted 12.2%. Most of the respondents were aged between 40 and 59 years
(47.1%). The level of education was assessed because it was an important
factor in understanding household vulnerability to disasters. The majority of
the respondents (39.8%) attained only primary education as their highest level
with 38.9% having no schooling at all. 14.5% had secondary level education and
only 0.09% had attained tertiary level of education. The majority of the
households heads are married (90.5%) with 7.2% of widowed. Most of households
that is 62.90% had more than 10 members.
4.2.4.2 Location of
settlement and type of construction
The location of settlements in the targeted area led to increase
household vulnerability to flood disasters. As observed during the field
survey, most of the settlements are located near the river as the river is the
main source of water in the study area. The proximity to the river body
facilitates the access to water for their various activities.

Photo 2: Use of water in the community, Photograph
taken during field work
The field survey carried in the scope of this study shows that
the vulnerability of the building structure depends on the building materials.
A total sample comprised of 221 respondents were household heads .The majority
of the households interviewed (74.7%) lived in building made up of clay walls
with thatched roof. Of the households, 13.1% lived in clay walls with
iron/tiles sheet roof's building, while 4.5% and 5.9% of the respondents lived
in brick walls with iron/tiles sheet roof and hurdle or banco walls with
thatched roof buildings, respectively. The majority of households therefore
lived in the type of houses that make them susceptible to floods.
 
Photo 3: House made in Banco and straw Photo
4: House made by clay wall with destroyed by the 2010 flood in Tokpli county
thatched roof, Photograph taken during Source: PDNA, 2010
field work
4.2.4.3. Livelihood patterns of respondents
The socio-economic status of this community constitutes another
source of vulnerability. The social economic status of households is an
important factor in assessing their vulnerabilities to disasters (Wisner, et
al. 2004:12). Almost all people of the community in the study area depend on
agriculture. The interview reveals that the main source of income for the
assessed households are agriculture activities (crop production) 90% and 7.2 %
of respondents who do not have agriculture as main activities have it as
secondary activities. 65.05% of the total respondents depend solely on
agriculture activities. Most of the surveyed households have a limited
livelihood options, for most of them indicate having no secondary livelihood
sources. Those who have a secondary activity mention second livelihood sources
such as trading, breeding, fishing, hunting, palm oil production.
The marital status of household head played an important role in
determining the livelihood strategy. Those who are married have a diversity of
livelihoods as opposed to singles, and widowed household heads "figure ".
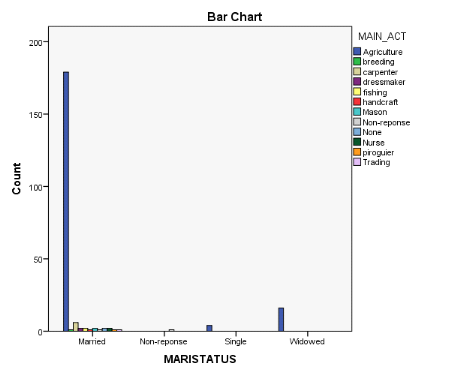 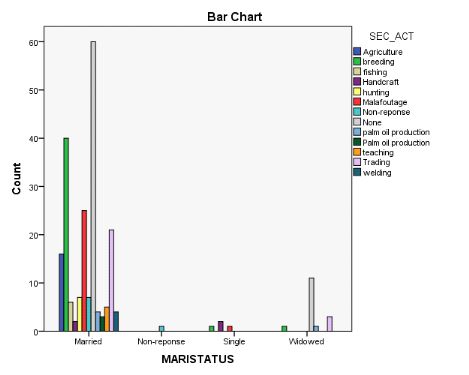
Figure 13: Livelihood Strategies by Marital Status of
Heads of Households
| 


