2.2.3. Sustainable development
According to WENDY H. (1997:69), sustainable development is a
process by which members of the society, starting from the most
disenfranchised, increase their personal and common capacities critically to
reflect, decade and read their world and organizes according to sustainable
improvement of their own lives and those of their children
Sustainable development is structural change leading to
enduring widespread improvement in the wellbeing of societies and their
members. This process involves self-sustaining economic growth, technological
change, the modernization of instructions and changes in attitudes and values.
Economic Commission for Africa.(2002:51)
Common future of the world commission on environment and
development defines sustainable development as "a development that meets the
needs of the present without compromising the ability of the future generations
while also improving the wellbeing of current generations, particularly the
poor and vulnerable.
Sustainable development must respond to two questions:
1' The satisfaction of Human needs and
v' The preservation and the conservation of the natural
resources.
Sustainable development integrates four dimensions of
priority:
+ The needs of the population;
+ The exploitation of the resources; + Development;
+ The protection of the environment
These four dimensions of sustainable development are explained by
the figure below
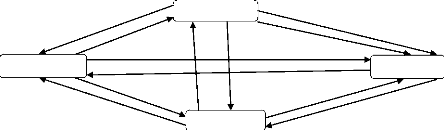
Population
Development
Environment
Resources
It shows the equilibrium between
population-development-environment-resources. Toyne (2003:125)
2.2.2.3.1. Integration of environmental conservation
in agricultural sector for sustainable development
In 2000, it was estimated that Rwanda had a population of 8.13
million people living in an area of 26,338Sq Km making it the country with the
highest population density on African main land. Only an estimated 10% of the
population lives in urban areas. The country?s economy is still highly
dependent on a rural Based agricultural economy.
Previously, agriculture in Rwanda prospered because of the
favorable temperature, good rainfall and fertile soils which contributed to the
expanding economy that provided support for the high population growth rates.
During the expansion phase, the economy was highly dependent on the lived
international coffee prices fell; the country suffered a massive trading
loss.
Consequently, the per capital income fell sharply during the
1980s and early the 1990s and agricultural inputs such as investments in
terracing and the use of fertilizers also fell.
In order to compensate against the falling productivity and
growing population, there was increasing encroachment on marginal farmlands,
hill sides, protected areas and forests. The rampant deforestation and lack of
appropriate intervention policies in soil conservation resulted in loss of
massive quantities of soil, reduced fertility and productivity.
This had a severe overall impact on the population?s wellbeing
as well as the country?s environment. The link between environment and the
poverty has not been fully analyzed and acknowledged in Rwanda.
However, the link between agriculture and environment in
Rwanda is very obvious as the examples of 90% of the population relies on
agriculture for their livelihoods, but many of them are not self-sustained as
their land plots are either too small or their quality too poor. The wide scale
environmental degradation, which for a major part is a result of unsustainable
agricultural practices, calls for urgent attention. Immediate actions are
essential to avoid further environmental degradation and the food insecurity
that would follow from further environment degradation Poverty environment
initiative/REMA (2007:32-33)
2.2.2.3.2. Integration of environmental conservation
in the commerce for sustainable development
This sector is very important for growth and technological
improvement and further, the sector is a major user of raw materials and energy
as well as a major source of environmental degradation. It is therefore key
that development of this sector is given the proper attention and guidance to
emphasize the positive role that it can play for achieving sustainable
development as well as economic growth. More efficient production processes
preventive strategies, cleaner technologies and procedures can be important
mechanisms for reducing impacts on natural resources and the environment.
Physical and economic impacts on the environment as a result
of commercial and industrial activity can be associated with the products or
technologies used operational scales and structural effects. Product effects
occur when commercial or industrial products themselves have an impact on the
environment.
Also, structural effects such as trade liberalization can
contribute positively to the national economy, but can also create higher
environmental impacts as a result of more pollution or a higher exploitation
rate of natural resources.
national growth. However, achieving this will require legal
frameworks, ongoing technical supports and facilitation from environment sector
as well as enforcement to ensure compliance.
If financial performance takes precedence, environmental
objectives are likely to be compromised or be subject to significant
constraints.
Compliance with Government regulations and policies remains
one of the most forceful drivers of environmental performance for most
companies, as it requires them to take mandatory actions or meet certain
standards. Strengthening the efforts for integration of environmental issues in
the sector, whether through the undertaking of EIAs (Environmental Impact
Assessment), the use of standards or other regulatory mechanisms, will
certainly contribute to more sustainable development of Rwandan economy.
Poverty Environment Initiative/REMA (2007:35-36)
2.2.2.3.3. Integration of environmental conservation
into economic growth for sustainable development
Rational and sustainable conservation of the environment and
natural resources is one of the aspirations of the Vision 2020. Rwandan economy
is primary dependent on natural resources and therefore environment and natural
resource degradation has adverse impacts on economic growth and the livelihood
of a majority of Rwandans. Recent explorative studies have linked and
environment has brought new insight in appreciating how natural resources and
environment are interlinked. Poverty environment initiative/REMA (2007:40)
2.2.2.3.4. The integration environmental conservation
in local government for sustainable development
To meet the objectives of Vision 2020, it is important that
adequate policy and legal framework exist to guide the behaviors of the use of
the environmental and natural resources whose action may have impact on the
environment. Sector decentralization strategies and set standards for
delivering environmental services can help to ensure that the relationship
between the decentralized government departments will serve the goals of both
decentralization and sustainable development of the environmental conservation.
Rwandan decentralization policy and program provide a great opportunity to
empower the local leader and involve the population
in improved management of the natural resources upon which the
majority depends on. Government of Rwanda (2007:32)
In order to ensure the sustainability of environment, Nyungwe
forest was declared a National Park and the national laws were also put in
place to stop hunting and protecting wild animals, fauna and flora. With a
special mandate, Rwanda office of Tourism and National Parks (NPs) was
established, to oversee nature, conservation, tourism promotion, implementation
of conventions and agreement on biodiversity, development and protection of
major historical, archeological and tourist sites and monuments. ORTPN
(2007:4)
Despite, all these efforts made to protect the natural
resources, pressure from local communities in Rwanda was high. A large
proportion of the recently established National Parks were gradually converted
to agricultural land overtime, within the period of40 years, NPs in Rwanda have
lost more than 50% of their initial area at the establishment, currently NPs
cover approximately 2,280sq km, which 8.6% of the total area of Rwanda
.ORTPN(2007:7)
Furthermore, local communities living near these NPs,
including the neighboring of Nyungwe National Park (NNP) especially Kitabi
Sector continue to exert a strong pressure in search of the resources which can
satisfy their needs. Therefore, that is why a special policy is needed for the
conservation of environment as a result of achieving sustainable development in
rural areas.
| 


