2. ERP System Implementation 2.1. What is an ERP
System?
ERP means "enterprise resource planning" and it is a computer
application. That enables the company to manage and optimize all of its
resources.
ERP provides availability of different modules that cover all
business needs such as undertaking, since commercial production, logistics,
finance, human resources, customer service, (all fields are present at an equal
level completeness). ERP System dependents on the different process and on the
different areas caused by the use of a common database.
ERP system provides the company with the enables to manage and
control several sites, languages and currencies simultaneously. Therefore, the
ERP system is fully recognized and used at international level.
Organizational and functional integration was built around the
knowledge of different management processes and interaction between different
services. The complexity of this integration is growing fast with the number of
areas covered and with the number of users, which itself is a technology that
is a set of techniques, expertise and practices.
- ERP technology
As the applications share the same information, the system must
be developed with
rules built inside the database. The development of the
screens and reports can be
minimized since each application does not require
duplication of share data update
capabilities. For instance, defining departments can be done in
one site and shared by all applications.
- Know-how and best practices
ERP systems require a big more effort in terms of planning and
resources implementation than stand-alone applications. Integration means that
all functional areas and business process's have to be considered prior to any
decision.
3. Implementation of ERP System
3.1. The architecture of the ERP project
The architecture of an ERP project consists in defining its
division into subprojects. The division into sub-projects is a breakdown into
different types of activity. Subprojects allow the implementation of the global
project, but each of them requires, for its realization, different techniques
involving specific skills. Project success depends on a good timing and
coordination between subprojects, which are the responsibility of the project
management.
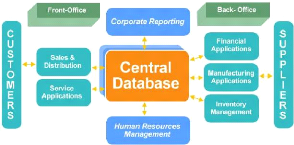
Figure 1. Architecture of an ERP Project
3.1.1. Change management
The role of this subproject is related mainly to users
training, data preparation as well as to organizational change. This subproject
must be conducted in parallel with the implementation of the ERP and it is
essential for the transition phase.
Change management is conducted by operational users and
accompanied by external consultants.
3.1.2. Technical structure
This subproject reviews:
- The technical infrastructure needed to run the software.
Infrastructure refers to servers, networks, workstations that give users an
access to the ERP. This infrastructure consists in hardware but also in
software (operating system, database system, utilities). It will be necessary
first for the team project and then for the production phase.
- The operating environment of the ERP itself and all the
components that are necessary for the implementation: interfaces, conversions
and database.
- All the adjustments to the standard product that the company
decides to implement. The activities will be related to their definition,
design, implementation, testing and documentation
These adaptations depend on the specific functions that the
company decides to maintain and which are not provided by the ERP. This means
modifications or creation of states or screens with or without modifications on
the standard chaining screens.
| 


