DEDICATION
To my Brothers and Sisters,
To all my Family and Knowledge,
Relatives, Friends and classmates.
DECLARATION BY THE CANDIDATE
Jean Claude KANYESHYAMBA hereby declare that the project
report entitled «OOIS of La GALETTE supermarket»
submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of
the degree of Bachelor in Information Systems and
Management is a record of bonafide project work
carried out by myself under the guidance of my supervisor.
I further declare that the work reported in this
project has not been submitted, either in part or in full, for
the award of any other degree or diploma in this institute or any other
institute or university.
Kigali: Signature of the candidate
Date: Jean Claude KANYESHYAMBA
INDEPENDENT INSTITUTE OF LAY ADVENTIST OF
KIGALI
(INILAK)
B.P. 6392 KIGALI, Tél:
55107311/55104697
E-mail: contact@inilak.ac.rw
Website:
www.inilak.ac.rw
BONAFIDE CERTIFICATE
This is to certify that the project report entitled
«ONLINE ORDERING AND INVENTORY SYSTEM OF LA GALETTE
SUPERMARKET» submitted by Jean Claude KANYESHYAMBA
(9867/08) to Independent Institute of Lay Adventists of Kigali in
partial fulfillment of the requirement for the award of the degree of
Bachelor in information systems and management is a record of
bonafide work carried out by him under my guidance.
Signature of the Supervisor
Signature of the Department Head
TURIHO Jean Claude MSc
ZIRARUSHYA Pierre Célestin
Academic year 2011
Date:................... Date:.................
Accredited by the Ministerial Order No 002/09 0f 09/04/2009
granting the Definitive Operating Licence
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost, We are most grateful and also extend our
lovely appreciation to the Mighty fortress is our God, a
bulwark never failing for his mercies endures forever, and by whom this work
has been made possible.
Sincere thanks goes to my
supervisor Mr. Jean Claude TURIHO, for his support throughout my entire
research. His continuous suggestions, critics, adherence and guidance made this
project a success.
I am grateful to all information system management lecturers
in the department of economics sciences for their efforts in availing the
required knowledge for entire duration of my course, and families we are going
to refer below. This work couldn't have been accomplished without their willing
moral, financial and technical support.
I acknowledge the support of La GALETTE supermarket for their
information data which helped in performance of this work.
I am also highly indebted to my friends for their support and
the sharing of everything developmental throughout my studies, may you achieve
for anything you struggle for.
Finally I thank who ever, in one way or another contributed to
the success of my project. God Bless you all.
TABLE
OF CONTENTS
DEDICATION
i
DECLARATION BY THE CANDIDATE
ii
BONAFIDE CERTIFICATE
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
iv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
v
LIST OF TABLES
ix
LIST OF FIGURES
xi
ABSTRACT
xii
LIST OF ABREVIATION
xiii
CHAPTER 1: GENERAL INTRODUCTION
1
1.1 Introduction
1
1.2 Statement of the problem
1
1.3 Interest of the study
2
1.3.1 Personal interest
2
1.3.2 Institutional interests
2
1.4 Objective of the study
2
1.4.1 General Objective
2
1.4.2 Specific objectives
2
1.5 Motivation
3
1.6 Challenges
3
1.7 Methodology approach
3
1.8 Scope of the project
3
1.9 Significance of the study
3
1.10 Expected results
4
1.11 Organization of the project
4
CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW
5
2.1 introduction
5
2.2 specific terminologies
5
2.2.1 Online
5
2.2.2 Supermarket
5
2.2.3 Customer
5
2.2.4 Product
5
2.2.5 Order
6
2.2.6 Invoice
6
2.2.7 Store
6
2.2.8 Payment
6
2.2.9 Registration
7
2.2.10 Administrator
7
2.2.11 Normal selling
7
2.2.12 Super-Selling
7
2.3 Comparative study
7
2.3.1 Online auction for vision finance
company
7
2.3.1.1 Strengths
8
2.3.1.2 Weaknesses
9
2.4 Personal contribution
10
CHAPTER III: THE ANALYSIS OF EXISTING SYSTEM
11
3.1 Introduction
11
3.2 Company description
11
3.2.1 History of La GALETTE supermarket
11
3.2.2 Structure of La GALETTE supermarket
12
3.3 Mission and vision
12
3.3.1 Vision
12
3.3.2 Mission
12
3.4 Process of existing system
12
3.4.1 Recording of product
12
3.4.2 Customer collecting product
13
3.4.3 Order process
13
3.4.4 Delivery process
14
3.4.5 Payment process
14
3.5 limitations and weakness of the system in
use
15
3.6 Proposed solutions to the problems
15
CHAPITER IV: ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE PROPOSED
SYSTEM
16
4.1 Introduction
16
4.2 Requirement specifications
16
4.2.1 Functional Requirements
16
4.2.2 Non- functional requirements
16
4.3 User Requirements Specifications
16
4.4 System Analysis
16
4.5 System design
17
4.5.1 Design and development of the system
17
4.5.2 Functional Diagram
17
4.5.3 Data Flow Diagram
18
4.5.4 Context diagram
19
4.5.4.1 DFD level 0 for whole OOIS
21
4.5.4.2 DFD level 1 for manage product
21
4.5.4.3 DFD level1 for manage customers
22
4.6 Ways of recording information
22
4.6.1 Entity Relationship Diagram
22
4.6.2 Designing the ERD
23
4.6.3 Entity Relationship Diagram
24
4.7 Conceptual Model of Data
25
4.8 Logical Data Model
26
4.9 The Conceptual Level
27
4.9.1 The Treatment Conceptual Model
27
4.9.2 Treatment Conceptual Model for Ordering
Product
28
4.9.3 Treatment Conceptual Model for Invoice
29
4.9.4 Treatment Conceptual Model for Delivering
30
4.10 Data Dictionary
30
4.11 Organizational Model of Process
33
4.12 Physical Data Model
36
4.13 Advantage of the new system
37
CHAPTER V: IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SYSTEM
38
5.1 Implementation overview
38
5.2 Description of tools used
38
5.2.1 Xampp
38
5.2.2 HTML
38
5.2.3 Macromedia Dreamweaver
38
5.2.4 My SQL
38
5.2.5 Apache
39
5.2.6 Php MyAdmin
39
5.3 Client-server Interaction
40
5.3.1 Characteristics of Clients and Servers
40
5.3.2 The client Server Architecture
41
5.3.3 Some common Internet protocols
41
5.4 Software testing
42
5.4.1Introduction
42
5.4.2 Unit testing
42
5.4.3 Integration testing
43
5.4.4 Validation testing
43
5.4.5 Black Box testing
43
5.5 Some User Interface Screenshots
44
5.5.1 Home page screenshot
44
5.5.2 Product category view screen
45
5.5.3 Customer shopping invoice
46
5.5.4 Customer login form for ordering
47
5.5.5 Authorized user login interface
48
5.5.6 Customer information interface
49
5.5.7 Customer suggestion interface
50
CHAPTER VI: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
51
6.1 CONCLUSION
51
6.2 RECOMMENDATIONS
52
REFERENCES
53
Appendices
54
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: Cardinality
26
Table 2: Data dictionary
31
Table 3: Organizational Modal of Process
35
LIST OF
FIGURES
Figure 1: Function Diagram
18
Figure 2: Context Diagram
20
Figure 3: DFD level 0 for whole OOIS
21
Figure 4: DFD level 1 for manage
product
21
Figure 5: DFD level1 for manage
customers
22
Figure 6: Entity Relationship
Diagram
24
Figure 7: TMC ordering product
28
Figure 8: TMC invoice
29
Figure 9: TMC of delivering
30
Figure 10: Physical data Model
36
Figure 11: A client and a server
41
Figure 12: the client-server architecture
42
Figure 13: Home page screenshot
44
Figure 14: Product category view screen
45
Figure 15: Customer shopping invoice
46
Figure 16: Customer login form for ordering
47
Figure 17: Authorized user login interface
48
Figure 18: Customer information interface
49
Figure 19: Customer suggestion interface
50
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this project is to design and implement online
ordering and inventory system for which the case study is La GALETTE
supermarket, specialized in the ordering of family use alimentation products
like bread, cake and fruits. The problem currently facing the La GALETTE
supermarket in the existing system; the activities like ordering online their
products, registration of customers and users details, also it doesn't easily
to control all store transaction details.
The main problems are make ordering online and to manage the
product on stock. The La GALETTE supermarket has no specific
software that helps us customers ordering their product online wherever they
are in the world and help us to manage its inventory.
This Application offers the ability to visit all products
recorded in supermarket, ordering product he/she selected, report and print
information about products stored and customers ordered products, finally it
lets the authorized user know how many products are remained in store and how
many order received.
To implement this application, setups are created and some are
installed on the server side and the other is installed on the client side.
LIST OF ABREVIATION
ASP: Active Server Page
BISM: Bachelor in Information System and
Management
CNLS: Centre Nationale de Lutter contre le
Sida
CSS: Cascading Style Sheets
DFD: Data Flow Diagram
DOM:
Document Object
Model
ERD: Entity Relationship Diagram
ERDM: Entity Relationship Data Model
FTP:
File Transfer protocol
HTML: Hypertext Markup Language
HTTP:
Hyper Text transfer Protocol
ICT: Information Communication Technology
INILAK: Independent Institute of Lay
Adventists of Kigali
IP: Internet Protocol
ISP: Internet Service Provider
LAMP : Linux, Apache, Mysql and PHP
LDM: Logic Data Model
MERISE: Méthode d'Etude et de
Réalisation Informatique pour les Systèmes
d'Entreprise
MINISANTE: Ministère de la Sante
MTN: Mobile Telephone Network
ODBMS: Object Data base Management System
OMP: Organizational Model of Process
OOIS: Online Ordering and Inventory System
OSMIS: Online Student Management Information
System
PHP: Personal Home Page or Hypertext
Preprocessor
PMD: Physical Data Model
RRA: Rwanda Revenue Authority
SMTP: Simple Mail Transport Protocol
SQL:
Structure Query Language
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
TMC: Treatment conceptual model
WWW: World Wide Web
XAMPP: X Apache, MySQL Perl and PHP
CHAPTER 1: GENERAL INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction
Today, the business is done online worldwide, the management
of institutions and company is done through network technology using internet,
all the systems of information management has been digitized. All these
innovations have the aim to simplify life by making a lot of things easily and
in a short time. Within this framework of ideas that our project: Online
Ordering and Inventory system which can be used by La GALETTE Supermarket as
my case study is developed as final work to fulfill the requirements of
obtaining BISM. As I started, many companies and institutions in our region,
particularly in our country, have lack of designed web based application that
could help and offer better service to customers, employees and administrators.
As La GALETTE supermarket has different types of product that are registered in
different register. These products have to be managed and stored or registered
and selling through on internet.
1.2 Statement of the problem
The problem currently facing the La GALETTE supermarket in the
existing system; the activities like ordering online their products,
registration of customers and users details, searching the products that are to
be put into their system, Also it doesn't easily store all transaction details.
Administrator does not properly and easily know situation of stock, and
sometimes the product are not verified on time. The number of product must
purchased is not followed. The main problem are make ordering online and to
manage the product on stock. The La GALETTE has no specific software
that help us customer ordering their product online wherever you are in the
world and help us to manage its inventory. These cause some problems such
as:
v It is not possible to sale the product online and customer
or client cannot order goods from wherever they are.
v It is very difficult to control and manage their
inventory.
That is why the La GALETTE need a software for using to
control all its inventory and all transaction related to ordering product.
The software will also manage La GALETTE to provide the right reports in real
time. There is a need of system that might be used to store different
activities' information easily and then, use those stored information to make
decision depends on privileges belongs to the users.
1.3
Interest of the study
This study entitled «OOIS of members La GALETTE
supermarket» was prompted by the following considerations.
1.3.1
Personal interest
The project will enable us to delve into different
technologies and better understand their working and hence a competitive edge
on the job, it will allow us to put in practice different skills and the
theoretical knowledge acquired during our studies and will provide us with a
hand on experience in software development.
1.3.2
Institutional interests
v Improve the response to the client, employees and
administrator.
v To carry out a good management of recorded information.
v The implementation of the management system will dispense
product in La GALETTE supermarket to manage institutional resources in an
efficient, effective and accountable.
v To increase number of product because ordering will be
online both at supermarket.
v To help RWANDA to achieve goal of making the use of ICT the
key tools in transformation the country.
1.4
Objective of the study
1.4.1
General Objective
The general objective of this project is to implement a web
based application that provides an OOIS of La GALETTE supermarket.
1.4.2 Specific objectives
The main specific objectives of the project are:
v The customers or clients will be able to order goods online
from wherever they are
v Conception and development of software for registering,
controlling all information from the different daily activities.
v This application will help the clients, employees to get
their services or product online using the keyword.
v Designing a database application that will store all
transactions and uses stored information to make some desired decision.
v Guarantee security of the system by basing on the users' and
clients privileges.
1.5 Motivation
The choose of this project is motivated by two main reasons;
the problems that this supermarket has for all time, such as: La GALETTE hasn't
any system or web based help us the customers for ordering product using
internet and the customers hasn't possibilities to access the product via
internet. Another reason is related to my own needs of developing any software
which will facilitate the customers for solving the problems said above.
1.6 Challenges
In this project, when there are interruption of power the
system can found different disability and the customers can't access it, small
producers and the people of the village where we haven't power they can't use
this system, and the records of product will take a long time because of number
of the product.
1.7 Methodology approach
For achieving this project, we preferred to use system
analysis and design, documentation technique, electronic research, observation
and investigation.
1.8 Scope of the project
Online ordering and inventory system is an application that
will permit the customers to get the information by asking information easily
wherever they are if they have access to the internet; the project is very
broad reason why we have been limited to the LA GALETTE supermarket (case
study) especially for:
v Product management
v Customer management
v Ordering, delivering
1.9
Significance of the study
v To the researcher: the researcher will have a strong
knowledge about the information management within public or private
organization and will have an opportunity to practice his knowledge of the
concepts learned from the class as an information technology undergraduates.
v To the La GALETTE managers: management and members of La
GALETTE will enjoy quick and goods online services and will have a friendly and
efficient system, it will be also a time of advertising of your product.
Furthermore, data will be more secure and relations between the La GALETTE and
its client or customer will be greatly improved.
v To the INILAK and future researchers: the INILAK and other
researchers who will be interested in this case study, can use this project for
the purpose of acquiring practical knowledge on how to control, manage or how
to create web application for OOIS of business company.
v To the government of RWANDA: this study will provide
relevant information that may help the government while making policies for
such organizations.
1.10 Expected results
The expected results are:
v Keeping the based information of customers and products
v Customers will be able to ordering product we want
v Providing the reports where those information are required
v Obtain a database for storing products and customers
information
1.11 Organization of the
project
Project is divided into six chapters:
v The first chapter is the general introduction which contains
background, statement of the problem, interest of the study, objective of the
study, hypothesis of the study, methodology used, scope of the study,
significance of the study, result of the study and the organization of the
study.
v The second chapter: presents the specific terminology, the
comparative study and the personal contribution in this study.
v The third chapter: describes the existing system.
v The fourth chapter: is concerned with the analysis and
design of the system.
v The fifth chapter: examines the implementation of the
system.
v The sixth chapter: gives the conclusion and the
recommendations/Future work
CHAPTER II: LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 introduction
The purpose of this part is to provide a brief description
about terms that are used during development of this project. It deals with
theoretical concepts and fundamentals that support this project. It provides
definitions and characteristics of technologies used. We will focus mostly on
our research which is based on the collection, identification, and accessing
the information whenever and wherever the volunteer are, if he has access to
internet.
The second part of this chapter will be focused on the
comparative study of works done in attempt to solve the found problems; it
means all researches done in order to get solution on our problem. The last
session of this chapter is our contribution to solve the same problem but
through the different ways from others.
2.2 specific terminologies
2.2.1
Online
The terms online describes a system which is connected to a
larger network available over the internet, refers to accessing a remote
computer via a terminal and the state of a computer when it is turned on and
connected to the Internet via an ISP.
2.2.2 Supermarket
A large
store
that
sells a
variety of
food and
household
items to
customers.
2.2.3 Customer
A
party
that
receives
or consumes
products (
goods or
services)
and has the
ability
to choose between different products and
suppliers
or a
person,
company, or other
entity which
buys
goods and
services produced
by another person, company, or other entity.
2.2.4 Product
In general, the product is defined as a "thing produced by
labor or effort" or the "result of an act or a process", and stems from the
verb produce, from the Latin prôdûce (re) '(to) lead or
bring forth'. Since 1575, the word "product" has referred to anything produced.
Since 1695, the word has referred to "thing or things produced".
In
marketing, a product is
anything that can be offered to a
market that might satisfy a
want or need. In
retailing, products are
called
merchandise. In
manufacturing,
products are purchased as
raw materials and sold
as
finished goods.
Commodities are usually
raw materials such as metals and agricultural products, but a commodity can
also be anything widely available in the open market. In
project
management, products are the formal definition of the
project
deliverables that make up or contribute to delivering the objectives of the
project. In insurance, the policies are considered products offered for sale by
the insurance company that created the contract.
2.2.5 Order
A confirmed request by one
party to
another to
buy,
sell,
deliver, or
receive
goods or
services
under specified
terms
and conditions. When accepted by the
receiving
party, an order becomes a
legally
binding
contract.
2.2.6 Invoice
A commercial document that itemizes a transaction between
a buyer and a seller. An invoice will usually include the quantity of purchase,
price of goods or services, date, parties involved, unique invoice number,
and tax information. If goods or services were purchased on
credit, the invoice will usually specify the terms of the deal, and
provide information on the available methods of payment or a
bill issued by one who
has provided
products or
services to a
customer, In
asset-based
lending,
invoice means
account
receivable.
2.2.7 Store
A place of deposit for goods, for large quantities, a
storehouse, a warehouse, a magazine. A place where merchandise is offered for
sale, a shop.
That
which
is
accumulated,
or
massed
together;
a
source
from
which
supplies
may
be
drawn;
hence,
an
abundance;
a
great
quantity,
or
a
great
number.
2.2.8 Payment
The
partial or
complete
discharge of an
obligation by
its
settlement in
the form of the
transfer of
funds,
assets, or
services equal to
the
monetary
value of part or all of the
debtor's
obligation. Compensation,
discharge
or
performance
of an
obligation,
or
reimbursement,
by giving over something that is of satisfactory
value to
its
recipient,
such as
money.
2.2.9 Registration
The term registration is the process of adding new
descriptions to the registry database. In computer vision, is also sets of data
acquired by sampling the same scene or object at different times, or from
different perspectives and is the act of enrolling, a document certifying an
act of registering.
2.2.10 Administrator
A person for the performance or management of administrative
business operations
2.2.11 Normal selling
Normal selling is the process of selling product at la GALETTE
supermarket for customers who buy products it means that it is not necessary to
make an order of product you want, the payment done immediately at cashier.
2.2.12 Super-Selling
Are the customers who take product at La GALETTE supermarket
and reseller in different area of Rwanda that product are bread, they give
order of quantity needed to the chief of bakery and pastry, and the employees
of bakery and pastry prepare those order according to proforma invoice, after
preparing those order chief of order checking and count for verify if number of
order are the same on the number of proforma invoice, if are the same they
deliver to customer who are waiting out of supermarket, the payment done at the
office of general director.
2.3
Comparative study
In this section, we are going to describe some works which
have the same way like this work. Which are online auction for vision finance
company.
2.3.1 Online auction for vision finance
company
According to Mr. RUMONGI Charles, student of mount Kenya
university he decides to develop online auction for Vision Finance Company
which are also very popular because they offer lower transaction costs than
auctions and offer a bigger market for rare and collectable items that may not
be available in one region, but can be bought through online auctions and
shipped almost anywhere in the world. He chooses that topic to help vision
finance company by developing a system which will help the company to manage
easily your materials, in such way I found this topic in the same way with mine
because my work is OOIS for La GALETTE supermarket which will help La GALETTE
administrator to manage easily his product and help us their customers to use
online services.
2.3.1.1 Strengths
There are many advantages that online auctioning has over
"real life" auctions, which is one of the reasons why online auctioning is one
of the most popular forms of e-commerce to date. One of the reasons for its
success is that it enables sellers to promote their goods to an extremely large
and diverse range of customers. Instead of just marketing to consumers in the
area of an auction, the market has increased to become global. As a result,
more consumers may be interested in buying a particular good, therefore driving
up the price value. The large global market can also have the reverse effect on
price value, as because there are almost billions of items available in the
online auctioning website, it is common to find overlooked and therefore
underpriced items.
Another advantage of auctioning online as opposed to
auctioning is that it is easier to find information and records containing
details of the previous history of the seller. This way, if someone has a
tendency for selling a product, taking the money, then not sending the item to
the buyer, it will be posted on the online auctioning site and people will know
to be wary of that buyer. This has resulted in sellers being more cautious and
more than in the auctioning world (Dysart; 2004; p.68).
According to Julie Vallone, of Entrepreneur magazine, many
businesses also use online auctioning sites to test their new products. They do
this to gauge how popular a product seems to be and what price range they
should be using when they introduce it to the retail market (Vallone; 2000).
Another advantage of online auctioning is simply the novelty factor that it has
as it is still considered a new concept. Many people will be drawn to auction
sites such as EBay just because they have heard about it from some other medium
and are curious to see what it is. Many of these people may be drawn in and
soon become avid buyers and/or sellers.
2.3.1.2 Weaknesses
Despite the enormous popularity
and many advantages of auctioning online, the concept also comes with its fair
share of disadvantages. One of the most common disadvantages with auctioning
online is that many bidders seem to be so caught up with an auction and the
thrill of beating another person to the last bid that they are spending more
than they can afford, and possibly more than the retail price they would pay
for the same item.
Fraud is another large and seemingly unavoidable disadvantage
of online auctioning. Unlike auctions, it is much easier for sellers to bogus
items they do not possess and collect money from the bidders without ever
sending them their items. There have been many reported cases where people have
been charged with fraud after placing nonexistent items on online auctioning
websites, but for every one of these reported cases, there are many more that
go unreported. This situation also happens in reverse, where buyers bid for an
item, the seller sends them the item believing their money is in the mail, and
it is never received. It is much harder to trace a person in the virtual world
and as opposed to the real world. For more detailed information about the issue
of fraud within online shopping, please see Online Auctioning Sites -
Security and Fraudulency
Unfair negative feedback for sellers is also another
disadvantage of online auctioning. Some sellers will make extra effort to
please all their customers, however one unreasonable customer that is
impossible to please can affect their reputation forever by placing negative
feedback on the website. This is why becoming a regular seller on online
auctioning sites can be extremely time consuming, as sellers must go out of
their way to meet all their customers' demands and requests (such as emails
requesting more details of the product and shipping, postage and handling
costs) so that they can avoid being labeled as unreliable or dishonest by their
customers.
2.4 Personal contribution
Our contribution is to improve La GALETTE supermarket online
services which will help customers and La GALETTE supermarket management will
have a reliable tool and customers will enjoy quick, secure and good online
services, Our contribution also is about providing the useful database which
contains information that will help the La GALETTE supermarket customers to
know information about their product, price of product, help us to control, by
the category of each information or problem, the system will give you an
answer, it will be able to precise the category of product he/she want to
buy.
CHAPTER III: THE ANALYSIS OF
EXISTING SYSTEM
3.1
Introduction
In this section, we briefly describe the existing system of La
GALETTE supermarket and point out the problems caused by this system. To
develop OOIS of La GALETTE supermarket, the researcher spent some time studying
the system, talking to users and finding out how the existing system works and
what is required of it by identifying and collecting necessary documentation
relating to the system. Therefore, in this chapter researcher studies and
analyses the existing system focusing on the processes using.
3.2 Company description
La GALETTE is one of supermarket located in Kigali city,
selling different products from Europe continent and Africa continent, that
product are divided into three group such as: Group A, group B and Group C
v Group A: this group is composed by
alimentation products like soaps, fruits, chocolate, milk, rice, alcohol drinks
and non alcohol drinks, juice, sugar etc...
v Group B: this group also are composed by
different product from pastry and bakery like bread of diabetes person, cake of
sugar, cake of birthday and cake of wedding, this group produced by employees
of company but others product come from out from different suppliers.
v Group C: this group is composed by product
from butcher like Meats of cow, jambo meat, meat of pork etc...
La GALETTE Supermarket has different employees divided into
group enumerated above, salary depend on experience of each group but for every
employees who begin the net salary is 55,000Frw
3.2.1 History of La GALETTE supermarket
La GALETTE is a German supermarket chain. It has 3 stores
across Rwanda and 101 employees. It is planning to expand to Congo and Burundi
countries. La GALETTE is a wholly German company owned by the Michael Fietzek.
On 5th February 1997, La GALETTE opened its first store in Kigali
Rwanda, is a supermarket specialized in the ordering of family use alimentation
products. When a customer visits the local supermarket he is able to see the
entire product category and buy if he want or go and return back other day for
buying.
3.2.2 Structure of La GALETTE supermarket
La GALETTE Supermarket are represented by General Director
who take all decision, Administrative and finance services charges the
salaries of employees, payment of different activities like: Rwanda revenue
authority, social Security Fund of Rwanda, and other
government fund this department has different branches like Accountancy,
Secretary and Human Resource, has also department production services with its
branches pastry and bakery where they produce different products like bread,
cake and last department which is commerce services for preparing an invoice
delivery to customer, For my project I will focus on production department
services.
3.3
Mission and vision
3.3.1
Vision
To provide world-class service to
customers in its areas of focus, offering solutions that are based on business
and technology insights.
3.3.2 Mission
We focus on turning customer's vision into value driven
results. We are responsive and flexible so we can build business for our
customers. We provide seamless global services for our global accounts. Our
speed in decision making results in fast business benefits are a proven end to
end front to back office business solutions enable Our relationship model
supports client value creation.
3.4
Process of existing system
The processes that we want to describe are: recording product
on shelf, customer collecting product and payment after choosing items, in this
part we have two types of customers such as: Normal and Extra-customer.
3.4.1 Recording of product
At La GALETTE supermarket, before purchasing product from
different continent, they put on store according or following on type of each
product. They use physical inventory where every product purchased recorded by
using form of stock, when chief of store want to check the number which are
on store, they take all form for each product then count product for verify if
the number written on form matching on the number of product stored.
After purchasing new product or getting product from supplier
those products are recorded on stock, for selling product are recorded on shelf
of supermarket others to cold chamber (cheese, meat) or to fridge and freezer,
some time come from to cold chamber toward freezer, before recorded to shelf
checking expiration date of product.
All products are recorded according on group of each product,
group of alimentation product, group of pastry/bakery and butcher product.
After recording all products on stock and shelf, it is necessary also to record
on machine of cashier where recordable depending on group. There is a person's
loaded that action in supermarket who controller when shelf are take care or
occupy of products.
3.4.2 Customer collecting product
When client or customers enter in supermarket, saw the product
want in different group of product and there are some employees who can help us
or orient client/customer showing where product are placed. After choosing and
selecting products can take basket for storing goods, before going can check
price, expired date and ingredients then went to cashier. Arriving there he/she
deposit around him, cashier take one by one entering on machine according also
on group of product when finished gives us to controller for making product on
free packing. When cashier finish those transactions, she/he calculate and show
client/customer on screen of machine and tell the customer total of money can
pay and give us invoice when customer or client needed.
3.4.3 Order process
Order processing" is the term generally used to describe the
process or the work flow associated with the picking, packing and delivery of
the packed item(s) to a shipping carrier between customer and order chief. The
specific "order fulfillment process" or the operational procedures of
distribution department are determined by many factors. Each distribution
department has its own unique requirements or priorities. Some of the factors
that determine the specific process flow of a distribution department are:
· The nature of the orders: customer offer to order chief
by using proforma invoice, the number of differing items and quantities of each
item in orders, example number of pain france, number of grand pain coupe and
number of sandwich.
· Time of availability: after deposit proforma invoice
and receiving it, order chief reply invoking when order will fulfilled.
3.4.4 Delivery process
Delivery process begins when the customer
first interacts with the service organization and ends when the delivery of the
desired service is completed and the customer exits the process. At La GALETTE
supermarket after getting order from chief of order, the agent of bakery and
pastry prepare the goods respectively quantities of order, when finish they
package according to each categories of product, chief of order check and count
if there no mistake done, when the number of order written to proforma invoice
are good prepared they give order for put out, before arriving to customer
there are also controller who check again for looking if there are some product
stolen, after those action customer get their order of items ordered, After
delivery that product, stump and original of proforma invoice are transferred
to office of general director.
3.4.5 Payment process
After selecting product and calculating total of money, the
payment of customer done in the following ways:
v Cash: where customer present cash to cashier or where
cashier receive money and customer get an invoice
v Cheques: where customer present check to cashier for
extra-person not every customer, example: MINISANTE, CNLS, Rwanda Revenue
Authority and Top tower Hotel
v Prepaid and Zip not yet used
In our case, an online payment will done using MTN mobile
money, where after paying La GALETTE supermarket administration will get
message from customer's ordering payment.
3.5 limitations and weakness of
the system in use
This results into some errors and or mistakes; they use slip
of stock or form of stock, which can cause different problem such as lack of
data. It has some lacks and failure which are the main reasons of developing
and designing a new system.
The existing system presents many problems relative to lack of
computerization of the OOIS for supermarket at La GALETTE it means that lack or
missing of online system.
3.6
Proposed solutions to the problems
With the existing system, it is difficult to keep up to date
information because it lacks a dynamic application connected to a database that
would automate the task.
The design of an OOIS for la GALETTE Supermarket
would solve the problems mentioned above which are very close to an inefficient
information system. Realization of this web application would allow sharing of
information between multiple interveners and would end the problems caused by
inappropriate information system by means of the below proposed solutions:
(i) Creation of a web application for online ordering in
order to help client, and putting your product in online which is not
experienced with the existing system.
(ii) Controlling and managing their inventory system that can
be operated by the proposed web application.
(iii) An online web application in which the reports will
contain all details, made and submitted on due time.
Upon implementation of this software, the system of selling
online and inventory system management will be much more secure, fast and
easily accessible to different client.
(iv) Update product and reporting up the criteria.
CHAPTER IV: ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF THE PROPOSED SYSTEM
4.1 Introduction
This chapter namely system analysis and design is created to
solve problems of existing system, it should describe the requirements
specification, functional requirement, non functional requirement, block
diagram and entity relationship diagram.
4.2
Requirement specifications
4.2.1 Functional Requirements
In
software
engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a
software system or
its component can be capturing the intended behavior of the system. This
behavior may be expressed as Services, tasks or functions the system is
required to perform. This part of the requirements document states in detailed
and precise manner what the application will do. In this study will focus on
ordering product, payment, delivering product to customer, checking product on
store. At least one machines connected to the network and a user are required.
4.2.2 Non- functional requirements
Non functional requirements are those characteristics that
cannot be expressed in this project. This new system created should not manage
all units done into supermarket such us suppliers, management of employees,
management of manufacturing of product and calculating all expenses. Any person
will not able to access for changing, deleting and to adding something to the
system without authorization of administrator.
4.3
User Requirements Specifications
The software requirements document is a written statement of
what the software will do. What the software does is directly supposed by its
users- either human user or other software systems. When an external system
submits a request of a certain form, it gets a particular response. The main
purpose of requirements document is to serve as an agreement between the
developers and the users on what the application will do.
4.4
System Analysis
Any system designer will first analyze the existing system to
point out the problems which are the system requirements creating need for a
new one. The system analysis in this study has been catered for in the research
phase during which the designer looked at how the existing operates and its
shortcomings. Here the target is to come up with an OOIS which would facilitate
the customers and then display the information about product needed for
customer and to users using appropriate programming languages and web server in
this case Easy PHP, HTML and Apache service respectively, here we will use
merise method.
Merise method: is a method that is used to
develop and to realize information technology. The principal objective of this
method is the realization of information system. This method helps in data
analysis and in data division in order to facilitate their handling.
4.5 System design
4.5.1 Design and development of
the system
The design of a system uses the functional specification as
source and produces the details that condition how system will assemble the
requirement identified during system analysis. The design process should take
care of the following:
· Recording product
· Apply for customer
· Ordering product
· Delivery product
· Check product
· Reporting
The detailed design of input, output, files, database, test
plan and other tasks are intended to be executed; data capture forms must be
designed, clerical procedures laid down and all aspects of the design must be
documented.
4.5.2 Functional Diagram
Function diagram is used to show system's functions that will
be constructed and the implementation process of data diagram. In addition,
function diagram will also be used to determine the appearance of smaller
process in that flow chart. Function diagram show to do not, how do. In
functional diagram, a function is divided into many smaller functions and each
smaller function contains many even smaller ones. Constructing diagram is a
process of division, from a higher function to appropriate smaller functions.
Diagram need to be presented clearly, simply, exactly, fully and balanced
function of the same level has the same level of difficulty need to be on the
same page. In the current system, the function hierarchy diagram is as
follows:
Online ordering and inventory
system
Order
Management
Report
Product
Management
Customer
Management
List of customer
List of product
Recording order
List of order
Registration of new customer
Registration
Update
Deliver product
Balance of stock
Update
VAT
List of sales
Search customer
Search product
Figure 1: Function
Diagram
4.5.3 Data Flow Diagram
DFD is a graphical representation of the «flow» of
data through an information system. DFDs can also be used for the visualization
of data processing (structured design). On a DFD, data items flow from an
external data source or an internal data store to an internal data store or an
external data sink, via an internal process.
It is common practice for a designer to draw a context-level
DFD first which shows the interaction between the system and outside entities.
This context-level DFD is then «exploded» to show more detail of the
system being modeled. With a dataflow diagram, users are able to visualize how
the system will operate, what the system will accomplish and how the system
will be implemented. Dataflow diagrams can be used to provide the end user with
a physical idea of where the data they input , ultimately has an effect upon
the structure of the whole system from order to dispatch to restock how any
system is developed can be determined through a dataflow diagram. In my case
DFD will be the intermediate of analyst and user of this system how the
customers make order up delivering date.
4.5.4
Context diagram
Is a diagram that represents the actors outside a system that
could interact with that system, This diagram is the highest level view of a
system, similar to Block diagram, showing a possibly software-based, system as
a whole and its inputs and outputs from/ to external factors.
In our case, external entities are the customers who will need
the various services from the system, and the Administration office who will
request the reports.
v From customer to the system: the system will provide
information using online system and customer access it without changing
anything and customer choosing the product and send order to the system, the
system accept or refuse, when the system accept it send to him an invoice, the
customer pay according to the invoice after the system give to him delivery
date of the product ordered.
v From administrator to the system: administrator requests
reports to the system and the system provide the report requested.
The detail information is presented in context diagram
below:
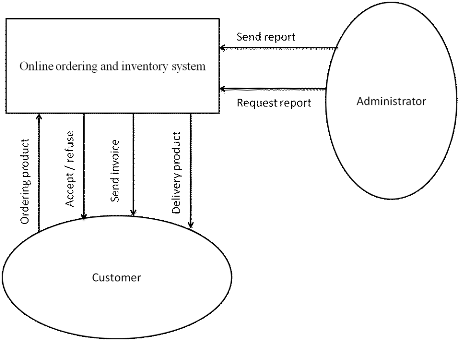
![]()
Figure 2: Context
Diagram
4.5.4.1 DFD level 0 for
whole OOIS
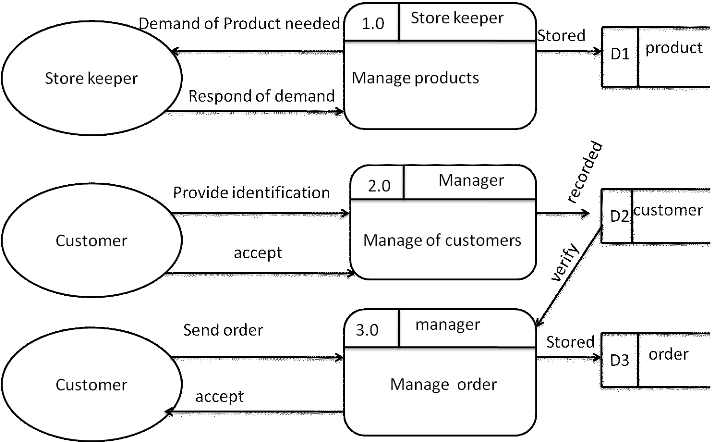
![]()
Figure 3: DFD
level 0 for whole OOIS
4.5.4.2 DFD level 1 for
manage product
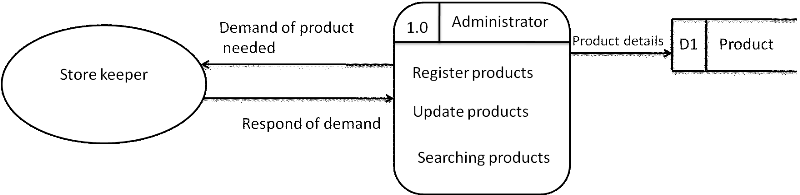
Figure 4: DFD
level 1 for manage product
4.5.4.3 DFD level1 for
manage customers
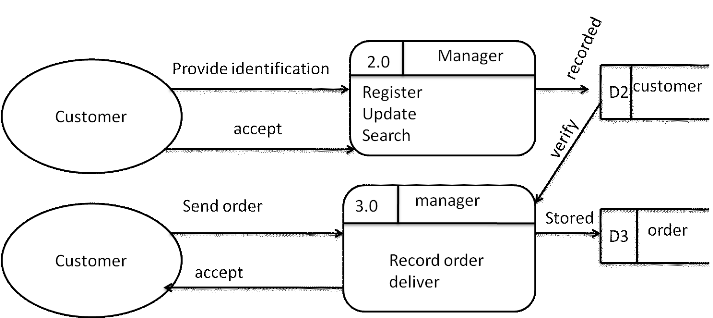
![]()
Figure 5: DFD
level1 for manage customers
4.6
Ways of recording information
The information will be recorded in My sql database. A
database contains different parts which are used to record and manipulate
information. The following steps elaborate on the components and design of an
ERDM.
4.6.1
Entity Relationship Diagram
An ERD is a specialized graphic that illustrates the
interrelationships between entities in a database. ERD often use symbols to
represent three different types of information. Boxes are commonly used to
represent entities. Diamonds are normally used to be solved while retaining its
essential features one-to-one relationships.
This type of relationship takes place when a single occurrence
of an entity is relationship to just one occurrence of a second entity.
The term entity is widely used in database circles and is used
to mean any distinguishable object that is to be represented in the database.
ERDM is based on a perception of a real world that consists of a collection of
basic object called entities and also of relationships among these objects.
4.6.2
Designing the ERD
Entities are described in a database by set of attribute, like
the attribute username, password, telephone number, employee id and address
describe the entity, employees in the ERDM illustrated below. The primary key
employee id is used to uniquely identify an employees (since it may be possible
to have two employees with same name, surname, etc) the entity relationships
are shown in diamond shapes. The set of all entities of the same type and set
of all relationships of same type are termed as an entity set and relationship
set respectively, the overall logical structure (schema) of a database can be
expressed graphically by an ERD, which is built up from the following
components:
Rectangle: represent entity sets
Ellipse: represent attributes
Diamonds: represent relationship among entity sets
Lines: links attributes to entity sets and sets and entity
sets to relationships
Process
Each component is labeled with the entity or relationship that
it represents.
4.6.3 Entity Relationship
Diagram
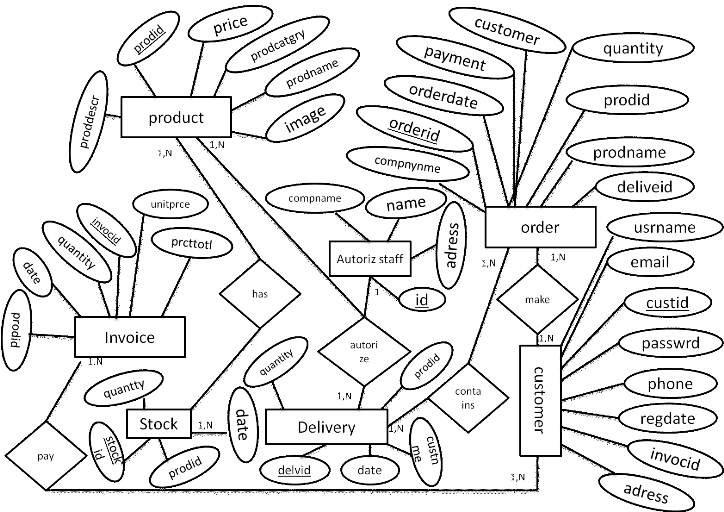
Figure 6: Entity
Relationship Diagram
4.7 Conceptual Model of Data
CMD has for goal to write under a formal way data that will be
used by the management information system. It is exactly a representation of
data, easily comprehensible, permitting to describe the system of information
by use of entities. This diagram permits to represent the structure of the
system of information for the data; this means the dependences or the relations
between different data.
The intervening elements in the modeling of the conceptual
model of data are:
Entity: an entity is the representation of a
material or immaterial element having a role in the
system that is to be described.
Attribute: An attribute is a characteristic
of an entity that we want to record or retrieve later.
Data : A data is the element of an entity. It
is the most important element of database.
Identifier: is a set of properties (one or
several) permitting to designate one and a unique
entity; it is a particular property of an object as there
can't exist two occurrences of this
object for which this property could take the same value.
Association: It makes possible to connect one
or more entities. These connections are stated via management rules. Contrary
to the entity, association is named with a verb. There are
different association's types.
Cardinalities: Cardinalities are a couple of
values (minimum, maximum).
The minimum cardinality corresponds to the minimal number of
times that each entity occurrence takes part in the
association occurrences. It generally takes values 0 or 1. The maximum
cardinality corresponds to the maximum number of times where each occurrence of
the entity takes part in the occurrences of association. It is at least equal
to 1. The infinite one is noted «N».
Table 1: Cardinality
|
Cardinality
|
Signification
|
|
1,1
|
One -to- one
|
|
1, N
|
One -to-many
|
4.8 Logical Data Model
Logical data models represent the abstract structure of some
domain of information it will Includes all entities (tables), attributes
(columns/fields) and relationships (keys) , Is independent of technology
(platform, DBMS), Is normalized to
fourth normal
form (4NF) used in development of this system.
1. CUSTOMERS (CustomerId, Adress,
InvoiceId, username, password, Email, Regdate, Phone)
2. PRODUCT (ProductId, Prodcategory,
Prodname, Proddescription, Image, Prodprice)
3. INVOICE (Invoiceid, Prodid,
pricetotal, Unitprice, Date, Quantity)
4. ORDER (Orderid, Orderdate,
Customername, Quantity, Prodname, Prodid, Companyname, Deliverydate)
5. STOCK (Codestock, Prodid, regdate,
Quantity)
6. DELIVERY (DeliveryId, product,
Quantity, Customer, Datereceivable)
7. AUTORIZED STAFF (Id, name, Adress,
Companyname)
8. CONTAIN(ProdId, InvoiceId,
DateofCreate)
9. MAKE (CustomerId, OrderId, Productname)
10. PAY (CustomerId,InvoiceId,ProductId)
11. HAS (ProductId, Productname, StockId)
12. CONTAINS (OrderId, DeliveryId, Date)
13. AUTHORIZE (DeliveryId, Id, date of
receivable)
4.9 The Conceptual Level
4.9.1 The Treatment Conceptual
Model
The conceptual model of treatment permits to treat the
dynamism of the information system, it means that operations are achieved
according to events. This model permits to represent schematic way the activity
of an information system without making reference to organizational choices or
the means of execution therefore. That is to say it allows defining what must
be done merely, but it doesn't say when, how, nor where.
The event
An event represents a change in the outside environment to
the information system; it can also represent a change in the information
system itself.
An external event is a change of the outside universe of the
information system
Symbol used:
An internal event is an internal change to the information
system
Symbol used:
The Process
A process is a subset of
the activity of the enterprise. It means that the activity of the enterprise is
constituted of a set of process. A process is itself composed of treatments
regrouped in a set named operations.
Symbols used:
The Operation
An operation is a set of actions executed by the system
following an event, or to a conjunction of events. This sets of actions are
interrupted, that means that the events are not taken so much into
consideration, as long as the operation has not yet been accomplished.
The synchronization
The synchronization of an operation defines a Boolean
condition on the contributive events having to trigger an operation. These are
therefore conditions at the level of events governed by a logical condition
achieved by the logical operations: EITHER, AND and NO.
Symbol used:
4.9.2 Treatment Conceptual Model
for Ordering Product
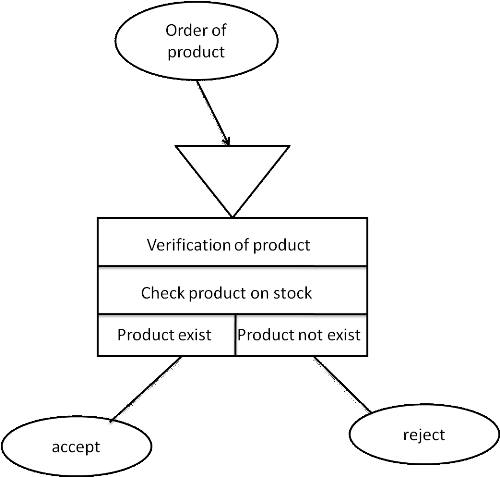
Figure
7: TMC ordering product
4.9.3 Treatment Conceptual Model for Invoice
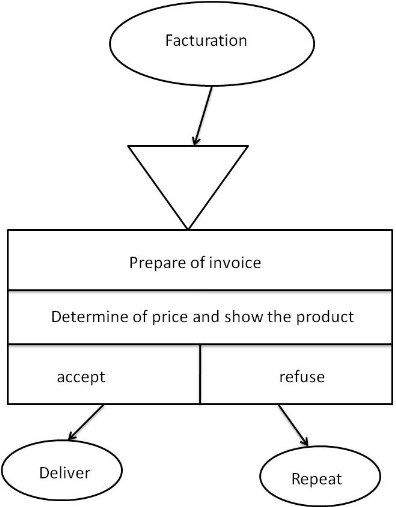
![]()
Figure
8: TMC invoice
4.9.4 Treatment Conceptual
Model for Delivering

Figure 9: TMC of
delivering
4.10 Data Dictionary
A data dictionary is a collection of descriptions of the
data
objects or items in a data model for the benefit of programmers and others who
need to refer to them or the dictionary of data is at a time the pillar of work
and the result of research and analysis of data. It is just like a depicted
picture of the entire work. This dictionary of data defines all categories of
data or data types, brief the all essential information about the software is
included.
Table 2: Data
dictionary
|
TABLE
|
FIELD
|
DESCRIPTION
|
TYPE
|
CONSTRAINTS
|
|
CUSTOMER
|
CustomerId
|
Identification of the customer
|
Varchar(15)
|
Primary key
|
|
InvoiceId
|
Identification of the invoice
|
Int
|
Foreign key
|
|
Username
|
Name of the customer
|
Varchar(14)
|
Not null
|
|
Email
|
E-mail using
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Password
|
Customer password
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Phone
|
Phone of customer
|
Varchar(10)
|
Not null
|
|
Regdate
|
Date of registration
|
Date
|
Null
|
|
Adress
|
Adress of customer
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
PRODUCT
|
ProductId
|
Identification of product
|
Varchar(10)
|
Primary Key
|
|
Prodcategory
|
Category of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Prodname
|
Name of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Productdescription
|
Description of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
Price
|
Price of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Image
|
Image of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
INVOICE
|
InvoiceId
|
Identification of invoice
|
Varchar(15)
|
Primary Key
|
|
ProductId
|
Identification of
the product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Foreign Key
|
|
Quantity
|
Quantity of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Date
|
Time of writing an invoice
|
Date
|
Not null
|
|
Unitprice
|
Price of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Pricetotal
|
Amount of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
ORDER
|
OrderId
|
Identification of order
|
Varchar(15)
|
Primary Key
|
|
ProductId
|
Identification of
the product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Foreign Key
|
|
Orderdate
|
Date of order
|
Date
|
Not null
|
|
Customername
|
Name of customer
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Quantity
|
Quantity
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Productname
|
Name of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Companyname
|
Name of company
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Deliverydate
|
Date of delivery product
|
Date
|
Not null
|
|
STOCK
|
Codestock
|
Identification of stock
|
Varchar(15)
|
Primary Key
|
|
ProductId
|
Identification of product
|
Varchar(20)
|
Foreign Key
|
|
Regdate
|
Date of registration
|
Date
|
Not null
|
|
Quantity
|
Quantity
|
Int
|
null
|
|
DELIVERY
|
DeliveryId
|
Identification of delivery
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Product
|
Product
|
Varchar(15)
|
null
|
|
Quantity
|
Quantity of product
|
Int
|
Null
|
|
Customer
|
Description of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
Datereceivable
|
Date of receivable
|
Date
|
Null
|
|
AUTORIZED STAFF
|
Id
|
Identification of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
Name
|
Name of authorized staff
|
Varchar(15)
|
Null
|
|
Address
|
Address of person
|
Varchar(15)
|
null
|
|
Companyname
|
Name of company
|
Varchar(15)
|
null
|
|
MAKE
|
Customerid
|
Identification of customer
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Orderid
|
Identification of order
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Product
|
product
|
Varchar(15)
|
null
|
|
PAY
|
Customerid
|
Identification of customer
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Invoiceid
|
Identification of invoice
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
Prodid
|
product
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
HAS
|
Stockid
|
Stock
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Productid
|
Product
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Productname
|
Name of product
|
Varchar(15)
|
Not null
|
|
CONTAINS
|
Orderid
|
Identification of order
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Deliveryid
|
Delivery
|
Int
|
Not null
|
|
Date
|
Date
|
Date
|
Not null
|
4.11 Organizational Model
of Process
The diagram shown below is there to represent OMP that is to
be done in the system. It seems there for describing properties of untreated
data of processes that had not been treated by the Conceptual Model of
Processes.
Task: Group of elementary operations executed
within a functional procedure (phase of execution).
C: Computerized
M: Manual
|
Period
|
Process
|
Nature
|
Workstation
|
|
When customer ordering product
Preparing invoice
Delivering product
|
|
C
C
C
|
Place
Any where within internet
Any where within internet
Anywhere within internet
|
Actor
customer
Accountant
Delivery office
|
Resources
Computer
|
Table 3: Organizational Modal of Process
4.12 Physical Data
Model
The PDM is used to design the internal schema of a database,
depicting the data tables (derived from the logical data entries), the data
columns of those tables (derived from the entity attributes), and the
relationships between the tables (derived from the entity relationships). The
features of the physical model of data include:
v Specification of all the tables and columns.
v Foreign keys are used to identify relationship between
tables.
v Physical considerations may cause the physical model of data
to be quite different from the logical model of data.
At this level, the data modeler will specify how the logical
data model will be implemented in the database schema. The steps for physical
data model design are as follows:
v Convert entities into tables.
v Convert attributes into columns.
v Modify the physical model of data based on physical
constraints.
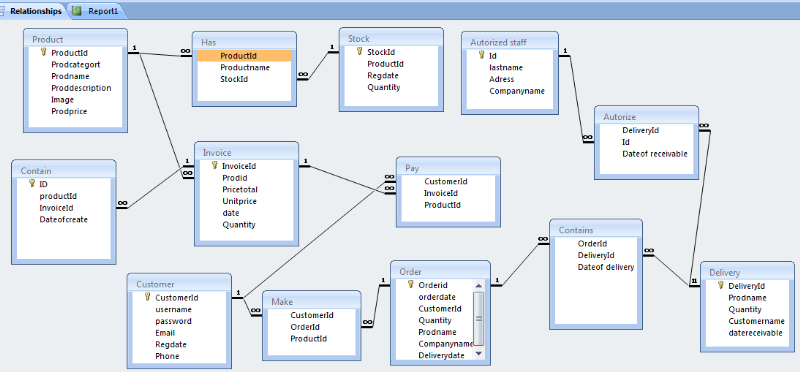
Figure 10: Physical data Model
4.13 Advantage of the new system
The OOIS of La GALETTE supermarket is developed to support the
existing system which presents some deficiencies. This new system will help to
reduce the imperfection of clients or customers within the La GALETTE
supermarket by replacing the existing system in order to benefit the advantage
of information technology in better management of La GALETTE supermarket and
other company of business.
CHAPTER V: IMPLEMENTATION
OF THE SYSTEM
5.1
Implementation overview
The fifth chapter putting a planned system into action and
examine in details the analysis and design of the online ordering and inventory
system of la GALETTE supermarket. The present chapter discusses the
implementation of the system, highlighting the testing exercise and describing
some of the main components of the system's Graphical User Interface. It will
give an output from programming language and other tools used to develop our
system.
5.2
Description of tools used
The tools used in designing an online ordering and inventory
system of la GALETTE supermarket are:
5.2.1 Xampp
Is a complete software package allowing using all the power
and flexibility that offers the dynamic language PHP.
5.2.2 HTML
Hypertext markup language has been used to design web pages,
forms, tables, and creating some links.
5.2.3 Macromedia Dreamweaver
Is the best tool (software) to create professional websites
and is now the easiest tool to build attractive website. For the first time we
can work in single environment to quickly create, build an internet
application. The back-and of the system which is the database was designed
using MY SQL.
5.2.4
My SQL
MySQL, pronounced either "My S-Q-L" or "My Sequel," is an open
source relational database management system. It is based on the structure
query language , which is used for adding, removing, and modifying information
in the database. Standard SQL commands, such as add, drop, insert, and update
can be used with MySQL.
MySQL can be used for a variety of applications, but is most
commonly found on Web servers. A website that uses MySQL may include Web pages
that access information from a database. These pages are often referred to as
"dynamic," meaning the content of each page is generated from a database as the
page loads. Websites that use dynamic Web pages are often referred to as
database-driven websites.
Many database-driven websites that use MySQL also use a Web
scripting language like
PHP to access information
from the database. MySQL commands can be incorporated into the PHP code,
allowing part or all of a Web page to be generated from database information.
Because both MySQL and PHP are both open source (meaning they are free to
download and use), the PHP/MySQL combination has become a popular choice for
database-driven websites.
5.2.5
Apache
Apache is primarily used to serve both static content and
dynamic Web pages on the World Wide Web. Many web applications are designed
expecting the environment and features that Apache provides. Apache is the web
server component of the popular LAMP web server application stack, alongside My
SQL, and the PHP /Perl /Python programming languages. Apache is used for many
other tasks where content needs to be made available in a secure and reliable
way.
One example is sharing files from a personal computer over the
Internet. A user who has Apache installed on their desktop can put arbitrary
files in the Apache's document root which can then be shared Programmers
developing web applications often use a locally installed version of Apache in
order to preview and test code as it is being developed.
5.2.6
Php MyAdmin
Php MyAdmin is a well known and popular open-source tool
written in PHP intended to handle the administration of My SQL over the
Internet. Currently it can create and drop databases, create/drop/alter tables,
and delete/edit/add fields, execute any SQL statement, and manage keys on
fields. My SQL is the most popular open-source database, used by millions of
developers and supporting numerous large dynamic websites and applications. My
SQL acquired this wide popularity by virtue of its open-source nature,
performance, reliability, robustness, and support for various platforms.
This popularity has also been helped by the existence of php
My Admin, the industry-standard administration tool that makes database
management easy for both the experienced developer and the novice. The powerful
graphical interface that it provides to My SQL has made php My Admin an
indispensable tool for My SQL and web developers. Every php My Admin user can
benefit from unlocking the full potential of this powerful application. Whether
you are an experienced developer, system administrator, web designer, or new to
My SQL and php My Admin, this book will show you how to increase your
productivity and control when working with your databases.
My SQL is a very popular Open Source relational database.
Database is a data structure used to store organized information. A database is
typically made up of many linked tables of rows and columns. For example, a
company might use a database to store information about their products, their
employees, and financial information. Databases are now also used in nearly all
e-commerce sites to store product inventory and customer information. Database
software, such as Microsoft Access, FileMaker Pro, and My SQL is designed to
help companies and individuals organize large amounts of information in a way
where the data can be easily searched, sorted, and updated.
5.3
Client-server Interaction
5.3.1 Characteristics of Clients
and Servers
In general, client software has the following characteristics:
· It is an application program that becomes a client
temporarily when remote access is needed, but performs other computation
locally.
· It is invoked by a user and executes for one session.
· It runs locally on the user's computer.
· It actively initiates contact with a server (CONNECT
primitive).
· It can access multiple services as needed.
In general, server software has the following characteristics.
· It is a special-purpose program dedicated to providing
one service.
· It is invoked automatically when a system boots, and
continues to execute through many sessions.
· It runs on a shared computer.
· It waits passively for contact from arbitrary remote
clients (LISTEN primitive).
· It accepts contact from arbitrary clients, but offers a
single service.
Note that the word server is (strictly) referring to
a piece of software. However, a computer running one or more servers is often
(incorrectly) called a server. Like most application programs, a
client and a server use a transport protocol to communicate.
Figure 12 illustrates a client and a server using the TCP/IP
protocol stack.
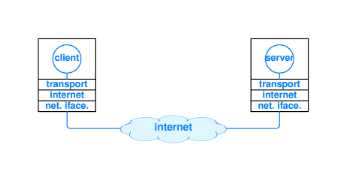
Figure 11: A client and a
server
5.3.2 The client Server
Architecture
The Internet revolves around the client-server architecture.
Your computer runs software called the client and it interacts with software
known as the server located at a remote computer. The client is usually a
browser such as
Internet Explorer,
Netscape Navigator or
Mozilla. Browsers interact with the server
using a set of instructions called
protocols.
These protocols help in the accurate transfer of data through requests from a
browser and responses from the server. There are many protocols available on
the Internet. The
WWW,
which is a part of the Internet, brings all these protocols under one roof. You
can, thus, use HTTP, FTP, Telnet, email etc. from one platform - your web
browser.
5.3.3
Some common Internet protocols
·
HTTP: used on the WWW for transferring web pages and files contained in web
pages such as images.
·
FTP: employed for transferring files from one machine to the other.
· SMTP: used for email.
· Telnet
Protocol: Used to open telnet sessions.
The web employs a connection-less protocol, which means that
after every client-server interaction the connection between the two is
lost.
Let us now examine the client-server inter-communication with three
models
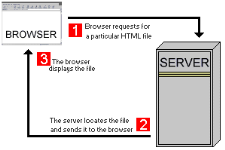
Figure 12: the
client-server architecture
5.4
Software testing
5.4.1Introduction
The testing phase is the
stage that follows the implementation of the program with the aim to verify
whether it responds to the existing problem or it does what it has to do.
It also involves the examination of the functionality of
program in general to ensure that the software responds to the needs of the
users.
This will verify the performance of the program in matters of
security and portability. The bottom line is that the software should be
delivered, not only working correctly but also satisfying other attributes such
as usability and maintainability. The following test methods were used to try
to uncover all possible errors and verify that the system fully satisfies its
requirements. It is worth mentioning that we have tried to follow the best
practices suggested by all software engineering researchers.
5.4.2 Unit testing
We used this method of testing in purpose of taking smallest
piece of testable in our application, isolate it from the remainder of the code
and determine whether it behaves exactly as we expect.
Each unit is tested separately before integrating them into
modules to test the interfaces between modules.
5.4.3 Integration testing
Integration testing is a logical extension of unit testing. In
its simplest form, two units that have already been tested are combined into a
component and the interface between them is tested. A component, in this sense,
refers to an integrated aggregate of more than one unit. In a realistic
scenario, many units are combined into components, which are in turn aggregated
into even larger parts of the program. The idea is to test combinations of
pieces and eventually expand the process to test your modules with those of the
groups.
Eventually all the modules making up a process are tested
together. Beyond that, if the program is composed of more than one process,
they should be tested in pairs rather than all at once.
5.4.4 Validation testing
Test validation is a procedure that demonstrates that a test
is job-related and correlates to on the job-performance. There are
three main types of validation:
Content validation is a procedure where the
content of the job in question is analyzed, matched and compared, (function by
function) to the abilities measured by the test. This shows that the test is
related to the job.
Concurrent validation is a procedure which
tests individuals currently in the position, and the statistically compares the
test results, after a certain time, to on-the job performance.
Predictive validation is a procedure which
tests individuals when they are hired, and then statistically compares the test
results, after a certain time, to on-the job performance.
5.4.5
Black Box testing
Black testing takes an external perspective of the test object
to derive test cases. These tests can be functional or non-functional, through
usually functional. The test designer selects valid and invalid inputs and
determines the correct output. There is no knowledge of the test object's
internal structure.
This method of test design is applicable to all levels of
software testing: unit, integration, functional testing, system and acceptance.
The higher the level, and hence the bigger and more complex the box, the more
one is forced to use black box testing to simplify. While this method can
uncover unimplemented parts of the specification, one cannot be sure that all
existent paths are tested.
5.5 Some User Interface
Screenshots
For this project, we have many forms such as: Home page,
product category, Customer shopping invoice, Customer login form for ordering,
Authorized login form, Customer information form and customer suggestion
form.
Some of these forms are going to be shown and more described
below.
5.5.1 Home page
screenshot
The home page is the first page which shows what our system
does.

Figure 13: Home
page screenshot
5.5.2 Product category
view screen
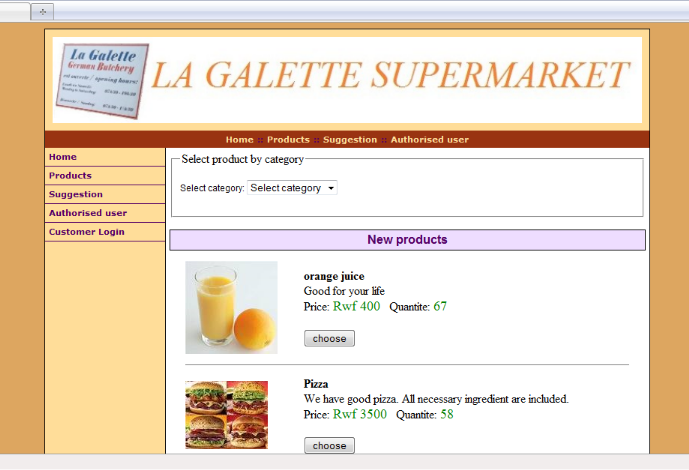
Figure 14: Product category view screen
5.5.3 Customer shopping invoice
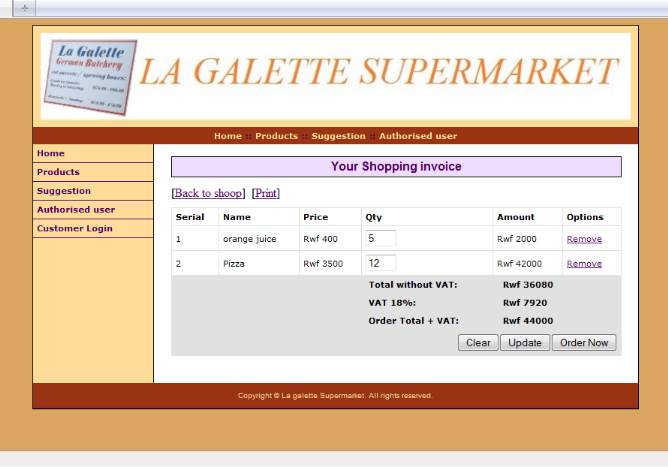
Figure 15: Customer shopping invoice
5.5.4 Customer login form
for ordering
This is the form that helps us the customers to be registered
and where can fill when ordering product.
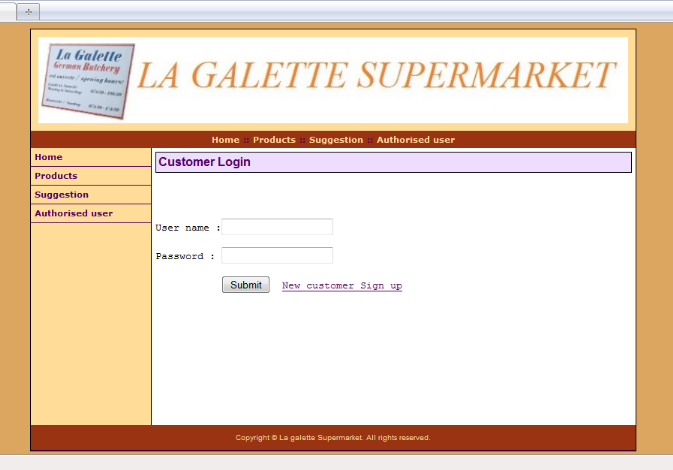
Figure 16: Customer login form for
ordering
5.5.5 Authorized user
login interface
This form that allows the administrator to login to the
system, for add new products, updating product, controlling stock and others
activities of all systems.
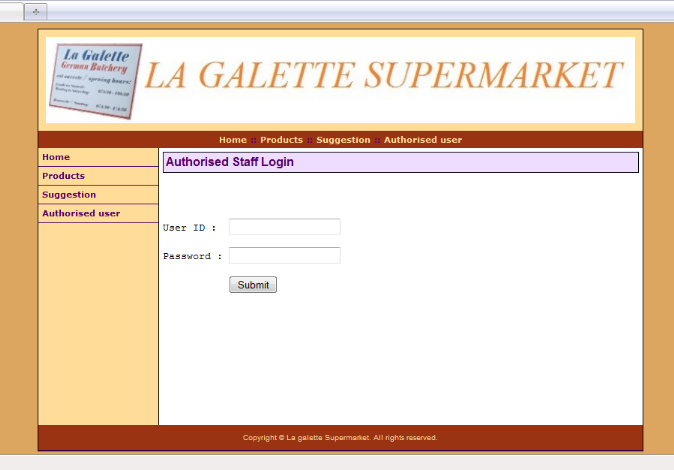
Figure 17:
Authorized user login interface
5.5.6 Customer information
interface
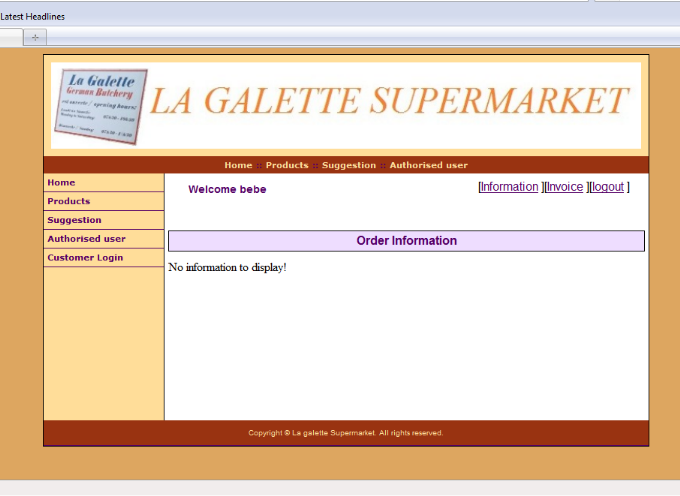
Figure 18:
Customer information interface
5.5.7 Customer suggestion
interface
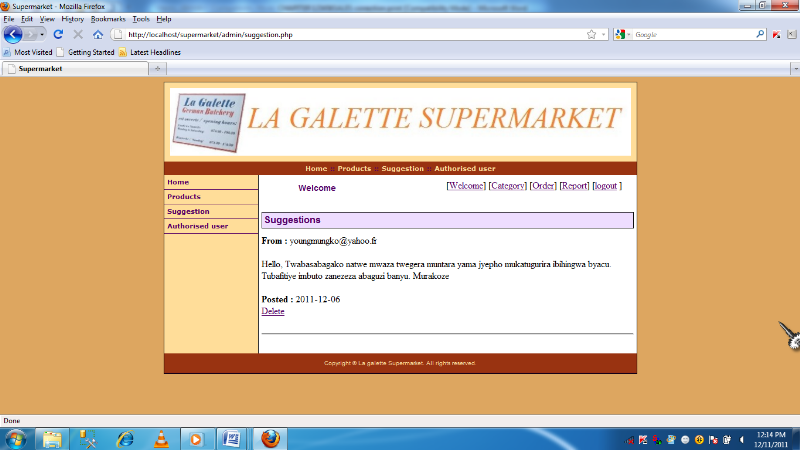
Figure 19: Customer suggestion interface
CHAPTER VI: CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATION
6.1 CONCLUSION
The core objective of the current project was to design and
implement OOIS.
This objective has been achieved successfully with the best
practices in designing OOIS.
The administrator of la GALETTE supermarket will have the full
control of the Online Ordering and Inventory System.
The choice of the topic was motivated by our desire to
apply the knowledge acquired during our studies in developing a real -world
application that satisfies not only its specifications, but also the industry
standards as far as software engineering is concerned.
The requirements were drawn from a careful analysis of
the existing system in use and its problems, and the analysis, design and
implementation were guided by the provision of a system that effectively and
efficiently solves the problems identified. The result of our project
is the OOIS for La GALETTE supermarket in which a module for recording
products, ordering products module, a payment process of checking customers
before delivering product ordered and a reporting module are fully implemented.
OOIS has the various features such
as:
v Allowing the user register a new customer, recording
products, updating, deleting products and other activities
v Knowing the quantity of order that have been received for
every day
v Knowing the quantity of products that remain in store for
every day
v Knowing the number of completed and remaining hours for
every course.
v Knowing the quantity of all products stored.
v Generating report for the whole product and order received
or sending
v Printing options
This Application has been developed with flexibility to be
modified later easily and has been tested on machines having windows operating
system.
6.2 RECOMMENDATIONS
For further researchers especially INILAK students and other
interested to improve in this project we recommend:
v To add more features like payment using credit card.
v We recommend La GALETTE supermarket to implement this
application at least in the ordering department to test the benefit of it. And
later this can be expended to the whole supermarket.
REFERENCES
a) Books and publications
1. Horak, Ray, Uyless Black, and mark Miller,
Communication Systems and Networks: Vocie, Data and
Broadband Technologies.IDG Books, 1996.
2. Janet Valade.PHP & MYSQL for Dummies. Wiley
Publishing inc. Second Edition, 2004.
3. Kayata Wesel, Ellen. Wireless Multimedia Communication:
Networking Video, Voice and Data. Addison-Wesley, 1997.
4. M. Kumar and S.I. Feldman, «Business Negotiations on
the Internet,» proc. inet'98, Geneva Switzerland, July 21-23 1998.
5. Tim Converse and Joyce Park with Clarck Morgan. PHP5
and MYSQL Bible. Wiley publishing inc., Canada 2004.
b) Courses
1. KAGORORA Samson, Web programming course, independent
institute of lay Adventists of Kigali, 2009.
2. BATAMULIZA Charlotte, E-commerce course, independent
institute of lay Adventists of Kigali, 2009.
3. KAGARAMA Jean Baptiste, System Analysis and Design Course
notes, independent institute of lay Adventists of Kigali, 2009.
c) Websites
1. Point of sale/www.codessources.com /accessed on
29th.November.2011
2.
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/supermarket.html,
16th of November 2011
3. http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/customer.html,
16th of November 2011
4.
http://www.businessdictionary.com/definition/order.html,
16th of November 2011
5.
http://www.investopedia.com/terms/i/invoice.asp#ixzz1dVRBxRER,
16th November 2011
6.
ttp://thinkexist.com/dictionary/meaning/store/,
16th of November 2011
7.
http://www.investorwords.com/3634/payment.html,
16th of November 2011
8.
http://www.thefreedictionary.com/registration
, 16th of November 2011
Appendices
| 
