|
Academic Year
|
2016/2017
|
|
Program
|
Msc Wine Management
|
|
Submission date
|
January 10th
|


1
PROFESSIONAL THESIS

Student's Name & First name: BOUCHARD
Antoine
|
Thesis subject and Tutor's comment:
Is there a move away from wine to whisky in the European
market?
|
Professor Tutor's Name, First name: CROUCH
Roberta
Mark .../20
2
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
I would first like to thank my tutor Professor Roberta Crouch
of the School of Wine and Spirits Business. The door to Roberta Crouch office
was always open whenever I ran into a trouble spot or had a question about my
research or writing. She consistently allowed this paper to be my own work, but
steered me in the right direction whenever she thought I needed it.
I would also like to thank one expert who was involved in my
research project and whose help has been very valuable: Professor Michael Moss
of Northumbria University. Without his incredible knowledge about history and
whisky, his passionate participation and input, my research would have not been
complete.
My sincere thanks also goes to Professor Pierre Joulié,
Head of the Msc Wine Management Program at the School of Wine and Spirits
Business, whose passion and endless dedication for the Msc WM is astonishing
and enable students like myself to spend a memorable year. I am gratefully
indebted for his commitment and support throughout my studies.
To my girlfriend, thank you for reading, offering me advice
and supporting me through this adventure.
Finally, I must express my very profound gratitude to my
family and especially my parents for providing me with unfailing support and
continuous encouragement throughout my years of study and through the process
of researching and writing this thesis. This journey would have not been
possible without them, they have always been here to support me emotionally and
financially as well. They never stopped believing in me and always wanted the
best for me. They gave so much of their time, energy, always showed what it
meant to be dedicated and I am forever in their debt.
Thank you,
Antoine Bouchard
3
ABSTRACT
The purpose of this thesis is to answer the following question:
Is there a move away from wine to whisky in the European market?
This research fits into a perspective of studying the consumption
of wine and whisky in this market.
The first stage if this article is giving an overview of wine and
whisky consumption in the Old and New world with trends of the past 5 years,
taking into account the production evolution. The second stage is focusing on
the worldwide whisky market: production methods, labelling and market
trends.
The third stage is presenting the analysis of around 150
responses to a specific questionnaire, allowing us to get a more in depth view
of the wine and whisky market.
The final stage aims to discuss about the overall results and
future tendencies.
Key words: wine and whisky consumption, European market,
quantitative research, Old world, New world, wine and whisky trends.
4
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Acknowledgments 2
Abstract 3
Table of Contents 4
Introduction 5
Literature review 6
I- European Wine & Whisky markets 7
1) Old & New World Wine & Whisky consumption 7
2) Focus on the European market 11
3) Trends and changes during the last 5 years 16
II- Worldwide whisky market 23
1) Overall picture, main producing countries 23
2) «The Judgment of London» - Scotch vs Japan 26
3) New incomers 28
III- Questionnaire 33
IV- Discussion 48
1) Market trends conclusion 48
2) Consumer trends and expectations 53
3) Where are the Wine & Whisky markets going? 57
Conclusion 62
Bibliography 63
Appendices 78
5
INTRODUCTION
On one hand, whisky is trending and is becoming more and more
popular. For instance, France is currently the biggest whisky drinker
worldwide. On the other hand, wine, despite its important awareness and
domination notably in terms of consumption is going through a change in
behaviour in Europe (but not only). Indeed, a noticeable decrease in wine
consumption is observed in many European countries. The purpose of this article
aims to see what are the evolutions in wine and whisky consumption: Are there
more whisky drinkers to the detriment of wine drinkers? What are the trends in
the different countries? What are the drivers of the consumption changes? What
could we forecast for a near future?
Thus, the first part of this research is aimed to get a global
overview on the European Wine and Whisky market with the overall consumption of
both alcohol beverages and the different trends. The second part is designed to
have a whisky focus with the different producing countries as well as new
incomers in order to see their influence on the consumption. The third stage is
an exploratory research with a snowball sampling (quantitative survey) which
aims to put in evidence different consumption behaviours for both wine and
spirits. The survey will help us estimating the price people are ready to pay
for a good bottle of wine and/or whisky, in which circumstances do they like
drinking, when and the frequency. The last and final part is a discussion. It
will be based on the quantitative survey results analysis and supported by
other documents study to figure out what are the consumer behaviours and
expectations. The conclusion will try to forecast where both European wine and
whisky markets are going.
6
LITERATURE REVIEW
France can boast about a great heritage as regards to wine as
well as spirits (Cognac, Armagnac, Anise drinks), but it should be noted that
French are quite fond of another distilled alcohol but rather confidentially in
the country: whisky (La consummation de whisky: une étude
exploratoire du comportement du consommateur dans le contexte français,
M-F. GAUTHIER, C. LABORDE, B. MAZIERES, p.3).
Where does this dynamism and enthusiasm come from? The
«flexibility» in terms of means of consumption (in cocktails, neat
etc.) gives whisky more opportunities and it is reinforced by brands activity
and distributors with regards to advertisements and promotion (Le whisky,
superstar des spiritueux toujours en croissance, M. BAILLY).
According to Guillaume Deglis head of Vinexpo, the consumption
tendencies for the next five years will be supported by whiskies as well as
bourbons since they managed to bring innovation
to their offer. Brown alcoholic drinks (including whiskies)
are surfing on this cocktail, parties in bars trend more and more praised by
women and millennials. The whisky market should thus increase from 9% from now
to 2018, Bourbon from 19% (Whisky et bourbon, nouveaux chouchous du
marché des spiritueux, P. DENIS).
As of today, the spirits universe has never been as much
diverse and multi-coloured. Ranges of spirits in supermarkets shelves and in
specialised shops are so varied and internationalised and
the demand for luxury drinks has never been so important.
Bars, cafes, restaurants, clubs have now a cocktail menu that is getting bigger
and bigger (Encyclopédie des Alcools et Spiritueux, A. DOMINE, 2009,
1st ed. H.f. Ullman, p.15). Whisky's good health is notably due
to Europe's consumption.
What about wine? The wine market is not going well everywhere
in the world, in Europe as well. By 2018, worldwide wine market should rise by
3.7% which is not a lot compared to
whisky to reach 2.732 billion of 9 litres boxes, which
represents 32.78 billion bottles. China
where consumption progression levels were reaching explosive
rates (+70% between 2009 and 2013), consumption has suddenly slowed down since
2013 because of Beijing's anti-corruption
measures (Whisky et bourbon, nouveaux chouchous du
marché des spiritueux, P. DENIS). Generally speaking, Europe also
has a decreasing wine consumption but is this drop due to a better consumption?
Is it benefiting whisky consumption?
7
I. European Wine & Whisky markets
1. Old & New world wine & whisky consumption
Many evidences have revealed that winemaking is known for
millennia. With current level of knowledge, the scientific consensus is that
winemaking has been first performed in Caucasus region, probably in Armenia.
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, produced by the fermentation of the grapes.
Worldwide, the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) has drafted in
1928 a resolution which states the legal definition of wine: «no other
product that those obtained by the alcoholic fermentation of fresh grapes juice
can get the wine appellation».
Since 1973, OIV has decided that wine can be obtained only by
the complete or partial alcoholic fermentation of fresh grapes, whether or not
crushed, or of grape must.
The wide variety of wines existing in the world can be
explained thanks to the variety of vineyards, wine varieties, winemaking
methods, or ageing. That is why we have red, rosé and white wines, dry
or sweet ones, or even still or sparkling. Viticulture has spread all over the
world and many countries are wine producers.
All over the world, wine names in the different languages have
in common the V letter (or its variant W) and the N: vera (Albanian),
Wein (German), wine (English), vino (Spanish,
Italian, Croatian, Czech), vin (Danish, French, Islandic, Romanian and
Swedish), vein (Estonian), viini (Finish), ... with 2
exceptions: ardo (Basque), and bor (Hungarian) (Indifferent
Languages).
There are more than one million winemakers in the world who
produce approximately three billion cases of wine each year. The production is
projected to have approximately grown by 2.2% in 2015 (274 million
hectolitres), due to solid harvests thanks to great climatic conditions in many
countries which allowed the vineyards to get matured grapes and perfect
conditions for harvesting.
According to the Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV, 2015),
the world wine consumption represented 240 million hectolitres in 2015, which
equals 32 billion 75cl bottles, and it has increased by 0.9 billion hectolitres
last year.
It is important to notice that the consumption/production ratio
is not really balanced.
The overall demand is increasing but is it the case everywhere in
the world?
About two thirds of the world wine consumption relies on only ten
countries.
Furthermore, the wine business is changing shape: The Old
World (which basically represents Europe) leads the wine consumption for now
but it is gradually losing its pole position.
8
Yet, these outcomes confirm a change in this consumption from
the traditional producers such as France or Italy to other wine producers,
although more recent, but also wine enthusiasts, the United States and China.
There are indeed new actors from the New World (outside the traditional area of
wine-growing).

As you can see on this graph, and looking at the variation
2015 vs 2014:
- The first consuming country are now the United States, which
overtook on France since 2012 and it keeps increasing.
- At the second and third place, we found the traditional
consuming countries (France and Italy) with a decreasing trend in France and a
stable consumption in Italy.
- Germany, China, UK and Argentina wine consumption show a
slight increase, while Russia's and Australia's consumption are declining.
There is a noticeable rise of consumption in countries outside
Europe even though wine is undeniably one of the most popular alcoholic drink
there.
Spirits are also popular alcoholic beverages in the world and
whisky belongs on the top alcoholic beverages and is one of the most popular
spirits.
The word whisky is English and came from the Celtic word
uisge in Scottish Gaelic (or uisce in Irish Gaelic).
«Uisgue» or «uisce» means simply
«water»; by adding »beatha», you get the Celtic
word «water of life» («uisge beatha» in
Scottish Gaelic and «uisce beatha» in Irish). When English
people has discovered this spirit, they have only kept the first part of the
word and wrote it their way: «whisky».
Whisky finds its origin in Ireland. The legend says that Saint
Patrick, the patron saint of the Irish, has brought himself the secret of the
distillation in Ireland at the 5th century. This secret has then
crossed the sea to join Scotland. Irish and Scottish are still claiming the
fathering of this famous beverage!
Whisky has a slight advantage compared to some beverages, for
instance Cognac or Champagne (governed by an appellation system): it can pretty
much be produced anywhere.

Source: Wikipedia
9
And so, whisky is everywhere. Scotland, Japan, the United
States, Ireland, India, Sweden, Australia, New Zealand, South Africa ...
Furthermore, there is another way to spell the word
«whisky» which is «whiskey». Should we say
whisky or whiskey then? Well, it differs geographically: the American and Irish
write «whiskey» and the Scottish, Canadians and the rest of the world
write «whisky». Where does this come from?
It started during the 19th century. Scotch whiskies
were of poor quality and were inadequately distilled in Coffey stills (see
photo on the right). For exportation in the US, the Irish distillers wanted to
discern their production from the Scottish competitors, therefore they added an
«e» to point out their difference. Nowadays, Scotch is one of the
greatest spirits in the world but the spelling still varies. Americans still
spell their whisky with an «e» but some distillers prefer the
Scottish spelling (Maker's Mark for instance for their Scots ancestors).
But what is whisky?
Whisky is a term that designates spirits obtained by the
distillation of malted and/or non-malted cereals, then aged in wooden barrels
and containing at least 40% alcohol.
There are different types of whiskies depending on the raw
materials entering in their recipe, or on their production process:
- A Single Malt whisky is made of malted barley from a single
distillery.
- A Pure Malt whisky is also elaborated with malted barley but
from several distilleries. - A Blend is a mix of malt and grain whiskies from
different distilleries. It can also be a mixture of two or more whiskies that
will be bottled and sold as one whisky.
These three `whisky types' can be produced anywhere.
However, there is on top a national appellation system. Thus
Scotch, the most popular whisky but also the best-selling whisky can only be
produced in Scotland.
It is the same with the Irish whiskey in Ireland, or Bourbon in
the United States.
To be considered as a Bourbon, the whisky has to be produced
in the US, the grain mash must be at least 51% corn and the mixture also has to
be stored and aged a minimum of 2 years in charred oak containers.
Rye whiskey can refer to Canadian whisky or American whiskey
and must be distilled from at least 51% rye.

10
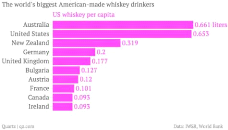
Regarding the consumption, here is a graph showing the biggest
whisky (and/or whiskey) drinkers in the world.
According to this Euromonitor analysis:
- France, Uruguay and the United States ascend to the top 3
- The original producing countries (Ireland and UK) arrive
respectively in 7th and 8th position - India (in
9th position with 1,24L/capita, is by far the world's biggest
drinker due to its population: approximately half of the world's whisky is
drunk there). Some interesting remarks on to the Indian market: They are not
only the biggest whisky consumers, their whiskies are also part of the world's
top 10 whiskies (in volume). United Breweries, an Indian conglomerate is also
the world's largest whisky company by volume. It owns several important
subsidiaries, notably United Spirits Limited (which manufactures McDowell's),
the world's best-selling whisky according to The Millionaires' Club (Officer's
Choice and McDowell's No. 1 are respectively the top 2 whiskies sold in the
world).
Why are these whiskies so powerful on the international market
and yet not very well-known, even from whisky amateurs?
First off, they benefit from their own national market. With
1, 2 billion habitants and a middle class boom, India is the world's first
whisky market. So when Scotch producers sell 90 million whisky cases in the
world, meanwhile approximately 120 million of local whisky cases are being
consumed in India!
Problem is, according to regulations, the Indian whisky
(except Amrut, actually sold in the European market and others) is simply not
whisky. Distilled from molasses (the liquid obtained
11
after the cane sugar extraction), it is sometimes mixed with a
little bit of malt or grain whisky. Outside of the subcontinent, it would be
labelled as Rum, thus it cannot be sold on the European market or anywhere else
as `whisky'.
Outside the United States, Australians, New-Zealanders,
Germans and British are big consumers of American whiskey.
Concerning the US, Beam is responsible for more than 40% of
the US Bourbon sales which accounts for almost half of the American whiskey
market. According to the International Wine and Spirit Research, the United
States consumes roughly 70% of the whiskey it makes.
2. Focus on the European market
Let us now have a look on the consumption trends for wine and
Whisky in the 5 main European countries:
France:
Whiskies: With more than two hundred million bottles
sold every year, whisky (Scotch, Bourbon, Rye or Japanese) is the most consumed
spirit in France to the detriment of Cognac. In the wine country, whisky is the
king of spirits.
As we saw previously, with 2.15 litres per capita, it
represents nearly 40% of the total spirit consumption (Fédération
Française des Spiritueux, FFS).
Overall, 120.9 million litres of whiskies have been consumed
in France in 2015 (FFS). With a market share close to 40%, whisky surpassed
pastis (73.84 million litres, 24% market share), rums (30.31 million litres,
9.9% market share) or white alcohols (tequila, gins, vodka, 29.56 million
litres and 9.6% market share).

Spirits market share
Source: Nielsen
Eaux-de-vie
0,50%
White alcohols
9,62%
Armagnac
0,20%
Calvados
0,20%
Rums
9,92%
Cognac
0,20%
Liquors
9,12%
Aniseed drinks
24,15%
Bitters
4,41%
Whiskies
39,48%
Others
2,20%
12
Nearly 80% of spirits (77.2%) are bought in
supermarkets/hypermarkets. The rest is divided in away-from-home catering,
specialised retail shops... According to the FFS, the spirits turnover is 4.6
billion euros in 2015. In 2014, about half of the total turnover (46.9%) was
generated by whisky sales (2.09 billion euros). In volume, there is a slight
decrease of -0.5% of spirits sales (279 million).
Wine: France's wine consumption is regularly declining
since the early eighties.
Since 1980, France AgriMer performs every 5 years a survey on
wine consumption in France. 4000 people, representative of the French
population, are interviewed, in order to understand the real behaviors of
people in wine consumption: motivations, frequency, quantity, and also opinions
and attitude that people can have vs wine. Last survey was made in 2015
(8th edition). According to this survey, 51% of people drinking wine
were drinking every day or nearly every day in 1980 while in 2010, only 17% of
the population drinking wine were drinking every day. The percentage of people
drinking wine occasionally in 1980 was 30% and 45% in 2010, an important
increase compared to the freefall with more «regular drinkers».
The proportion of French who never drink wine keeps growing
and all changes in drinking habits are observable through generations'
attitudes.
According to the results of the 2015 survey, wine perception
is improving. A renewed interest is observed between 2010 and 2015, with a more
important part of the population declaring liking wine taste. This trend
correlates well with the growing interest of French people for cooking, the
come-back of home-made food, cookery programs, and wine and food pairing.
13
Wine is more consumed at the aperitif moment, especially white
and rose wines (red wines are more associated to the lunch moment).
Wine seems to move from one of the components of a lunch to a
more cultural drink.
The UK:
Whisky:
It is interesting to analyse the information provided by IWSR
(International Wine and Spirit Record). This agency claims to be the leading
source of data and analysis on the alcoholic beverage market. It covers 155
markets in total.
According to the IWSR, the whisky market represents 1.2
billion bottles in 2015. The spirit market is indeed quite significant in the
UK: with 139 million bottles of gin, 58.5 million bottles of vodka, 1.1 billion
litres exported to foreign markets (2013) which 28.2 billion pounds in economic
activity.
Vodka is the N°1 consumed spirit, representing nearly 30%
of the UK spirit consumption, and Whisky arrives 2nd with 25.56%.

Spirits market share
Source: The IWSR (2013)
National Spirits
0,05%
Brandy
6,30%
Tequila
Cane
0,60%
0,10%
Gin / Genever
8,90%
9,00%
Rum
29,89%
Vodka
Flavoured Spirits
19,59%
Whisky
25,59%
:
18,49% 6%
1,1%
Wine: According to the IWSR, the UK wine market is the
6th largest wine market in the world. UK wine production represents
only 0.01% of the local consumption and so UK must import nearly the totality
of its consumption. Indeed, the industry generates 17.3 billion pounds in
economic activity to the British economy and 10 billion pounds in sales.
14
More than 80% of wine sales take places retail outlets, the
remaining sales are through bars, restaurants and hotels (in other words
away-from-home catering).
UK is an important wine consumer. According to the OIV, the UK
reached 12.9 millions of hectolitres in 2015. It is a small growth compared
with 2014 and it also counterbalance the drop between 2013 and 2014.
Wine is the most popular alcoholic drink in the UK according
to the Wine and Spirit Trade Association (WSTA) and is not just limited to
connoisseurs. It is actually the preferred choice for millennials (in that case
people between 25 and 34 years old) when it comes to drinking with over half
(57%) picking wine over other alcoholic drinks. Also, women tend to drink more
wine than men.
White wine is favoured over red consumption (47% of all sales
in 2015 versus 42%). Rosé wines also share a small percentage (11%).
Sparkling wines shows the most important growth thanks to Prosecco and Cava and
are perceived to have a better value for money than Champagne. Fruit flavoured
wine as well as low-alcohol wine also show potential for the future and can be
a threat to still Rosé wine (United States Department of Agriculture
(USDA)).
Ireland:
Whiskey: Ireland ranks in the top 10 for biggest
whiskey consumers. With 1.24 litres per capita, the country is head to head
with India and is almost overtaking the United Kingdom. Overall, spirits
consumption has increased from 1.9% from 2014 to 2015.
Worldwide sales of Irish whiskey keep rising: a 10.1% growth
with 62 million litres in 2013 (55.8 million litres the year before (source
IWSR)).
Ireland knew an intricate story with whiskey. It was not so
long ago the world whiskey leader but it went through tough times and the most
affected city was actually Dublin, the spiritual mother of Irish whiskey, where
it all began. It was abandoned in 1976 after Jameson's pot still fire stopped.
At that time, Irish whiskey hit rock bottom: while Scotch whisky conquers the
world, it was just considered as a bizarre, an odd beverage barely used to
rinse out someone's glass.
What was in the past a proud industry at a global scope was
reduced to two companies producing bad quality whiskies (a pure euphemism),
which totally accepted their ignorance of the Irish pot still tradition. Dark
times for Irish whiskey, almost vanished due to war, trade restrictions,
Prohibition, economic difficulties etc.
It was only in 1987 when the Irish entrepreneur John Teeling
founded the Cooley distillery. His sons, Jack and Stephen worked for the
company until 2012 when it was bought out by Jim
15
Beam. They simply figured that they wouldn't be satisfied
working for an important group. Anyway, the demand for whiskey was rising,
consumption too, awareness as well notably thanks to the group Irish
distillers' Jameson (Pernod Ricard) and their important marketing. From the
eighties until 2012, there was only three companies which distilled whiskey. In
May 2015, five companies distilled whiskey. With more than twenty distilleries
under construction or planned, new actors, a growing (and reborn) reputation,
American consumers as a support, Irish whiskey is getting better.
Wine: Wine is not the most popular alcoholic drink in
Ireland, beer is. With almost half of alcohol consumption (47%), beer won't be
dethroned anytime soon. Wine is actually the second most consumed alcoholic
drink with a 27,7% market share, followed by spirits (18,7%) and cider (6,6%)
(Source: Irish Revenue Commissioners Clearance Data).
Women are more likely to drink wine than men (61% versus 39%
(TGI Data 2015). Also, wines from Chile are the best-selling wines with a 25.3%
market share (more than 2 million cases), followed by Aussie wines (18.1%, 1.5
million cases) and France (14%, 1.2 million cases). Wine sales are mainly
through off-trade (grocery, independent retail etc.) with 80.9% market share,
the rest is on-trade (away-from-home network: bars, restaurants etc.) with
19.1% (Source: IWA Country of Origin Survey, AC Nielsen and other trade
reports).
Italy:
Whisky: Overall, Italians drink less alcohol now.
In last international ranking, Italy is at the 32nd
place (Source Euromonitor survey).
In less than 10 years, we observed a 23% decrease in rate of
alcohol consumption which makes an average of 4.4 drinks per week in 2014
(versus 5;6 drinks per week in 2006). This fall is actually due to a drop in
wine consumption over this period (31%). However, the consumption of beer and
spirits remained the same.
Wine: Regarding the consumption, the country
experienced a modest growth and is behind France and the United States.
As we said previously, the country's falling drinking rates is
due to many things.
Eating habits which changed with lunch losing its position as
a «family meal», wine is now mainly consumed during dinner (before it
was usually drunk during both). Also, the proliferation of non and
low-alcoholic drinks played a central role in wine consumption habits with a
growing «health awareness».
16
On the production side, Italy dethroned France and became the
world's biggest wine producer with 48.9 million hectolitres (versus 47.4
million hectolitres). It represents a 10% increase compared to 2014 (source
OIV).
Germany:
The following graph shows Germany's alcohol consumption. As you
can see there are two sets of line: The first set on the left show data from
West Germany since data from the East was difficult to gather. The second set
shows data when Germany was finally reunited.

Whisky: On average, spirits consumption remained stable
throughout the years.
22nd in the ranking of the whisky consuming countries,
with 0.45 litre/capita;
Wine: Germany saw a small growth in wine consumption with
20.5 million hectolitres.
Even if Italy dominates wine production, it has been surpassed
by Germany for the consumption. It is actually the first time Italians have
been overtaken by Germans according to the Organisation of Vine and Wine
(OIV).
3. Trends and changes during the last 5 years
It is interesting to have a look at worldwide alcohol
consumption on the health side. The World Health Organisation (WHO) publishes
regular reports on this topic. According to the WHO, 48% of the world adult
population has never consumed any alcohol. But what about the rest?
The drinker's geography commonly claims a wide prevalence of
alcohol consumption in Western countries and Russia, while temperance is
demonstrated by African countries, Arabian region and South East Asia.
17
The more a country is developed, the more its alcohol
consumption is high. On the contrary, developing countries show lower
consumptions.

Let's have a look at this map representing the alcohol
consumption per capita (considering only 15+ people) in each country, the
repartition is slightly different: if a wide part of the population of the
developing countries, like India and Africa, is indeed abstinent from alcohol,
the part of their population who drinks alcohol grow up the consumption volume
of these countries.
If 48% of the world adult population has never consumed any
alcohol, the consumption per capita is underestimated.
Regarding the type of alcohol consumed, more than a half of
the alcohol consumed in the world is part of the spirit family, followed by
beer (34.8%) and wine (8%).

The American continent (AMR) consumes more beer vs spirits,
while this proportion is reversed in Pacific countries (WPR). The same trend,
even majored, is assessed in South East Asia (SEAR). Middle East countries
(EMR), the spirits consumption is similar to the wine one. According to WHO
reports, Canadian people drink more than American or Australian people. Alcohol
consumption is low in Maghreb, but more important in Sub-Saharian Africa, South
Africa and Namibia.
But what happens in the «old world»?
18
The WHO is working to prevent potential health issues linked
to an excessive alcohol consumption (see advertising hereunder):

The WHO has also published the ranking of the alcohol
consumption in European countries (2005 data, Cf. appendix n°1).
The alcohol consumption is really variable depending on the
countries: Russian and their neighbors drink more than all the other countries.
Portugal is also clustered in the heavy drinkers with more than 14.5 liters per
capita, followed by Ireland and France and UK. Italy differentiate itself with
a significantly lower consumption (10.7 liters per capita). Let's have a look
at what is happening on the wine production side. We can indeed make a parallel
with the European consumption tendency. As we said previously, the Old World
continues to lose ground against the New World.
When we take a look to the following chart, it perfectly
illustrates this growing trend.

19
Europe is still leading this ranking, with Italy, France and
Spain but something is happening with New World countries. United States,
Argentina, Chile, etc. are progressively rising. When we actually compare their
wine production with their wine consumption, it is interesting to notice that
it is increasing as well:
- The US became the largest domestic market and the biggest
wine consumer,
- China, South America as well as South Africa's wine
consumption is slowly (sometimes
quite rapidly) but surely increasing, even though China's
production remained quite stable. Contrary to clichés, Russians are not
the biggest alcoholic beverage drinkers. The country that will know the
strongest consumption is China, with more than 1.5 litre of pure alcohol per
year and per capita till 2025. Even if Europe will remain the thirstiest region
of the globe.
Furthermore, China is not only becoming one of the top
winemakers in terms of production but also one of the top consuming countries.
Indeed, it is in the top 10 of the main wine producing countries
(9th position), right behind South Africa but in front of
Germany.
Who is behind this trend in New World countries?
Well, mainly Millennials (it generally applies to people who
reached adulthood around the 21st century). The «Y
Generation» that grew up in a growing electronics-filled, online and
social-networked environment has a strong interest in wine but not just
wine...
Millennials are playing a fundamental role in wine as well as
spirits consumption. While previous generation young people were mainly
consuming beer, millennials are abandoning
most commercial and popular beers (from macro-brews like
Anheuser-Busch with Budweiser, Leffe, Stella Artois, Hoegaarden and so on) and
are switching towards craft beers, wine and spirits.
A survey in 2015 found that more than 24% of interrogated
people wanted to decrease their beer consumption versus 8% for those who are
planning on increasing it. This trend is particularly noticeable amongst the
young. According to MorganStanley, millennials are losing interest in
macro-brews, are less interested than their elders and tend to prefer wine and
spirits. This interest for beer is fading: In 2013, 33% of millennials surveyed
said that beer was their favourite alcoholic beverage and in 2015, only 27,4%
cited so.
On the other hand, in France for example (which is part of the
Old Continent), young people do not have that much interest in wine, it is
actually the opposite. According to FranceAgriMer, wine consumption depends on
the age and the generation: The more a person gets older, the more he/she
consumes wine. In the eighties, more than 70% of French people over 15 years
old were wine consumers from the 20-24 years old age bracket. In 2015, people
who reach this rate are from 45-49 years old.
Individuals who are sixty to seventy grew up with wine at
pretty much all meals, it is part of their cultural heritage. The «Middle
Generation», which basically represents people in their forties of
fifties, perceives wine as an infrequent treat. They counterbalance this
weakened consumption by spending more money on wine (more qualitative, drink
less but better).
The «Y Generation», millennials, do not take
interest in wine before their late twenties.
Men (on the left) and Women's (on the right) wine
consumption in France

1980 1990 2000 2010 2015
22%
69%
9%
34%
22%
44%
24%
40%
36%
46%
28%
26%
25%
52%
23%

1980 1990 2000 2010 2015
37%
37%
27%
43%
40%
17%
47%
41%
13%
42%
47%
11%
50%
39%
11%
20
|
Non-consumers
|
|
Occasional consumers
|
|
Regular consumers
|
Source: FranceAgriMer. Enquête sur la consommation
du vin en France 2015
The number of regular drinkers is getting lower and lower
while the occasional drinkers are growing and the non-consumers remain pretty
stable for both genres when we hit the nineties. Numbers of non-consumers
doubled between 1980 and 1990. We observe this change for all three categories
during these ten years except for regular consumers who are lessening. This
drop in consumption is mirrored in other countries of the Old World.
In Ireland, women have more interest in drinking wine compared
to men (61% volume share versus 39%). Also, 35 to 44 years old people tend to
drink more wine than millennials (25% for women, 21% for men versus 5% for male
and 10% for female - TGI Data).
Wine market share (in volume) rose from 2005 to 2015 (19,9%
versus 27,7%), spirits market share increased as well in 2015, not by much
however (18,7% in 2015, 18,5% in 2005).
Generally speaking, wine consumption is in decline in Europe
except for minor rises in certain countries like United Kingdom and Ireland.
The French, Italian as well as German markets are projected for waning over the
next four years. Still, there is a «less but better consumption»
mantra growing in many countries. Wine is more and more seen as an elitist
drink rather than a standard alcoholic beverage.
As regards to whisky, we can observe some trends in terms of
consumption in many countries. For instance, here is a graph showing France's
alcohol consumption over the years:

21
As we can see, there is a noticeable decrease in wine
consumption whereas whisky consumption has remained stable (along with
beer).
What are the different tendencies? What happened during the last
five years (or more)?
22
During the last five years, Irish whiskey has been taking off,
rocketing especially in the US in terms of sales: Although it represents quite
a long time (between 2002 and 2014), whiskey sales have been gigantically
rising from 538%!
The demand for top of the range, limited-edition, exclusive,
innovative and rare whiskies is also soaring both in the Old and the New World
and it involves Bourbon, Scotch as well as Japanese whiskies. «A more
sophisticated and demanding consumer is emerging» (The Future of Irish
Whiskey p.7) because he/she is more and more knowledgeable, even sometimes
passionate and complex about their whisky choices. People want something
unique, something not available in every supermarket.
We have seen Japanese whisky exploding for the last ten years,
and it is really defying Scotch's domination. Indeed, Nippon's whisky started
to draw interest quite late mainly due to Suntory's marketing but is now part
of the greatest whiskies in the world by notably winning several awards.
Whiskies are also very popular for their nice cocktails. The Whisky Sour, the
Manhattan, the Godfather, the Rob Roy, so many names that make us want to try
them all (with moderation). It exists new formats for making cocktails, and not
just made with Bourbon or Rye, but with Irish whiskey, Canadian whiskies,
Japanese whiskies too (to drink during a meal with a refreshing highball) and
even Scotch!
In other words, people are looking for innovation (new types
of oak, casks, ageing processes...), they want to try new and more types of
whisky, from other places. It is a very intricate market. This complex market
is also draining the stock of old vintage whiskies (usually single malt Scotch)
which makes distilleries release more and more No Age Statement whiskies (NAS).
It gives them the opportunity to have whisky at disposal without having to wait
several years. Additionally, according to the IWSR, by 2020, whisky will push
the global spirits consumption to 3,2 billion cases. Whisk(e)y should also
overtake on vodka and «become the second-largest spirits category»,
right behind national spirits. Global consumption should grow to 467,5 million
cases. Where will the growth come from? Mainly from Asia with China and India
surpassing any other markets. Furthermore, there will be a rise not only in
North-American markets, Africa and Middle-East but also in duty-free
markets.
We will now discuss the whisky market in more details.
23
II. Worldwide whisky market
1. Overall picture, main producing countries
First thing first, let's talk about how whisky is made. There
are certain variations according to the type of whisky: Scotch, Bourbon, Irish
whiskey. But we will talk about the production process of the most spread
whisky: Single Malt. The first step in whisky making is malting. Barley is
steeped in water, subject to several humidification and oxygenation phases
which allow the embryo to «leave» its dormancy stage. Barley is then
spread out on malting floors in 30 to 50 cm layers to germinate and it is
frequently turned. During this process, enzymes are stimulated, it transforms
starch into a whitish flour from which sugar will be extracted when mashing
takes place. After 6 (up to 7 days) days of germination, the barley now named
`green malt', goes for kilning (in other words, drying). Malt houses are
equipped with ovens for peat fire that will add the smoke flavour (it is not
compulsory; some distilleries won't use peat) but also with burners which
insufflate warm air. Green malt is dried, cleared out of impurities and
germination is stopped.
The second step in whisky making is mashing. The dried malt is
ground, it is called `grist' at this point, and mixed with hot water in a vat
(mash tun). There are three stages in adding the water (which becomes hotter
and hotter), allowing the starch to be converted into sugar. The obtained
liquid, quite sweet, is called `wort'. The quality as well as the flavour of
the water plays a key role in the whisky character, it will vary according to
the country and the region (in Scotland for instance with the Lowlands,
Speyside etc.).
Now comes the third step: The wort is chilled to 20°C
(which is the temperature from which yeast will start to operate) and pumped
into fermentation tanks, `washbacks', where yeast is added. It feeds on the
sugar which transforms into alcohol and carbon dioxide. The liquid, now called
`wash' (lots of names) starts bubbling. Sugar needs forty to sixty hours to be
completely transformed into alcohol, the liquid obtained is a malt beer or
distiller's beer with 6 to 8% alcohol by volume.

24
The fourth step is the distillation in pot stills. The number
of distillations, the size, the pot still shape, the distillation speed, the
heating process but also the swan's neck inclination will influence the
character of the whisky. The wash is warmed up to the point where alcohol turns
into vapour. It passes in the Swan's neck into a worm condenser which is
immersed in running cooling water in order to transform the vapour into a
liquid. For Scotch, there is a double distillation: the wash is first distilled
in wash stills to detach the alcohol from the water, yeast and remains called
`pot ale' (solids that will be saved for cow feeding). What you get from the
wash still are `low wines' (about 20 to 25% vol.) that are sent to the spirit
still for the second distillation. This process is repeated until you get the
`high wines' (which are about 68% vol.) and they are filled into oak casks of
different sizes and types. Some of them might have contained Bourbon before,
Sherry or even wine for example. The cask will of course have an influence on
the whisky. All the distillates pass by the spirit safe which allows the
stillman to control and judge the different liquids obtained.
Unlike wine production, whisky production is not as influenced
by climatic hazards (except for barley agriculture but other than that, the
whole production is usually made indoors). According to the OIV, wine
production in 2016 should reach 259,5 million hectolitres versus 274 million in
2015 which represents a 5% drop, falling to its lowest level since 2012. This
is mainly due to global warming, variously affecting harvests around the world:
France's ones fell from 12% (spring hail and frost), the Champagne region from
30%, Italy decreased from only 2%, South Africa, Chile and Argentina
respectively 19%, 21% and 35%.
Here are the main whisky producers:
- Scotland: It is the main country producing whisky and also
the most well-known. With 1.5 billion bottles every year, we understand why. It
represents two third of the world's production. The Lowlands, the peninsula
Campbeltown, the Speyside (about half of the distilleries in the country are
established there), the Highlands (it comprises the north of Scotland,
including the islands) and finally Islay, form the five regions of Scotland
producing whisky and they all have their specificity. Scotland produces Single
Malts but also Blends.
25
- The United States and Canada: North America produces Bourbon
(mainly made out of corn) with very specific elaboration methods. The Tennessee
whisky differentiate itself from the Bourbon because of the «Lincoln
Country Process», a filtration through three layers of maple charcoal. We
can of course mention Jack Daniel's as an example. Canada produces
approximately 21 million cases of whisky. The US, produces about 37 million
cases of whiskey. According to the Distilled Spirits Council of the United
States, the country exported 235 million whiskey bottles last year. France is
no exception, with 8 million litres sold in hyper/supermarkets in 2015, it
represents a 12% growth and these sales has been overtaking Scotch's ones for
the third year now. This success is explained by their «rounder»
aromatic profile, the cocktail trend and it is not going to stop anytime soon.
Important groups like Jim Beam, Brown-Forman invested in order to increase
their production capacity. Besides, the number of microdistilleries and of
smaller actors keeps growing. However, American whiskeys still have to prove
themselves. According to Thierry Benitah, La Maison du Whisky CEO, there is
usually not more than five or six American whiskey references in wine shops but
on the other hand, Bourbons and Ryes benefit from cocktails renewal success and
are more and more found in CHR (cafes, bars, hotels, restaurants), especially
in independent cocktail bars which are reaching tomorrow's consumers: 25 to 35
years old people.
- Japan: It is the 4th whisky producer in the
world. The country has been producing whisky for almost a century. The Japanese
production method is based on the Scottish model therefore their whiskies are
either Single Malts or Blends very renowned on the market thanks to the quality
of the water, very pure, just like in Scotland. Japan actually took a step
ahead in terms of Blend whiskies notably thanks to Hibiki which was awarded
several times best Blend in the world (for the 21 and 30 years old).
- Ireland: The country produces about 7 million cases of
whiskey and it keeps on growing. Irish whiskey goes through three rounds of
distillation before being bottled. There is a use of both malted but also
non-malted barley. The aromatic profile of whiskey is usually smooth, light,
floral and fruity style. It is also naturally non-peaty although peat is
omnipresent in the country. As we said earlier, Irish whiskey has been through
ups and downs but especially ups these past few years: Last year, 70 million
litres have been sold (a 12% increase compared to last year), Irish whiskey is
the category with the most important progression. In France (again),
hyper/supermarkets sales are carried by brands such as Jameson, Paddy or
Tullamore Dew, with approximately 3 million litres sold in 2015 (V&S news).
Irish whiskey's shelves are becoming more and more enriched in wine shops.
26
Why so much enthusiasm for these whiskeys? Their aromatic
profile is quite distinct, easier to drink because fruitier and more refined.
This market is not yet mature so there definitely is a good potential for the
next years.
2. «The Judgment of London» - Scotch vs Japan
The 24th of May of 1976 will forever be a cursed
date for Bordeaux wine producers. On that day, a blind tasting put an end to
their historical and famous Crus Classés supremacy because Californian
wines went straight on to the first place, not Bordeaux. This was the Judgment
of Paris. The 18th of April of 2008 feels pretty much the same for
Scotch producers.
London International Spirits Challenge, April 18th of 2008,
after a 200 samples blind tasting, a plethora of experts awarded the Yoichi 20
years old as the best single malt in the world and the Hibiki 30 years old as
the best blend in the world. Two whiskies made in Japan, something to give
shiver to Scotch producers. This is what I would propose to call the `Judgment
of London'.

Outside Scotland, press blame the distilleries to savour their
success and this consecration didn't surprise whisky amateurs. They have been
discovering this Japanes
beverage for the last couple of years. Japanese whisky is not
only successful in
competitions but also in wine merchant shelves. In France,
world's first market
for single malt, their sales double every single year: 30,000
bottles in 2006, 70,000 in 2007 and it rocketed to 800,000 bottles in 2014.
With barely 10,000
bottles ten years ago, this is quite an impressive rise.
Regarding premium
whiskies (those that you wouldn't dare mixing with Coke and
those which price is higher than 25€), it currently represents about one
twelfth of France's
Scotch imports. But the gap is slowly tightening: hypermarkets
and retailers
like Carrefour or Nicolas decided to bring Japanese whiskies
on the shelves
and they still keep on coming.
At first, it does seem a bit like David and Goliath, Scotland
being the mighty warrior with more than 110 distilleries, an old tradition and
a great awareness all around the world to such an extent that whisky and Scotch
could be synonyms. In comparison, Japan is still small: about ten distilleries
with quite a young experience in whisky making. Japanese discovered whiskies in
1853 when the American commander Matthew Perry - who ran the war fleet which
aim was to force Japan to open up its barriers for trade - distributed some
cases in order to facilitate negotiations. Nippon's first attempt to reproduce
whisky was a failure (they tried to distil it
27
with rice, corn or millet instead of barley). It was only in
1918 and only then, when Masataka Taketsuru, a graduated chemist working for an
eau-de-vie producer in Osaka, left to Scotland to discover the secrets of
Scotch making. After 2 years of internships in Speyside distilleries, he came
back to Japan in 1920, his mission accomplished and with his Scottish wife,
Rita. The former company he worked in went bankrupt but he was hired by
Shinjirô Torii, Suntory's founder. He built the first whisky distillery
`Kotobukiya' (later renamed Suntory) in Yamazaki, in Kyoto suburbs. Under his
wife influence, Taketsuru partnered with other shareholders to create Nikka
(named Dai Nippon Kaju before), he established the Yoichi distillery in
Hokkaido, the northern island (he chose Hokkaido because it reminded him of
Scotland climate and terrain).
Nowadays, Suntory and Nikka are the main Japanese whisky
makers. The first one sells his single malts under the Yamazaki label but also
Hakushu, another distillery. The second one sells its bottles under Yoichi and
Miyagikyo brands, the two distilleries names. There are many whisky varieties
just like Scotch, with peaty characters, malty etc. For top of the range
whiskies, `single casks' are much less expensive than Scottish single casks,
which became quite unaffordable. As to Japanese blends, many are commercialised
under Nikka or Suntory and their blending (going up to 30 malts, the youngest
giving the age to the bottle) integrate some Scotch. Nikka acquired Ben Nevis,
the oldest Highlands distillery, Suntory got Bowmore, Auchentoshan and Glen
Garioch, 3 renowned whiskies.
How did Japanese manage to surpass Scottish masters? It is
kind of like Toyota's approach, which allowed the company to become the world's
first automobile manufacturer: to pay an important attention to the quality and
to have a consistent follow-up of customers' expectations. Ulf Buxrud, just as
famous in the world of whisky as Robert Parker in the world of wine, highlights
the fact that Nippon's desire of perfection pushed them to take into account
the yeast biochemistry allowing barley fermentation and to create new
low-boiling distillation techniques. For certain whiskies, they even modify the
American whiskey filtration technique by using bamboo wood coal and not maple
tree in order to obtain a lighter and silkier texture. Finally, regarding the
ageing, Nikka and Suntory use - besides traditional European or American
barrels which contained Sherry or Bourbon - Japanese oak barrels, a very
aromatic wood that gives an exceptional character to the whisky.
On the marketing part, Nippon's whisky benefited since the
fifty's from specialised bar created at that time, some of them belonging to
Suntory or Nikka. The `Cask Bar' in Tokyo (Roppongi neighbourhood) or the
`Nemoto' in Sapporo, Hokkaidô for instance have a nice «Carte des
Whiskies» with 2.500 different bottles (mainly Scotch). These efforts in
terms of quality,
28
creativity by making more and more sophisticated whiskies
didn't push Suntory nor Nikka to develop an export strategy, their attitude
being really modest. Can you imagine their surprise when European journalists
came to Japan in order to discover its distilleries, were simply astonished by
the quality of whiskies. It has been conveyed to amateurs through the famous
«Whisky Magazine», to whisky blogs like Malt Maniacs and incited
Japanese to do even better. At the beginning of 2000, Nikka asked Thierry
Bénitah, head of La Maison du Whisky (who was already distributing Nikka
and Suntory's products in France), to become its agent for Europe. In 2004, the
worldwide success of Sofia Coppola's movie «Lost in Translation»,
where we saw Bill Murray shooting an advertising in Tokyo for Suntory Hibiki
had the effect of a launching campaign. It pushed Suntory to proudly
«Japanised» its label, Roman letters now appearing in small
characters.
Japan had a whisky boom especially during the seventies and
eighties, even Sake distilleries were changed to produce whisky in order to
meet the demand, the Japanese and especially the world's thirst. In other
words, Japanese whisky's future is bright.
3. New incomers
Besides the rise of American and Irish whiskeys, the
development of New World whiskies shakes up the market. Should we mention the
success of Japanese whiskies again? According to IWSR, in 2015, Nikka From The
Barrell, one of Nikka's best sellers had an audacious growth with a 50.7%
increase. Today, despite a more expensive price positioning, Nippon's whisky
brands are growing (new brands are appearing like Yamakura, Okayama for
instance).
Now, in the same area, should we consider India as a main
actor? Since the country sold 120 million bottles of their `whisky', it does
deserve some credits. As we said, what they are calling `whisky' is made
notably from molasses and (sometimes) mixed with Scotch. It is not only a huge
consumer (9th biggest drinkers in the world, 1.24 litres per capita
- Source Bonial) but also an important producer. Indeed, it also produces
whisky that meets European regulation standards: Amrut which has been awarded
several times, Paul John and both are focusing on the premium whisky market and
selling their products on the European market and the US market.
Remaining in Asia, and close to India, there is another whisky
producer: Taiwan. With the Kavalan distillery and the more recent Omar
distillery, these two deserve a special mention as well. Kavalan is
particularly getting noticed, gaining popularity thanks to several awards. In
2016, the Kavalan Solist Amontillado won the award of the best single cask
single malt of the
29
world (World Whisky Awards). The warm weather in the country
affects the maturity of the whisky. It indeed matures more quickly however the
Angels' Share is also more important. The Angels' share happens when the whisky
ages in barrels, where 2 to 3% of the liquid evaporates every year (it is
actually taken into account in distilleries' stocks). Taiwanese's Angels' Share
goes up to 15% per year. Furthermore, the country in the 20th
biggest whisky drinker in the world (0.63 litres per capita).
Back to the Old World now, France is also finding its place in
the world of whisky. Whisky consumption depends on the region (even if the
country is the world most important whisky drinker) and French distilleries
production capacity are quite modest for now. According to Philippe
Jugé, founder of the «Fédération du whisky de
France», 700,000 bottles of French whiskies were sold last year. Indeed,
from consumer, France also became a whisky producer in the eighties. Benefiting
from a certain know-how in spirits production, the country of wine couldn't
miss the opportunity to differentiate itself in whisky production as well.
In the beginning of the eighties, the Breton distillery
Warenghem was producing liquors (crème de cassis, Elixir d'Armorique),
until it decided to go on the more promising whisky market. The first French
whisky distillation occurred in 1983 for a release on the market in 1987.
Nowadays, Armorik (the name of the whisky) sells about 250.000 bottles per year
mainly in Bretagne but it is getting remarked in France and around the world.
In 2013, Armorik Double Maturation was awarded as the best European single malt
for the World Whiskies Awards (WWA). Alsatian as well as Breton whiskies even
got their own Protected Geographical Indication (PGI, IGP in French, Indication
Géographique Protégée).
France now produces approximately 700.000 bottles of whisky
per year. Why did France waited so long before producing whisky? Since the
country was already distilling other spirits like Cognac, Armagnac, Calvados,
even Rum, it is quite intricate. France currently has around 40 malt
distilleries which also pushed the creation of the French version of the Scotch
Whisky Association, the «Fédération du whisky de
France». According to Philippe Jugé, France is a wine country and
distilleries are usually in wine regions and even fruit regions. French
know-how leant towards these eaux-de-vie. With phylloxera destroying Cognac and
pretty much all wine regions in the 19th century, when Scottish were
ready to invade markets with their blends, French consumers started consuming
whisky.
Later on, Anglo-Saxons pulled it off in both World Wars,
Hollywood golden age was embellishing whisky's image and some French companies
already invested in some Scotch distilleries (like Pernod Ricard which owns 14
of them), all these factors were not really contributing to France's whisky
production development. Furthermore, distillers didn't have
30
the tools required to make whisky. For instance, French
distilleries alembics or pot-stills are smaller because more adapted to other
spirits but it made distillers think about other ways to make whisky instead of
just copying Scotch. Last but not least, and it might sound very strange but
one of the reason why France waited so long to make whisky is because of... An
Icelander volcano. France was indeed producing whisky, some old papers back in
the 18th century proved that a «grain eaux-de-vie aged in
barrel» (the definition of whisky) was produced and consumed. However, a
volcanic eruption in Iceland had dramatic consequences. Laki, a volcanic
fissure erupted for nine months until February 1784, causing lava to pour out
of the system, creating an ash cloud filled with toxic and therefore lethal
elements («poisonous hydrofluoric acid and sulfur dioxide compounds»,
Wikipedia), which caused Iceland to loose half of its livestock (mainly sheep),
causing famine and killing about a quarter of the population. But it didn't
stop there and the volcanic cloud, pushed by winds reached Europe in a couple
of days. Some consequences were even observed in North America and Asia. It
indeed blocked sun rays, causing a very harsh and difficult winter. It even
generated a climatic disorder: polar summer, violent thunderstorms, etc.
France's harvests didn't survive these weather changes which caused famine to
shake up regions. It seems that around 1789, some kind of prohibition occurred.
Barley, grain, was so scarce that distilling was forbidden. Thus, whisky
production was lost in time, forgotten and it took 200 years for France to get
back on its feet and decide to produce whisky again. According to Nicolas
Julhès, head of the «Distillerie de Paris», a French craft
whisky distillery, French whiskies will become the greatest whiskies of the
world. Why? Because producers usually distil in smaller pot stills (a quality
pledge) and above all, the country has the best ageing specialists thanks to
Cognac and wine.
As we can see, distilleries are being created all around the
world to accommodate local tastes first and potentially other markets.
Sweden is part of the movement with ten new distilleries that
started producing whisky since 2013. Sweden whisky has indeed been trending for
the past few years thanks to several distilleries. There is the Smögen
distillery, the Box distillery which opened in 2010 but is producing whisky at
a smaller scale. For instance, its 700 bottles batch was sold out in one day in
2014. Another distillery called Hven is also producing at a small scale but got
several awards notably at the International Wine & Spirit Competition since
2013. What really helped Swedish whisky to get noticed is due to Mackmyra
Distillery. It is the largest distillery in the country with a production
capacity of 1.2 million litres a year. It grew bigger and bigger since 1998,
when a group of friends decided to create the first Swedish whisky and
distillery. Where does this idea come from? One day, a group of friend (eight
to be precise) had an important meeting
31
during a cold night after a long ski day around a bottle(s?)
of single malt(s). One of them wondered why was there no whisky made in Sweden
and someone replied that since the water is so pure, barley is also cultivated,
climate is fresh and humid, why not trying to make whisky? Which they did.
Mackmyra is well-known for its innovative approach notably with
its «Gravity distillery», built in the middle of a forest, near
Mackmyra village. The 35 meters high tower is almost a 100% green with organic
waste being recycled in biofuel for example and its energy consumption reduced
to minimum thanks to the law of gravity. The distilling process runs from the
top, where the malt is pumped in, to the bottom and goes through several steps
floor by floor, from ricing to grounding, from fermentation vats where water
and yeast are added to pot ls, to finally finish its way into the barrels where
it will age. Ingredients are wedish, same goes for casks, made in Swedish oak.
The Swede distillery didn't ant to copy Scotch whisky, the group of friends
wanted to create their own

Swedish recipe. They experimented at least 170 different
formulas before getting to the final results and thus what they really wanted.
An important community gathered around the project, like friends, relatives,
strangers and they participated in elaborating the whisky recipe by tasting
different formulas, bringing their know-how, giving advices, suggestions. They
also tried different types of yeast, barley, maturation process... Until the
distillery found «its» Swedish whisky. Six different single malt
cuvées have been
released between 2005 and 2007. These batches were 3 years
old, limited editions in order to «test» the market. The enthusiasm
was immediate and it kept on growing. The innovation doesn't stop here. Indeed,
not only the five maturation warehouses are located in particular sites (old
iron mine, maturation storehouses half-buried in the middle of the forest), but
the ageing part is also quite original. Small 30 litres barrels are stacking up
in the different cellar rooms but why using these smaller casks? In comparison,
Bourbon casks can hold up to 180 litres, Hogshead 250 litres etc. The point is,
it accelerates the ageing process thanks to a tighter proximity of the alcohol
with the wood. In 2008, the «First Edition» was launched, becoming
their first regular bottled whisky, and since then, Mackmyra has grown
internationally. The company got several awards, notably the Best European
Single Malt of the world last year at the World Whiskies Awards.
Swedes are producing whisky but they are also amongst the top
whisky drinkers in the world (15th biggest drinker with 0.86 litres
per capita). For instance, Scotch exports increased by 10 million pounds
between 2003 and 2013 to 36.4 million pounds according to the Scotch Whisky
32
Association. They like peaty whiskies but they also enjoy
discovering new grounds, like Japanese whisky. With Mackmyra and other
distilleries making whiskies, some newcomers opening, Swede whisky's future
looks quite promising.
When we talk about whisky production, the first country in
your mind is not Italy, however, it can might be the case for wine. But Puni
proves us wrong by entering the single malt world. The young distillery
(created in 2010) is the only Italian distillery made in the region that locals
describe as the «Highland of Italy» is located near Switzerland and
Austrian borders, in the Italian Alps where the water is pure. Another whisky
producer to add to the list of whiskies of the world, getting bigger and
bigger.
We will finish on two other important whisky producers who
also happen to be two major rugby nations: Australia and New Zealand. For those
who missed the first half-time, whisky remained
marginal for quite a while. Thus we might wonder why British
settlers preferred imposing rugby
rules (and cricket) when they settled in the Pacific instead
of whisky distillation, although both countries have plenty of pure water,
arable lands to sow barley, even peatlands and above all,
English, Irish and Scottish emigrants even brought their pot
stills (their know-how too), whisky
still remained quite small compared to other alcoholic
beverages. When we know that New Zealand probably applies the most liberal
legislation about domestic distillation, we might find
that strange (according to the Custom Act of 1996, domestic
distillation is legal, free of
taxation). Both rugby nations got along to play the whisky
scrum together. The Food Standards Australia New Zealand Act 1991 gives a
rather general definition of a spirit (and therefore
whisky): «Spirit means an alcoholic beverage which
contains at least 37% alcohol by volume,
consisting of: a potable alcoholic distillate, including
whisky [...] produced by distillation of fermented liquor derived from food
sources, so as to have the taste, aroma and other
characteristics generally attributable to that particular
spirit; or such a distillate with any of the following added during production:
water, sugars, honey, spices.» - Food Standards Code-- Standard 2.7.5.
Kiwi whisky is getting noticed notably by Jim Murray, author
of the Whisky Bible. This «Bible» is released every year and just
like wines with Robert Parker, he grades whiskies according to the tasting. He
gave 95/100 to the Kiwi whisky South Island Single Malt 21 years old. The same
whisky got an award at the World Whiskies Award in 2013 as the best aged single
malt. Originally, New Zealand whisky was born in the South Island (where it is
the coldest), and there are (for now) few distilleries there.

33
As for Wallaby whisky, even though All Black might win the
rugby gam Australia played its whisky cards right. Tasmania is the whisky land
of the countr The floating island, south of Melbourne, with its
«Scottish» climate and thanks
to many pioneers like Sullivans Cove, Hellyer's Road, Lark who
managed to make Aussie whisky recognized worldwide. Volumes are not very
important,
for instance, around thirty distilleries were created these
past few years with
about half in Tasmania, and the «biggest» distillery
Hellyer's Road makes
100,000 litres of pure alcohol which represents a third of
Edradour's
production that is supposedly the smallest distillery in
Scotland. Wallaby
whisky is again quite confidential but has a great awareness
around the world. For example, Sullivans Cove French Oak Cask has been awarded
as the world's best single malt at the 2014 World Whiskies Award, quite
impressive. Again, Tasmanian whisky managed to get a good reputation across the
ocean thanks to several awards. Australian are also significant whisky
drinkers, with 1.3 litres per capita, it is the 4th biggest whisky
drinker in the world (versus 14th for New Zealand with 0.87 litres
per capita).
I had the chance to meet Michael Moss several times. This
professor at Northumbria University is a real whisky expert and notably wrote
`The Making of Scotch Whisky'. I asked him: - What do you think about new
incomers in the whisky industry (countries such as India, Taiwan, France,
Sweden etc.)? He answered: - «You need to distinguish between volume
producers and craft distillers. Some volume producers, such as Nikka, are
excellent. The craft distillers will need to prove themselves, there will be
successes and failures. Some may only cater for a local market, but will almost
certainly be able to make a living. Across the piece the trick will be to
position the product in such a way as to attract sales and build a market, and
not to sacrifice quality in a search for volume.»
III. Questionnaire
In order to investigate by a quantitative study, customers'
behaviours in terms of wine and whisky consumption, I have defined a list of
questions the research question «Is there a move away from wine to whisky
in the European market?».
This survey has been posted on social medias, conveyed through
emails, and thanks to the snowball effect, this questionnaire got 146
respondents. The first question being about drinking alcohol, 129 of
respondents actually answered that they do drink alcohol so those will be taken
into account for the rest of the survey.
34
Overall, we observed that spirits consumption is getting more
and more popular, and although whisky consumption is quite low compared to
wine, people are tending to drink whisky more than they used to. Furthermore,
people are also more likely to drink less wine, but better wine. You will find
the questionnaire in the appendix (Cf. appendix n°3) and also some in
depth statistics and correlation for the questionnaire in appendix 4 to 6.
Here is the descriptive analysis per question1:
Question 2: In an average month, how often would you
drink wine (red, white or sparkling), even if it's just one glass? (Answer 0 if
you don't drink wine)

|
Question 2
|
In an average month, how often would you drink wine (red,
white or sparkling), even if it's just one glass? (Answer 0 if you
don't
drink wine)
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Wine (Red, White, Sparkling)
|
129
|
0
|
9.36
|
30
|
As we can see, on 129 respondents and on average, people are
drinking wine (even just one glass) at least nine days in a regular month.
1 Moyenne = Mean. Cf. all graphs.
35
Question 3: In an average month, how often would you
drink whisky, even if it's just one glass? (Answer 0 if you don't drink
whisky)

|
Question 3
|
In an average month, how often would you drink whisky,
even if
it's just one glass? (Answer 0 if you don't drink
whisky)
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Whisky
|
129
|
0
|
1.82
|
30
|
On the other hand, on average, people are drinking whisky around
two days in a normal month.
36
Question 4: Of all the alcoholic beverage(s) you drink,
please indicate what percentage you allocate to all these categories, where the
total must equal 100%.

|
Question 4
|
Of all the alcoholic beverage(s) you drink, please
indicate what
percentage you allocate to all these categories, where the
total must
equal 100%.
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max
|
|
Whisky
|
129
|
0
|
4.82
|
30
|
|
Wine and Sparkling wine
|
129
|
0
|
47.51
|
100
|
|
Rum
|
129
|
0
|
8.08
|
70
|
|
Beer
|
129
|
0
|
28.86
|
95
|
|
Other spirits
|
129
|
0
|
10.73
|
85
|
This question aims to define the «allocation»
percentage between alcohol beverages, in people's consumption: Wine and beer
are coming in first with respectively 48% and 29%. 5% is allocated to
whisky.
37
Question 5: How much do you agree with the following
statements?

|
Question 5
|
How much do you agree with the
following
statements?
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
I drink wine more often than I used to
|
129
|
1
|
4.12
|
7
|
|
I drink whisky more often than I used to
|
129
|
1
|
2.22
|
7
|
|
I drink more spirits (vodka, gin etc.) in general more often than
I used to
|
129
|
1
|
2.8
|
7
|
|
I think that all wines are pretty much the same, regardless of
what they cost
|
129
|
1
|
2.04
|
7
|
|
I think that all whiskies are pretty much the same, regardless
of what they cost
|
129
|
1
|
2.21
|
7
|
|
Are you willing to buy less wine but better quality (assuming
that better quality means more expensive)?
|
129
|
1
|
5.02
|
7
|
People disagree on the fact that they are drinking more whisky
but also about the fact that all wines and whiskies are the same regardless of
what they cost. However, they agree about drinking more wine than before. The
key learning that comes out of this chart is that people agree on the fact that
they are willing to buy less wine but better quality, even if it's more
expensive.
38
Question 6: Of all the wine you drink, please indicate
what percentage is Red, White, Sparkling wine or Rosé where the total
must equal 100%.

|
Question 6
|
Of all the wine you drink, please indicate what
percentage is Red, White, Sparkling wine or Rosé where the total must
equal 100%.
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Red
|
129
|
0
|
41.61
|
95
|
|
White
|
129
|
0
|
34.33
|
100
|
|
Sparkling wine
|
129
|
0
|
12
|
80
|
|
Rosé
|
129
|
0
|
12.05
|
50
|
People are tending to drink more red and white wines.
39
Question 9: When do you typically drink wine?

|
Question 9
|
Nb.
|
%
|
|
When do you typically drink wine?
|
129
|
|
During lunch
|
39
|
30.23%
|
|
During dinner
|
106
|
82.17%
|
|
At social events
|
122
|
94.57%
|
|
At professional events
|
59
|
45.74%
|
|
To relax (e.g. after work or whilst watching TV etc.)
|
68
|
52.71%
|
Generally speaking, people are drinking more during social events
and dinner.
40
Question 10: Please indicate how often, you buy wine from
the following locations:

|
Question 10
|
Please indicate how often, you buy wine from the
following
locations:
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Wine store
|
129
|
1
|
3.74
|
7
|
|
Grocery store, Supermarket
|
129
|
1
|
5.02
|
7
|
|
At the domain, Château etc.
|
129
|
1
|
2.73
|
7
|
|
Online
|
129
|
1
|
1.54
|
7
|
On average, people are more frequently buying wine in grocery
stores and supermarkets. Specialised wine stores come in second position.
Online buying remain quite marginal.
41
Question 11: When dining at a restaurant, club, bar or
attending to an art/dance/theater show, how often do you order wine?

|
Question 11
|
When dining at a restaurant, club, bar or attending to
an
art/dance/theater show, how often do you order wine?
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Restaurant
|
129
|
1
|
5.39
|
7
|
|
Club / Bar
|
129
|
1
|
3.31
|
7
|
|
Wine Bar
|
129
|
1
|
5.32
|
7
|
|
Art / Dance / Theater show
|
129
|
1
|
2.74
|
7
|
People often order wine in restaurants and wine bars.
42
Question 12: Of all the whisky you drink, please indicate
what percentage is Mainstream (found in supermarkets), Specialist (more
confidential, found in wine/whisky stores) or Craft (unique, very
confidential), where the total must equal 100%.

|
Question 12
|
Of all the whisky you drink,
please indicate
...
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Mainstream whisky
|
86
|
0
|
60.16
|
100
|
|
"Specialist" whisky
|
86
|
0
|
31.78
|
100
|
|
Craft whisky
|
86
|
0
|
8.06
|
100
|
People are mostly going for mainstream whiskies.
43
Question 15: When do you typically drink whisky?

|
Question 15
|
Nb.
|
%
|
|
When do you typically drink whisky?
|
129
|
100%
|
|
Before dinner (aperitif)
|
26
|
20.16%
|
|
At the end of a meal (digestif)
|
37
|
28.68%
|
|
At social events
|
54
|
41.86%
|
|
At professional events
|
11
|
8.53%
|
|
In cocktails
|
43
|
33.33%
|
|
To relax (e.g. after work or whilst watching TV etc.)
|
25
|
19.38%
|
|
I don't drink whisky
|
47
|
36.43%
|
People (when they do drink whisky), tend to drink whisky at
social events (54%), in cocktails too (43%) and at the end of meal as a
digestif, as an after-dinner drink.
44
Question 16: Please indicate how often, you buy whisky
from the following locations:

|
Question 16
|
Please indicate how often, you buy whisky from the
following
locations:
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Wine/Whisky store
|
129
|
1
|
2.78
|
7
|
|
Grocery store, Supermarket
|
129
|
1
|
3.54
|
7
|
|
Online
|
129
|
1
|
1.19
|
7
|
|
At the distillery
|
129
|
1
|
1.54
|
7
|
People are more likely to buy whisky in grocery store and
supermarkets, just like wine.
45
Question 17: The statements below include different
reasons for drinking whisky. You don't need to answer this question if you
don't drink whisky.

|
Question 17
|
Nb.
|
%
|
|
The statements below include different reasons for drinking whisk
...
|
86
|
|
...for pleasure
|
66
|
76.74%
|
|
...to celebrate something
|
35
|
40.7%
|
|
...because I want to be socially accepted
|
10
|
11.63%
|
|
...to get drunk
|
34
|
39.53%
|
We can conclude that people are drinking whisky for pleasure
firstly with 77% and to celebrate something with 35% which is related to
drinking whisky during social events.
46
Question 18: What is your gender?

|
Question 18
|
Nb.
|
%
|
|
What is your gender?
|
129
|
100%
|
|
Male
|
46
|
35.66%
|
|
Female
|
83
|
64.34%
|
Question 19: How old are you?

|
Question 19
|
How old are you?
|
|
Nb.
|
Min.
|
Mean
|
Max.
|
|
Please indicate your age
|
129
|
18
|
29.01
|
62
|
Question 7 & 13: According to you, what does a
decent bottle of wine & whisky cost? Not for a special occasion but for
good drinking.
|
Wine price average
|
|
Total
|
1665,8 €
|
|
Respondents
|
129
|
|
Mean
|
12,91 €
|
|
Whisky price average
|
|
Total
|
3976,85 €
|
|
Respondents
|
129
|
|
Mean
|
30,83 €
|
47
|
USD mean
|
EURO mean
|
AUD mean
|
|
Wine
|
14,03
|
€
|
12,67
|
€
|
17,58
|
€
|
|
Whisky
|
31,62
|
€
|
30,89
|
€
|
32,91
|
€
|
For these questions, we converted all foreign currencies in
order to get the Euro change. We can observe that the perception for the price
of a decent bottle of wine and whisky is quite close according to these charts.
The main average price for wine is approximately 13€ and 31€ for
whisky. For American and European drinkers, the average prices for a good
bottle of wine and whisky are respectively around 13 or 14€ and 31 or
32€.
48
IV. Discussion
1. Market trends conclusion
For a long time, going up to the mid-2000's, the European
Union was producing more wine than needed. Back then, producers who couldn't
sell their harvest were paid (at least those which were unsold) thanks to
governments `emergency distillation' rights, a program where the grape surplus
production was converted into industrial ethanol. The EU acknowledged that this
practice was killing prices for successful farmers, producers and was
perpetuating this production excess. After many years negotiating between
producing countries, the EU established the Common Market Organisation (CMO)
which slowly got rid of the `emergency distillation' program to end up
terminating it by mid-2012. A brand new program was put into place, it
consisted in paying European growers to uproot 175,000 hectares of
«economically unsustainable and lesser quality vineyards» (The
League: Worldwide Supply and Consumption Patterns, the State of Wine Industry
2016). To give an idea, it represents the equivalent of about 87% of planted
wine grape land in California. Main producing countries such as Italy, France,
Spain, Portugal or Hungary have been major contributors to the CMO.

According to the OIV graph here, we can look at the evolution
of worldwide production and consumption on a fifteen year period. We can
observe the decline of wine production between 2004 and 2012, followed by a
sudden production peak in 2013. On the consumption side, we have an ascendant
curve till 2008, followed by a drop in 2009, and then reaching a stability zone
for the following 6 years. When the production goes up, the demand doesn't
always go along. The two figures actually never cross or meet!
The gap symbolises the production excess, did someone ever
wonder where does this surplus go?
This fissure between production and consumption is expanding,
but is - a tiny bit - mitigated by the demand for wines to be used for retail
and industrial purposes like vinegar, brandy...
49
Again, it is clear that the gap is not going to tighten any
time soon, is it because Europe is overproducing (or overplanting) again?
According to the OIV, both demand and supply are balanced, however, a slowing
worldwide per capita consumption might make this balance frail, precarious
(especially in Europe).
We will see on the following map that wine consumption in
Europe has pretty much decreased throughout the years:

There is a noticeable shift in wine consumption in Europe away
from important producers but also significant consumers such as Spain, Italy,
France towards other countries, mainly from the New World, like Australia,
China or the United States (Argentina being the only exception). Nowadays,
about 39% of wine is drank outside Europe, this percentage was around 30% in
2000.
As we mentioned earlier, the US became the biggest wine
drinker in the world. Since 1998, higher consuming countries like Spain, Italy,
France, even Portugal have been experiencing substantial drop in wine
consumption per capita and by 2006, Europe producers were making around 150
million cases more than they could sell. Certain European countries are less
affected by this trend, notably the UK and Germany who respectively represent
13 and 15% of the total world import volume, which makes them the biggest
importing countries and they are followed by the US with 11%.
50
Other market trends in the wine industry and hot topics are
also occurring:
- Sustainability: Many customers are looking for organic
wines, biodynamic wines made without fertiliser or chemical substances, or too
much sulphur, made in sustainable practices.
- Geographical Indications (GI) opportunities: It allows
certain wines but also products to be identified and originated in a certain
country/region/locality where it is made. It can be valuable since your wine
can be distinguished amongst many other although the system is quite renowned,
even in supermarkets for lesser quality wines.
- Wine fashion: There are some `wine fashions' trends
occurring and it seems to hop from one country to another. For instance, if a
certain wine is successful in one European country market, the Domaine,
Château or company producing it will introduce it in another European
country market. A current example of a trend happening now is aromatic wines as
well as wine cocktails. Both are pretty trendy in Germany and the UK and both
are expected to spread out across other European countries with a «good
outdoor culture» in for the next years according to CBI. These
`fashionable wine trends' tend to be periodic in Europe meaning that the
popularity of certain kinds of wine is varying throughout the years. For
instance, sparkling wine is still very fashionable in many European countries
while Rosé wine seems to be losing customers' interest in numerous
European markets. Full bodied red wines are also losing their momentum whereas
elegant wines and more `easy-to-drink' wines seem to come back again. One
growing trend are lighter style reds as well low alcohol wines, it is gaining
in popularity.
- Changes in retail: Wine categories are shifting because
tastes are more and more taken into account as well as drinking moments,
becoming a crucial point in wine suppliers marketing strategies. For example,
in Netherlands, wines are not sorted by country but according to tastes and
occasions in retails. Since customers are paying less attention to wine origin
in certain countries, this might help new exporters (from the New World
mainly). However, in the UK, retailers actually went back to sorting their
wines by country since it is working better with British consumers.
- Packaging innovations: There is a push for innovative
packaging other than regular glass bottles. It comes from several factors like
quality conservation, price, sustainability etc. The acceptance of new
technological innovations in wine packaging (like screw caps for bottles,
bag-in-box or BIB) varies from one European country to another. While most
Northern as well as Western European countries appear to accept these
technologies (more for the high-volume segment though), Eastern European
countries look like they have more difficulties
51
to do so. In pretty much all import markets, customers have
been uncertain about going from traditional glass bottles to innovative
packaging particularly in both premium and super-premium segments. In spite of
that, some alternatives are gradually rising, being more and more accepted by
the public. Certain BIB are quite trendy, a good example would be BiboVino in
France, a company making BIB with good quality wines.
The premium market is soaked in new innovations notably in
packaging with Kuvée for example, an innovative way of drinking your
wine. It is basically a smart bottle that enables you to keep your wine for
thirty days thanks to a `pick and click' system. You choose a bottle of wine
and you click it into the Kuvée bottle (which is the wine dispenser), it
also gives you information about the wine, the producer, the country of origin,
suggested pairings... The on-trade (Cafes, Hotels, Restaurants) is quite
receptive to packaging innovation, especially screw caps.
- Online sales are also becoming more important. In France,
one French over three bought wine on the Internet in 2016. According to SOWINE
(study made with more than a thousand respondents), although this is quite
occasional, generally once a year, 13% of wine purchases were made online in
2016 versus only 10% in 2013. The progression is quite significant since the
majority of customers are making their wine purchase in retailers with 78% of
purchases (SOWINE), the rest being divided with wine shops (47%) and
domain/château (29%) purchases (total does not equal 100% because people
can use different channels). To buy wine, French consumers usually go on wine
producers' websites but also private sales websites (like Cdiscount). Online
wine shops come in third position followed by `Drive Retail' websites.
Globally, online sales were about 600% higher in 2015 compared to 2006 which
represents 5.4 billion euros (CBI), however they are still quite small
especially in Europe. The online market can be interesting again for new
entrants like New World wine producers but since buying on the internet is
quite occasional, it might not revolutionise or change wine consumption and
wine purchases in Europe.
Can these trends help wine consumption to get back on its
feet?
Consumption trends are changing and evolving. In several
segments, people are drinking less but better and this is the case for wine and
whisky.
Regarding whisky, there is an increasing scarcity of old
whiskies. According to Donald MacKenzie, Whisky Brand Ambassador of Dugas, this
phenomenon is explained by the whisky industry that got old malts customers
used to prices not valued enough compared to the market value. Few years ago,
the industry had substantial stocks of old malts resulting from a
52
decreasing consumption of younger whiskies - blends - in the
seventies and eighties, which resulted in these stocks, 30 years later. At the
same time, the industry hammered consumers with the motto `the older, the
better' which is not necessarily true. The age statement is one of the quality
component of a whisky but it is not the only one. The fact remains that regular
customers an old whisky will still be better than a young one. Nowadays,
distillers and actors of the industry have to train consumers in order to
convince them (thanks to tastings) that this statement is not always true. This
explains the success of important spirits/whisky exhibitions like the Whisky
Live for instance where many kinds of whisky of different ages are exposed and
available to taste.
Also, as we said previously, Scotch is not the only whisky in
the world anymore. The `battle' with other nations is still on even if Scotland
remains the predominant actor with more than a hundred distilleries, thus the
country should keep its status for quite a while. Furthermore, most of new
actors - except Ireland - are claiming to take their legitimacy from the
Scottish history. We could mention (again) Japan for which whisky legacy gets
its roots from its time spent in Scotland in the twenties thanks to Masataka
Taketsuru, the rightful founder of Nippon's whisky industry. Japanese whisky is
seducing because of its amazing quality, an up-to-date packaging, quite modern
but very classy and classical. However, volumes are quite poor and are first
allocated to the Japanese market.
As to Ireland, after its difficult desert crossing, there
definitely is a renewal of Irish whiskey with new distilleries openings which
are, once more, able to produce good quality whiskies. Other European countries
are also producing beautiful whiskies, in a very original way and customers
love it.
According to Donald MacKenzie, a market trend that is actually
occurring notably because of a lack of old whiskies, are No Age Statement (NAS)
whiskies. Many distilleries are now producing NAS, along with aged whiskies but
it will keep on growing. Also, atypical ageing in new types of cask (other than
Sherry or Bourbon) attracts customers. There is actually an enormous pressure
on certain sectors like Bourbon barrels with the American industry looking for
a way to modify some laws, so they don't have to use new oak for Bourbon
because the cost is expensive and it gives a flavour that can be too
prevalent.
Michael Moss said previously that we needed to distinguish
between volume producers and craft distillers. There is actually a craft
spirits wave, a trend that is getting bigger and bigger and a study made by
Mintel proves it. In 2015, one launch of an alcoholic drink over seven (14%)
was labelled as «craft» drinks (in 2012, only 5% were categorised as
«craft»). The movement was born in the United States, in the brewery
and microbrewery world. The craft
53
phenomenon is gaining ground and is seizing the spirits
market. The demand is increasing thanks to both North-American and European
consumers (respectively representing 49% and 42% of craft launch). This
tendency is quite small on this important market but craft alcoholic beverages
are going through an important expansion conveyed by a significant demand for
more authentic, local, interesting, characteristic and less industrial spirit
brands. Jonny Forsyth an analyst specialised in drinks at Mintel says that more
than half of American consumers (55%) consider that craft brands are of better
quality. Europe follows the same path with nearly half of French (55%), German
(50%), Italian (53%) and Poland (46%) consumers being more attracted to
alcoholic drinks coming from small distilleries rather than coming from big
brands. In United Kingdom, 37% of costumers are ready to pay more for getting
craft spirits.
But who are these alcohol craft amateurs? The Y Generation
plays a key role in the growth of craft spirits. Its «singular» and
«creative» spirit attracts and suits to the generation's consumption
habits (Jonny Forsyth). Whisky actually remains leader in terms of craft
spirits launch with 43% of release on the market in 2015 (a significant rise
compared to 2011 with 37%). The whisky category is followed by gin with 23% of
craft spirits launch in 2015 (a major increase again, compared to 2011 with
only 9%). Gin is much praised by small businesses and start-ups for its
production which lasts a couple of days when that of the whisky and other brown
alcohol lasts years. In France, the number of microbreweries and
microdistilleries is exploding because of the substantial demand, where people
are more and more well-informed, stricter but also more keen on aromatised
drinks. The design of the packaging as well as the marketing are seizing the
opportunity, which gives room to bigger players like Diageo or Pernod Ricard to
find their place in this growing market and surf on the trend.
The arrival of small and confidential producers can have a
positive impact on the market. They usually attract millennials. However, with
higher production costs, less experience in distillation, ageing, blending, we
often get expensive whiskies with a quality that doesn't match the price.
Whisky is a matter of time, experience, dexterity, maybe more than other
spirits.
2. Consumer trends and expectations
Population is ageing in Europe. Data from Eurostat shows that
the European population is getting older and older. By 2050, almost 30% of the
European population is projected to be 65 years and older compared to 2015 with
19%. This is actually leading to an increasing niche in the European wine
market and in this niche, customers tend to drink wine less often.
Percentage of the European population
54
The wine industry is trying to adapt to this trend, notably by
producing (thus selling) wine in smaller packages or with innovative packaging
that would conserve wine better and for a longer time.
Population by age groups
20 15 10 5 0
25

20,9
20
18,8
17,6
17,5
16,7
21,4
20 18,9
0-19 years 20-34 years 35-49 years 50-64 years 65 years
and older
2015 2050 Source: Eurostat
As we said previously, millennials are also to be watched for
both wine and whisky markets. They are indeed the young generations of wine and
whisky costumers and they are usually more intrepid when it comes to their
taste. As regards to wines, they are undoubtedly gaining interest in new
producing regions, more affordable prices and especially wines that are
produced in a sustainable way (cf. market trends in the previous part). Their
impact on the wine industry is growing and according to a British study,
millennials picture wine as a `social drink' which means that they buy wine
preferably on the on-trade channel that accounts for 29% of wine's volume (Wine
Intelligence, 2016). The wine market needs to become more reactive, receptive
to millennials' needs which will necessitate a stronger prominence, attention
on empirical as well as emotional commitment with costumers in communication.
It is important to remain visible on social media since this can be significant
as a strategy in order to promote your wine (the feasibility might depend on
the European country and its laws regarding alcoholic beverages), generate
brand awareness by being diverting, captivating, and enticing at the same time
or you will lose (probable) prospects interest and also miss traction. Apart
from social media like Facebook, Twitter or YouTube, wine application on
smartphones are benefiting from a growing popularity as well with apps like
Vivino, Delectable, Wotwine... It helps consumers getting access to information
in an easier way, with ratings, reviews, food pairings on wines thanks to
bigger and bigger communities.
55
Concerning whisky, here are several customer trends and
behaviours in whisky that will emerge or that will confirm some malted
tendencies:
- People will often (but not always, thank goodness) lean
towards lower quality whiskies that are overwhelming our retails shelves and
that are cheap (usually around 15€ or less). In France for instance, it
represents around 90% of whisky sales in 2014. The awards of the best-sellers
go to William Peel (17.5 million litres), Label 5 (10 million), Grant's (9
million) and Clan Campbell (8 million) in 2014. According to Le Figaro, in 2015
the top 3 bestsellers were Jack Daniel's, Ballantines and Clan Campbell. As you
can see, on one hand, there is no single malt and prices are pretty low
(nonetheless, Scotch remains France's favourite whisky even though Jack
Daniel's is a Tennessee whiskey). Let's just not forget the American (and not
Scottish) proverb that says «There is no bad whiskey. There are only some
whiskeys that aren't as good as others.» - Raymond Chandler. On the other
hand, prices can also be quite high because of the pressure on single malts
stocks which provokes a growth of prices. A 12 years old single malt usually
cost around 30 euros, it can go up to 50 euros for a premium bottle and 70
euros and more for older malts.
- The retail market is a major channel for whisky purchases.
It tries to adapt and improve their whisky offer. Indeed, supermarkets are
striving to propose a more and more important selection of whiskies. As we can
see on appendices 7 and 8, important supermarkets chains like
Intermarché in France are endeavouring to give advices from their own
professionnals with the different types of major aromas in whiskies.
- The premium malts market, `prestige' or `super-premium' is
the one that progresses the most with 10% or more according to segments like
on-trade for instance and some people are ready to spend huge amount of money
for a bottle that they probably won't even open. A bottle of Dalmore Brilliance
vintage 1926 got up to a quarter million euros and found an owner. With the
growing scarcity of old whiskies, with a need of cash flow, distilleries are
producing more and more NAS whiskies. Moreover, although millennials are
getting interested in whiskies, they are still persistent with other spirits,
especially 18 to 24 years old with the famous Vodka Red Bull mix and are not
always going for Dad's drink.
- In less than a year, flavoured whiskies took our glasses by
storm. Technically, they don't deserve the term `whisky' since they are
flavoured and bottled at 35% alcohol volume instead of a minimum of 40%. You
can actually find pretty much everything in the bottle but it is essentially
honey flavoured (with Jack Daniel's, Jim Beam, Paddy), spicy flavoured, maple
flavoured, vanilla, cherry, apple... Customers love it, and these types of
whisky are aimed to target women, youngsters, or to introduce consumers to some
`kind of whisky'.

56
The Scotch Whisky Association and European Union guidelines
state that no ingredients can be added to whisky except water and caramel
colouring, otherwise it cannot be labelled as `whisky'. The SWA also said that
flavoured whisky needs to be differentiated from Scotch and whisky so it has to
be labelled as `spirit drink'. What ignited this revolution? Customers' thirst
for adventurous and new flavours. People are keen on trying spicier foods,
appealing cocktails so flavoured whisky is part of this new wave. Plus, that
kind of `spirit drink' are likely to be more straightforward, smoother, easier
to drink, making it a good entry point again for those who would like to start
drinking spirits. One little exception, an actual naturally flavoured whiskey,
an American whiskey to be precise, has been awarded as the World's Best
Flavoured Whisky in 2016 at the World Whiskies Awards (the whiskey was the Knob
Creek Smoked Maple Whiskey, Kentucky Straight Bourbon, quite a long name). How
do customers drink it? Well, either neat after dinner, mixed into cocktails, or
as a pre-game drink...
- As we said earlier, the craft wave is getting bigger and
bigger. People are succumbing to the small producer label. Malt-maniacs,
looking for less traceability are turning towards both young and/or
microdistilleries which are (according to them) restoring attention to details,
providing excellent raw materials, production methods that are sometimes more
vintage: Corsair in the US, Puni in Italy, Glann ar Mor or Eddu in France, Box
in Sweden, the list is quite exhaustive. The craft Bourbon phenomenon,
`hand-made' Bourbon managed to invade and convince the American market by
saying that small is always beautiful, not sure if this is always true.
- Customers will also be unfaithful to Scotch: They will drink
less and less Scotch and drink more Japanese, American, or Irish whiskies since
the Malt empire dominance is making it rest on its laurels, not really a good
time. People will go for the Solist cuvee of the Taiwanese whisky Kavalan, an
accelerated aging Indian whisky Amrut or the original maturing of the Mackmyra
distillery, but also peaty styled whiskies like Hellyers Road from Tasmania.
- Customers will eventually go for 3.0 whiskies. The number of
distilleries and malts being limited, the whisky amateur that as an important
curiosity appetite will go for blends from blenders and independent bottlers
whose imagination can simply be exuberant and their quality astonishing. For
instance, blends from John Glaser of Compass Box, a small independent company
specialised in blending that makes beautiful and stunning blends;
57
Ichiro's Malts blends from Ichiro Akuto; the Exclusive Casks
from the Creative Whisky Company... The list goes on forever.
- The cocktail trend is also coming back. In France,
especially in Paris with a plethora of whisky bars opening, cocktails are
gaining in popularity.
- Remember customers' curiosity we were talking about? This
inexorable quest of novelty is making limited editions, small batch, special
packaging, duty-free exclusivity bloom, big times. Marketing will sometimes
take the upper hand to the detriment of quality.
- We will finish on one noteworthy trend that is actually
valid for wine too, Europe drinks less but better. Budget-prices blends are
slowly starting to decrease (-3%, which represents 2 million litres less in
2014 according to Slate), Single Malts sales are remaining stable, and premium
whiskies sales are on the other hand rocketing.
Generally speaking, European wine consumption is gradually
falling with important losses noticed in major consumers and producers. In
spite of this decline, quality wines sales have been going up as well as
imports.
To my question: - `What are the current trends in whisky
consumption?', Michael Moss answered:
- «[...] you only have to look at the duty free
offerings, there is a definite shift to premium products, particularly malts
with lots of range extensions. I think there is room for more quality blends,
such as those offered by Compass Box, partly because malts are not to
everyone's taste and we can also expect growing competition from rum now that
Cuba has been rehabilitated. Demand for basic blends in the export market will
continue, but just like big label wines margins will be tight.»
3. Where are the Wine and Whisky markets going?
Let's discuss about the results of the questionnaire and its
analysis.
First of all, this questionnaire gives us a view on a limited
consumer sample (129 people) so it cannot be considered as statistically
robust. We have indeed to take the results with some precautions.
We can say that we might have a high proportion of Wine
lovers, and so, based on this research we also might say that there is not a
move away from wine to whisky, at least for the moment. Wine seems more
accessible, often more affordable too, lower in alcohol and perhaps less
difficult in terms of taste compared to whisky, explaining that the customers
interviewed tend
58
to prefer wine. Also there is a notion of conviviality here as
wine is more frequently seen at tables with two, three, four or even more
people. We tend to see wine at family lunch/dinner(s) more than a bottle of
whisky. Even if it is possible to do a whisky and food pairing, it is not as
popular and common as wine pairing.
Whisky is more confidential, and usually consumed and
appreciated either at the end of a meal (as a «digestif», where
premium whiskies are savoured), or at the aperitif moment (where very often,
you get a very cheap bottle of whisky to mix it with soft drinks like Coke and
share it with friends). Wine is probably not the first option in these
particular consuming occasions.
In the early 2016, the new Department of Health limits on
alcohol consumption was acted in the UK. It informed British that previous
`safe' limits are no longer so. Indeed, British have been told that they should
drink no more than seven glasses of wine per week so they can keep health risks
low. This is just an example of a much wider and global trend regarding this
raising awareness about potential negative effects associated to alcohol.
Customers are indeed being more and more mindful of health issues about alcohol
consumption, and this attitude shift about drinking is putting the wine
industry under pressure, especially in many developed markets, like the
European one. People are encouraged to drink less. The younger generations are
probably even more concerned by these health messages, but they show also show
a strong interest in new original tastes. The search for new sensations while
having a more responsible consumption are the key drivers of younger
generations alcohol consumption. This might be a problem for the spirits
industry thus, the whisky industry as well. For now, this low alcohol pattern
is not well established in all European markets, for the wine industry either,
it depends on cultural and legislative differences amongst markets as well.
This plays a key role in customer's sensitivity and acceptance about lower
alcohol wines.
For instance, Germany which has the highest percentage of low
alcohol wine drinkers in 2016 (47%) but this is notably due to the fact that
wine styles in Germany are naturally (and usually) low in alcohol. New world
countries are more sensitive to this trend with Canada for example which had an
important increase with 7 million Canadians buying lower alcohol wine in 2015,
versus 5.1 million in 2014.
Over the past few years, lower alcohol wines have been more
and more seen but still remain as a niche market despite the growing interest.
This number of lower alcohol wines drinkers in France went down so is it really
happening everywhere in Europe?

59
Preferences between higher/lower alcohol wines differ
according to traditional differences too. In countries like in the UK or
Scandinavian countries, low alcohol wines get lower tax and are thus more
popular.
Concerning whisky, many professionals believe that we will get
to see more progression and expansion of the NAS sector, even and especially in
the premium segment which will give more opportunities to smaller producers or
new distilleries to break through when they start a business. According to Matt
Chambers and Karen Taylor, co-founders of Whisky for Everyone (a blog), this
NAS trend won't be in the entry level products but in the higher priced segment
and in both domestic as well as travel retail markets. People are more driven
by the taste profile rather than age.
To my question: - `Where is the whisky market going (in the
UK, do you have an idea for other European countries)?', Michael Moss
answered:
- «Wise heads suggest alcohol consumption will continue
to fall, particularly amongst the middle class where margins are higher, so the
obvious strategy is to move up market with high quality distinctive products.
Compass Box [...] is a good example. We can also expect a number of the craft
gin distillers to enter the premium malt market with distinctive premium
products. Price competition ate the bottom end will continue, but income will
come from exports to developing countries. You can draw comparisons with
cigarettes.»
60
Another element of European economic environment may probably
impact the whisky market. Thursday, June 23rd, the European Union
went to sleep with 28 countries, it woke up with 27 in the morning, on Friday,
June 24th. Will Brexit have a consequence on the whisky industry?
Europe is Scotland's largest drinks export (Cf. Graph below) and approximately
represents no less than 4 billion pounds a year. According to the Scotch Whisky
Association (SWA), more than 90% of Scotch is sold but outside the United
Kingdom. It also said the European single market was "central to the success of
Scotch". The spirit is actually the most important contributor to the country's
balance of trade in goods thus without it, the trade deficit of the country
would be more significant. Furthermore, about a third of these exports were
distributed amongst the EU (3.8 billion pounds for exports, with 1.2 billion
pounds for the European market last year).
The SWA stated possible consequences for the Scotch
industry:
- The UK will sooner or later lose access to Europe's Free
Trade Agreement or FTAs (trades made with countries around the world to
reinforce economies, created jobs, it enables business in the European Union to
compete and export more effectively to countries outside the EU which also
gives better access to many resources), which will result in the loss of
tariffs decrease in many countries who ratified the agreement.
- The country will have to negotiate its own trade
agreement(s) and/or play by the World Trade Organisation rules.
- The UK may no longer be a member of the European Economic
Area (EEA).

- Rules on the food and drink sector are usually made at a
European level, if these laws are to be changed, then Brexit will be even more
difficult and the Scotch industry will need to adapt very quickly (for
instance, what if their Geographical Indication was removed? They may lose
their protection of the `Scotch whisky' label).
- The Europe membership gave UK distilleries an
«easier» access to many markets around the globe, including top
exports destinations such as South Africa or South Korea and of course European
countries as well.
- The industry could face another major problem: relabelling
costs which could represent a 3000£ cost for every product line a
distillery exports.
61
To sum up, if the UK still wants Scotch to be enjoyed
worldwide without commercial issues, new trade agreements need to be made
rapidly and the government has to clarify the situation as regards to the
Brexit transition.
Even if Brexit is acted, there seem to be a hesitation about
leaving the EU especially from Scotland. During a visit at the Glenkinchie
distillery (owned by Diageo) in May 2016, Liz Truss insisted on the fact that
the EU single market is really important because of certain standardised
regulations on labelling, certifications, licences or trade agreements that
made Scotch exports rocketing. She said: «Europe has a taste for Scotch
and the industry will do better if we remain in the EU because whisky producers
have [...] easy access to the Single Market of 500 million people».
Leaving the EU [...] «could lead to years of negotiations on new trade
deals - with no guarantees at the end.». Having said that, there is no
apparent benefits to the Scotch industry, it might lead to more paper work,
higher tariffs, more difficulties at borders etc.
The fate of Scotch and all the British whisky is at stake and
members of the European Union (think of France for instance since it is the
world's top whisky drinker) but other countries too could also be affected and
having the opportunity to see Scotch whiskies on our shelves might get more
complicated and scarce.
To my question: - `Do you think the Brexit will affect the
whisky market?' Michael Moss answered: - «Unless the UK is part of the
single market, there will be a 10% ad valorem tariff, which will be compounded
by export duty on the grain imported from Europe to make it. The UK does not
produce enough malting quality barley. Alternative sources are probably already
spoken for by domestic brewing and distilling industries, for example in
Canada.»
The fate of wine is also at stake here. The UK being the first
export market for Champagne for instance, France being the first supplier, it
might play to UK's disadvantage (problems with customs rights and so on).
62
CONCLUSION
In this research paper, we had an overview of the European
wine and whisky markets, enabling us to understand current situation and the
potential evolutions in the near future. Then, we went through an in-depth
review of the worldwide whisky market, understanding the current situation on
the production area and consumer's new behaviours. A specific questionnaire
allowed us to investigate people's consumption habits and their expectations on
their favourite drinks. Finally, we had a discussion in order to summarise
market tendencies, consumer trend and try to figure out the future of both Wine
and Whisky markets.
I will let the final words to Michael Moss.
To my question: - `Is there a move away from wine to whisky?',
he answered:
- «[...] This is a difficult question. A problem the
whisky industry has always had is to break into the premium market. Look at the
wine in your shop priced above an average bottle of Scotch. It has never
managed to aspire to Armagnac. Even a good number of the bespoke gins are more
expensive. The reason is that it began as a working man's drink and has never
lost that association. This is not helped by fierce price competition in the
supermarkets. One reason that spirits may be popular is that certainly European
wines are moving up market, as quality improves.»
We may conclude that at the moment, there is no real move away
from wine to whisky. However, both wine and whisky markets are in a transition
period and will have to face new challenges.
The wine market will need to find out how to address to the Y
Generation consumer's expectations: search for sensations, a consumption that
won't only occur during meals, a more volatile consumption.
The whisky market will need to continue its quest for quality
and identity with a better recognition of the distiller's know-how. It may also
need to find a way to expand its consumption moments (not only during
`aperitifs' or `digestif'). Some premium are already starting to serve whiskies
by pairing it with meals...
63
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Adventures in Whisky Land. (2015). Major Whisky Producing
Countries. [online] Available at:
https://adventuresinwhiskyland.com/2015/05/12/major-whisky-producing-countries/
[Accessed 24 Oct. 2016].
Alcoholireland.ie. (2016).
Per capita alcohol consumption in Ireland in 2015 was 10.93 litres of pure
alcohol per person aged 15+ - Alcohol Action Ireland. [online] Available
at:
http://alcoholireland.ie/home_news/per-capita-alcohol-consumption-in-ireland-in-2015-was-10-93-litres-of-pure-alcohol-per-person-aged-15/
[Accessed 3 Oct. 2016].
Baèar, F. (2015). The world wine industry is shifting
from old to new world.. [online]
http://www.evineyardapp.com/blog.
Available at:
http://www.evineyardapp.com/blog/2015/11/18/the-world-wine-industry-is-shifting-from-old-to-new-world/
[Accessed 13 Oct. 2016].
BAILLY, M. (2011). Le whisky, superstar des spiritueux
toujours en croissance. [online] lsa-conso.fr. Available at:
http://www.lsa-conso.fr/le-whisky-superstar-des-spiritueux-toujours-en-croissance,119674
[Accessed 29 Dec. 2016].
Belleville, R. (2014). Le whisky, spiritueux
préféré des Français. [online] L'Opinion.
Available at:
http://www.lopinion.fr/28-novembre-2014/whisky-spiritueux-prefere-francais-18880
[Accessed 24 Sep. 2016].
bonial.fr. (2015). Tour du monde des
buveurs de whisky. [online] Available at:
http://www.bonial.fr/info/consommation-whisky-monde/
[Accessed 2 Nov. 2016].
Borbia. (2015). Industry manufacturers insight publications
Marketing Reports. [online] Available at:
http://www.bordbia.ie/industry/manufacturers/insight/publications/bbreports/RecentMark
etingReports/The%20Future%20Of%20Whiskey.pdf [Accessed 18 Oct. 2016].
Buxton, I. (2016). Le Whiskey dans le sang. Whisky
Magazine, (62), pp.41-45.
64
Cahuzac, A. (2016). La France perd de son influence sur les
vins méditerranéens - Produits alimentaires. [online]
usinenouvelle.com/. Available at:
http://www.usinenouvelle.com/article/la-france-perd-de-son-influence-sur-les-vins-mediterraneens.N471553
[Accessed 8 Dec. 2016].
CBI Ministry of Foreign Affairs. (2016). Which trends offer
opportunities on the European wine market? | CBI - Centre for the Promotion of
Imports from developing countries. [online] Available at:
https://www.cbi.eu/market-information/wine/trends/
[Accessed 7 Dec. 2016].
Chambers, M., Taylor, K. and Hopkins, A. (2016). Experts
predict spirits trends for 2016. [online]
Thespiritsbusiness.com.
Available at:
http://www.thespiritsbusiness.com/2016/01/experts-predict-spirits-trends-for-2016/6/
[Accessed 13 Dec. 2016].
Chenal, Y. (2016). 8 juin 1783 - Eruption dramatique du
Laki. [online]
Herodote.net. Available at:
https://www.herodote.net/8_juin_1783-evenement-17830608.php
[Accessed 13 Nov. 2016].
Damgé, M. and Laurent, S. (2014). Comment la
population mondiale boit-elle de l'alcool ?. [online] Le Monde. Available
at:
http://www.lemonde.fr/les-decodeurs/article/2014/12/23/alcool-comment-la-population-mondiale-boit-elle_4545379_4355770.html
[Accessed 12 Dec. 2016].
Delaere, C. (2013). Le whisky le plus vendu au monde est
indien. [online] Les fleurs du malt. Available at:
http://lesfleursdumalt.blog.lemonde.fr/2013/04/19/whisky-indien-mcdowells/
[Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Delaere, C. (2015). La consommation de whisky dans le monde
augmente, et ce n'est pas grâce au scotch. [online] Les fleurs du
malt. Available at:
http://lesfleursdumalt.blog.lemonde.fr/2015/07/17/millionnaires-club-2015/
[Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
65
Delaere, C. (2015). Le whisky s'impose dans les bars... sous
forme de cocktail. [online] Les fleurs du malt. Available at:
http://lesfleursdumalt.blog.lemonde.fr/2015/05/18/whisky-cocktails-bars/
[Accessed 3 Nov. 2016].
Delaere, C. (2016). Le whisky retrouve (timidement) la faveur
des bartenders. [online] Les fleurs du malt. Available at:
http://lesfleursdumalt.blog.lemonde.fr/2016/01/15/whisky-bartender/
[Accessed 3 Nov. 2016].
Denis, P. (2015). Whisky et bourbon, nouveaux chouchous du
marché des spiritueux. [online] Challenges. Available at:
http://www.challenges.fr/finance-et-marche/whisky-et-bourbon-nouveaux-chouchous-du-marche-des-spiritueux_120976
[Accessed 28 Dec. 2016].
Denis, P. (2016). La production viticole mondiale au plus bas
depuis 2012 - L'Usine des Matières premières. [online]
usinenouvelle.com/. Available at:
http://www.usinenouvelle.com/article/la-production-viticole-mondiale-au-plus-bas-depuis-2012.N453347
[Accessed 2 Nov. 2016].
DIETSCH, M. (2012). What Is the Difference Between Single
Malt and Blended Whisky?. [online]
Drinks.seriouseats.com.
Available at:
http://drinks.seriouseats.com/2012/02/what-is-single-malt-scotch-what-is-blended-whisky.html
[Accessed 21 Sep. 2016].
Dominé, A. (2009). Encyclopédie des Alcools et
Spiritueux. 1st ed. H.f. Ullman, pp.306-381.
Durieux, C. (2016). Le jugement de Paris, le concours qui a
changé le monde du vin. [online] Blog Le Bon Gustave. Available at:
https://blog.lebongustave.fr/jugement-de-paris-concours-a-change-monde-vin/
[Accessed 17 Oct. 2016].
Ec.europa.eu. (2016). Agreements -
Trade - European Commission. [online] Available at:
http://ec.europa.eu/trade/policy/countries-and-regions/agreements/index_en.htm
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
66
Emen, J. (2016). Here's What 2016 Will Hold for Whiskey.
[online] Eater. Available at:
http://www.eater.com/drinks/2016/1/5/10659902/whiskey-trends-2016
[Accessed 16 Oct. 2016].
Emen, J. (2016). The Path Ahead: Whiskey Trends For The Rest
of 2016. [online] The Distiller Blog. Available at:
https://blog.distiller.com/whiskey-trends-2016/
[Accessed 18 Oct. 2016].
Ewing, H. (2015). PUNCH | The Irish Hello: Irish Whiskey
Reintroduces Itself to the World. [online] Punch. Available at:
http://punchdrink.com/articles/the-irish-hello-irish-whiskey-reintroduces-itself-to-the-world/
[Accessed 5 Oct. 2016].
Experience, T. (n.d.). Scotch Whisky Making | About Scotch
Whisky. [online]
Scotchwhiskyexperience.co.uk.
Available at:
https://www.scotchwhiskyexperience.co.uk/about-whisky/making
[Accessed 24 Oct. 2016].
Fabiani, D. (2016). Suntory & Nikka: 6 Whiskys to Die For
| All About Japan. [online] All About Japan. Available at:
http://allabout-japan.com/en/article/1913/
[Accessed 21 Sep. 2016].
FAW, L. (2016). Are Millennials Wine Snobs?. [online]
Forbes.com. Available at:
http://www.forbes.com/sites/larissafaw/2016/05/19/are-millennials-wine-snobs/#4771da242a2f
[Accessed 16 Oct. 2016].
Fédération Française des Spiritueux.
(2016). Repères 2015. [online] Available at:
http://www.spiritueux.fr/maj/phototheque/photos/pdf/ffs_reperes_2015.pdf
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Ferdman, R. (2014). The world's taste for whiskey,
visualized. [online] Quartz. Available at:
http://qz.com/166242/the-worlds-taste-for-whiskey-visualized/
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
67
Food Standards Australia New Zealand Act 1991. (2014). Food
Standards Code--Standard 2.7.5. [online] Available at:
http://www.foodstandards.gov.au/code/code-revision/FSANZ%20Code%20revision/47%20-%20Standard%202%207%205%2021%20Feb%2014.pdf
[Accessed 27 Nov. 2016].
Fortis, C. (2016). Le Scotch n'est plus le seul whisky au monde.
Vin & Spirit News, Hors-Série (Cavistes & e-commerce),
pp.50-52.
Foucaud, I. (2016). Le whisky, alcool
préféré des Français loin devant le pastis et la
vodka. [online] Le Figaro. Available at:
http://www.lefigaro.fr/conso/2016/03/15/05007-20160315ARTFIG00004-le-whisky-alcool-prefere-des-francais-loin-devant-le-pastis-et-la-vodka.php
[Accessed 6 Nov. 2016].
France AgriMer. (2015). Enquête sur la consommation de
vin en France en 2015 Le vin : transformation d'une composante de repas
à une boisson culturelle ?. [online] Available at:
http://www.franceagrimer.fr/content/download/40653/378474/file/Enqu%C3%AAte%20
sur%20la%20consommation%20de%20vin%20en%20France%20en%202015%20synth
%C3%A8se%20V3.pdf [Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Gallo, J. and Charters, S. (2014). Wine Business
Management. 1st ed. Montreuil: Pearson France, pp.13-24.
GAUTHIER, M., LABORDE, C. and MAZIERES, B. (n.d.). La
consommation de whisky : une étude exploratoire du comportement du
consommateur dans le contexte français. La consommation de whisky :
une étude exploratoire du comportement du consommateur dans le contexte
français, pp.2-19.
Gibbs, C. (2016). UK becomes a nation of wine drinkers.
[online]
Wsta.co.uk. Available at:
http://www.wsta.co.uk/press/731-uk-becomes-a-nation-of-wine-drinkers-as-wine-replaces-beer-as-our-drink-of-choice
[Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Giles, C. (2016). Wine Intelligence|Going down?.
[online] Wine Intelligence. Available at:
http://www.wineintelligence.com/going-down/
[Accessed 14 Dec. 2016].
68
Glass, J. (2016). Scotch vs. Bourbon vs. Rye: A Complete
Guide to Whiskey Varieties. [online] Thrillist. Available at:
https://www.thrillist.com/vice/rye-vs-bourbon-vs-scotch-whiskey-types-explained-guide-to-different-types-of-whisky-whiskey
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Grandsmalts.fr. (2013). La
géographie du whisky | Le Clan des Grands Malts. [online] Available
at:
https://www.grandsmalts.fr/category/la-geographie-du-whisky/
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
Hamieau, C. (2013). Puni, le futur whisky italien | Malts et
Houblons, le site des passionnés de bière et de whisky.
[online]
Maltsethoublons.com. Available
at:
http://maltsethoublons.com/2013/10/08/puni-le-futur-whisky-italien/
[Accessed 8 Oct. 2016].
Hare, A. (2015). The Irish Wine Market. [online] Irish
Wine Association. Available at:
http://www.abfi.ie/Sectors/ABFI/ABFI.nsf/vPagesWine/Home/$File/IWA+Report+2015.
pdf [Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Headley.co.uk. (2016). The
Definitive Ranking of the World's Million-case Spirits Brands 2016.
[online] Available at:
http://www.headley.co.uk/headturner/millionaires2016
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Hoffmann, P. (2014). The German Wine Market. [online]
http://academyofwinebusiness.com/. Available at:
http://academyofwinebusiness.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/07/German_Wine_Market_Hoffmann_Dieter3.pdf
[Accessed 10 Oct. 2016].
Hommelibre Blog. (2010). Islande, 1783: le Laki, volcan qui
déclencha la Révolution française. [online] Available
at:
http://hommelibre.blog.tdg.ch/archive/2010/04/17/islande-1783-le-laki-volcan-qui-declencha-la-revolution-fran.html
[Accessed 13 Nov. 2016].
Hopkins, A. (2014). Top 10 flavoured whisky launches.
[online] The spirits business. Available at:
http://www.thespiritsbusiness.com/2014/04/top-10-flavoured-whisky-launches/
[Accessed 11 Dec. 2016].
69
http://www.abfi.ie/. (2015). Vision for Irish Whiskey, A
strategy to underpin the sustainable growth of the sector in Ireland.
[online] Available at:
http://www.abfi.ie/Sectors/ABFI/ABFI.nsf/vPagesSpirits/Home/$File/Vision+for+Irish+
Whiskey+May+2015.pdf [Accessed 22 Sep. 2016].
http://www.thelocal.it. (2016).
Italy knocked off podium of wine consumption worldwide.
[online] Available at:
https://www.thelocal.it/20160425/italians-no-longer-top-wine-consumption-alcohol-drinker-drinking-usa-germany
[Accessed 12 Oct. 2016].
Humbert, F. (2014). Whisky, l'alcool mondialisé.
[online] Le nouvel Economiste | Politique & Economie, Entreprises &
Management, Art de vivre & Style de vie. Available at:
http://www.lenouveleconomiste.fr/dossier-art-de-vivre/whisky-lalcool-mondialise-24252/
[Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Huyghe, C. (2015). Happening Now: 2015 Wine Trends And
Predictions From Silicon Valley Bank. [online] Forbes. Available at:
http://www.forbes.com/sites/cathyhuyghe/2015/01/21/happening-now-2015-wine-trends-and-predictions-from-silicon-valley-bank/#1617a01d3963
[Accessed 5 Dec. 2016].
Hyslop, L. (2014). Scotland loses out as Japanese whisky
named best in the world. [online]
Telegraph.co.uk. Available at:
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/foodanddrink/foodanddrinknews/11204872/Scotland-loses-out-as-Japanese-whisky-named-best-in-the-world.html
[Accessed 17 Oct. 2016].
Indifferentlanguages.com.
(n.d.). Do You Know How to Say Wine in Different Languages?. [online]
Available at:
http://www.indifferentlanguages.com/words/wine
[Accessed 30 Dec. 2016].
Kuvée. (n.d.). How It Works. [online] Available
at:
https://www.kuvee.com/pages/how-it-works
[Accessed 9 Dec. 2016].
La Revue du vin de France. (n.d.). Apprendre à
déguster le whisky : Quels sont les pays producteurs de whisky ?.
[online] Available at:
http://www.larvf.com/,apprendre-a-deguster-le-whisky-quels-sont-les-pays-producteurs-de-whisky,13187,4298473.asp
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
70
La Revue du vin de France. (n.d.). Part des anges (angels'
share). [online] Available at:
http://www.larvf.com/,part-des-anges-angels-share-definition-dictionnaire-du-vin-vocabulaire-lexique,10355,4025430.asp
[Accessed 4 Nov. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2013). Des single malts venus du froid... mais
qui réchauffent. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/life/76322/Mackmyra-single-malt-whisky-suede
[Accessed 22 Nov. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2014). Comment boirez-vous votre whisky en
2014?. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/luxe/81823/tendances-annee-whisky-2014
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2014). Le whisky japonais à l'assaut du
monde. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/luxe/82287/whisky-japonais-assaut-monde
[Accessed 17 Oct. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2015). Australie ou Nouvelle-Zélande: qui
gagne le match du whisky?. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/story/109105/australie-nouvelle-zelande-match-whisky
[Accessed 22 Nov. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2016). Pourquoi la France a-t-elle attendu 300
ans pour produire du whisky?. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/story/113051/pourquoi-france-attendu-whisky
[Accessed 6 Nov. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2016). Voilà pourquoi le whisky
français sera bientôt le meilleur au monde. [online]
Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/story/113649/whisky-francais-bientot-meilleur-monde
[Accessed 6 Nov. 2016].
Lambert, C. (2016). Yoichi, le whisky japonais tel qu'on ne
le fabrique plus en Écosse. [online] Slate.fr. Available at:
http://www.slate.fr/story/117081/yoichi-whisky-japonais-ecosse
[Accessed 17 Oct. 2016].
Lcbo.com. (n.d.). Flavoured Whisky
Trend. [online] Available at:
http://www.lcbo.com/content/lcbo/en/catalog/spirits/flavoured-whisky-trend.html#.WE3MMqLhCCQ
[Accessed 11 Dec. 2016].
71
Lencquesaing, A. (2016). Les conséquences du Brexit
sur le marché du vin ... et pour iDealwine. [online] Le blog
d'iDealwine sur l'actualité du vin. Available at:
http://www.idealwine.net/consequences-brexit-marche-vin-idealwine/
[Accessed 29 Dec. 2016].
Léon, M. and Vingtier, A. (2009). Whisky
l'indispensable. 1st ed. Paris: Flammarion, pp.60-95.
Leslie, L. (2014). Sweden moves from devoted whisky consumer
to skilled producer. [online] Financial Times. Available at:
https://www.ft.com/content/5c68c62c-7fa1-11e4-b4f5-00144feabdc0
[Accessed 21 Nov. 2016].
Lyons, W. (2015). Is Japanese Whisky Better Than
Scotch?. [online] WSJ. Available at:
http://www.wsj.com/articles/is-japanese-whisky-better-than-scotch-1421250140
[Accessed 30 Nov. 2016].
Mackmyra. (n.d.). Mackmyra Whisky - Mackmyra. [online]
Available at:
http://mackmyra.com/mackmyra-whisky/
[Accessed 22 Nov. 2016].
Mackmyra. (n.d.). THE GRAVITY DISTILLERY - Mackmyra.
[online] Available at:
http://mackmyra.com/the-gravity-distillery/
[Accessed 22 Nov. 2016].
Mald, C. and Vingtier, A. (n.d.). Iconic Whisky Single Malts
& More. 1st ed. Editions de la Martinière, pp.14-72.
Marchetti, N. (2015). Pune Distillery Releases First Italian
Single Malt Whisky - The Whiskey Wash. [online] The Whiskey Wash.
Available at:
http://thewhiskeywash.com/world/puni-distillery-italian-single-malt/
[Accessed 25 Nov. 2016].
Marian, J. (2016). Wine consumption in Europe by country per
year per capita. [online]
Jakubmarian.com. Available at:
https://jakubmarian.com/wine-consumption-in-europe-by-country-per-year-per-capita/
[Accessed 15 Sep. 2016].
72
Masterofmalt.com. (n.d.).
Whisky Or Whiskey - Master of Malt. [online] Available at:
https://www.masterofmalt.com/whisky-or-whiskey/
[Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
McMillan, R. (2016). State of the Wine Industry 2016.
[online] Silicon Valley Bank. Available at:
https://www.svb.com/wine-report/
[Accessed 5 Dec. 2016].
Mercer, C. (2016). Key world wine consumption trends -
Vinexpo - Decanter. [online] Decanter. Available at:
http://www.decanter.com/wine-news/key-world-wine-consumption-trends-vinexpo-291224/
[Accessed 16 Oct. 2016].
Mercer, C. (2016). Top wine consuming countries in 2015 -
Decanter. [online] Decanter. Available at:
http://www.decanter.com/wine-news/top-wine-consuming-countries-2015-oiv-300080/
[Accessed 12 Sep. 2016].
Motion, H. (2015). Whisky to push global spirits consumption
to 3.2bn by 2020 - Drinks International - The global choice for drinks
buyers. [online]
Drinksint.com. Available at:
http://drinksint.com/news/fullstory.php/aid/5736/Whisky_to_push_global_spirits_consu
mption_to_3.2bn_by_2020.html [Accessed 12 Oct. 2016].
New Zealand Trade and Enterprise, London, (2008). Market
Profile for Wine in Continental Europe. [online] New Zealand Trade and
Enterprise, London, p.1. Available at:
http://www.iccnz.com/assets/Reports/European-Wine-industry.pdf
[Accessed 13 Dec. 2016].
Nierenberg, C. (2015). Less Vino, Please: Italian Drinking
Rates Drop. [online] Live Science. Available at:
http://www.livescience.com/52834-italian-drinking-rates-drop.html
[Accessed 8 Oct. 2016].
Oliver Cury, J. (2016). You'll Never Guess Which Country
Drinks the Most Whiskey. [online] Food & Wine. Available at:
http://www.foodandwine.com/blogs/youll-never-guess-which-country-drinks-most-whiskey
[Accessed 28 Sep. 2016].
73
Organisation Internationale de la Vigne et du Vin. (2016).
STATE OF THE VITIVINICULTURE WORLD MARKET. [online] Available at:
http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/4710/oiv-noteconjmars2016-en.pdf
[Accessed 12 Sep. 2016].
Organisation Internationale de la Vigne et du Vin. (2015).
GLOBAL ECONOMIC VITIVINICULTURE DATA. [online] Available at:
http://www.oiv.int/public/medias/2256/en-communique-de-presse-octobre-2015.pdf
[Accessed 16 Oct. 2016].
Plunkett-Hogge, K. (2016). The best whisky cocktail
recipes. [online] The Telegraph.
Available at:
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/food-and-drink/cocktails/the-best-whisky-cocktail-recipes/
[Accessed 18 Oct. 2016].
Pruett, M. (2016). The Real Difference Between Whiskey,
Bourbon, Scotch and Rye. [online] The Huffington Post. Available at:
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/michelle-pruett/whiskey-bourbon-scotch-ry_b_9548538.html
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Rouse, M. and Haughn, M. (2015). What is Millennials
(Millennial generation)? - Definition from
WhatIs.com. [online]
WhatIs.com. Available at:
http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/millennials-millennial-generation
[Accessed 13 Oct. 2016].
Samuel, H. and Phillips, J. (2016). Wine around the world:
who drinks the most?. [online] The Telegraph. Available at:
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2016/04/25/italy-drinks-less-wine-than-germany-in-historic-drop/
[Accessed 8 Oct. 2016].
Sandham, T. (2016). Forget about old single malts - give No
Age Statement (NAS) whisky a try. [online] The Telegraph. Available at:
http://www.telegraph.co.uk/food-and-drink/whisky/forget-about-old-single-malts---give-no-age-statement-nas-whisky/
[Accessed 19 Dec. 2016].
Satran, J. (2015). Millennials Hate Beer, Survey Finds.
[online] The Huffington Post. Available at:
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/2015/05/27/millennials-beer_n_7446460.html
[Accessed 13 Oct. 2016].
74
Schofield, H. (2013). Why are the French drinking less wine?
- BBC News. [online] BBC News. Available at:
http://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-21929287
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Schrieberg, F. (2016). How Brexit Affects the Whisky
Industry. [online] Forbes. Available at:
http://www.forbes.com/sites/felipeschrieberg/2016/06/24/how-brexit-affects-the-whisky-industry/#7b8726071542
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Schrieberg, F. (2016). How Scotch Whisky Microdistilleries
Are Changing the Industry (Part 1). [online]
Forbes.com. Available at:
http://www.forbes.com/sites/felipeschrieberg/2016/09/30/6-scotch-whisky-microdistilleries-that-will-change-the-industry-part-1/#505dc84c51b9
[Accessed 2 Nov. 2016].
Scotch-whisky.org.uk. (2015).
Scotch Whisky Association - Statistical Report 2014. [online]
Available at:
http://www.scotch-whisky.org.uk/news-publications/publications/documents/statistical-report-2014/#.WERKCqLhBPM
[Accessed 22 Sep. 2016].
Scotch-whisky.org.uk. (2016).
Scotch Whisky Association - Top 20 Export Markets 2015 - Volume &
Value. [online] Available at:
http://www.scotch-whisky.org.uk/news-publications/publications/documents/top-20-export-markets-2015-volume-value/#.WERE4aLhBPM
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
Scotch-whisky.org.uk. (2016).
Scotch Whisky Association - Brexit - what now for Scotch Whisky?.
[online] Available at:
http://www.scotch-whisky.org.uk/news-publications/news/brexit-what-now-for-scotch-whisky/#.WERQwqLhBPM
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
Spiritueux, la déferlante artisanale (craft). (2016).
Vin & Spirit News, Hors-Série (Cavistes & e-commerce),
p.56.
Suntory. (2008). Suntory | News Release | International
Spirits Challenge 2008: Suntory Whisky HIBIKI 30 YEARS Wins the Trophy the
HighestHonor. [online] Available at:
http://www.suntory.com/news/2008/10243.html
[Accessed 24 Sep. 2016].
75
Taylor, C. (2014). Irish whiskey sales growing despite global
consumption slowdown. [online] The Irish Times. Available at:
http://www.irishtimes.com/business/agribusiness-and-food/irish-whiskey-sales-growing-despite-global-consumption-slowdown-1.1830327
[Accessed 5 Oct. 2016].
The Rt Hon Elizabeth Truss MP, D. (2016). Leaving the EU
could put scotch whisky exports on the rocks (Archived) - Press releases -
GOV.UK. [online] Gov.uk. Available
at:
https://www.gov.uk/government/news/leaving-the-eu-could-put-scotch-whisky-exports-on-the-rocks
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
Thenzwhisky.com. (n.d.). South
Island Single Malt 21 Y.O. | The New Zealand Whisky Collection. [online]
Available at:
http://www.thenzwhisky.com/project/101/
[Accessed 27 Nov. 2016].
Utile et pratique. (n.d.). Les pays producteurs de whisky -
Utile et pratique. [online] Available at:
http://www.utile-et-pratique.fr/les-pays-producteurs-de-whisky/
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
Vin, L. (2016). Plus d'un Français sur trois a
déjà acheté du vin sur Internet en 2016.
[online] Le Figaro - Le Figaro Vin. Available at:
http://avis-vin.lefigaro.fr/economie-du-vin/o128076-un-francais-sur-trois-deja-achete-vin-sur-internet-en-2016
[Accessed 4 Dec. 2016].
Vins-bordeaux-negoce.com.
(2015). Union des Maisons de Bordeaux | UMB | Wine in France. [online]
Available at:
http://www.vins-bordeaux-negoce.com/reperes-economiques-2/le-vin-en-france/?lang=en
[Accessed 20 Sep. 2016].
Whisky.com. (n.d.). Types of Whisky
casks -
Whisky.com. [online] Available
at:
https://www.whisky.com/information/knowledge/production/background-knowledge/types-of-whisky-casks.html
[Accessed 28 Oct. 2016].
Whisky.fr. (2016). Les Etats-Unis : le pays du bourbon et du
rye - Maison du Whisky.
[online] Available at:
http://www.whisky.fr/whiskey-americain
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
76
Whisky.fr. (n.d.). Le Japon : l'autre pays du whisky -
Maison du Whisky. [online] Available at:
http://www.whisky.fr/whisky-japonais
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
Whisky.fr. (n.d.). L'Ecosse : le pays au plus grand nombre de
distilleries - Maison du Whisky. [online] Available at:
http://www.whisky.fr/whisky-ecossais
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
Whisky.fr. (n.d.). Les types de whiskies - Maison du
Whisky. [online] Available at:
http://www.whisky.fr/achat/alcool/whiskies/types.html
[Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
Whisky.fr. (n.d.). L'Irlande : le pays du whisky léger
et très fruité - Maison du Whisky. [online] Available at:
http://www.whisky.fr/whiskey-irlandais
[Accessed 23 Nov. 2016].
Whiskyforeveryone.com.
(2011). What is the difference between whisky and whiskey? -
whiskyforeveryone.com.
[online] Available at:
http://www.whiskyforeveryone.com/whisky_basics/whisky_or_whiskey.html
[Accessed 17 Sep. 2016].
Whiskyforeveryone.com.
(n.d.). Information on whisky and whiskey producing regions the world -
whiskyforeveryone.com.
[online] Available at:
http://www.whiskyforeveryone.com/whisky_regions.html
[Accessed 23 Oct. 2016].
Whiskyinvestdirect.com.
(n.d.). Worldwide whisky production | WhiskyInvestDirect. [online]
Available at:
https://www.whiskyinvestdirect.com/about-whisky/world-whiskies
[Accessed 24 Oct. 2016].
Whiskymag. (2013). Whisky Magazine World Whiskies Awards
2013. [online] Available at:
http://www.whiskymag.fr/actualites/whisky-magazine-world-whiskies-awards-2013/
[Accessed 6 Nov. 2016].
Wikipédia. (n.d.). History of wine. [online]
Available at:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_wine
[Accessed 13 Dec. 2016].
Wikipedia. (n.d.). Laki. [online] Available at:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Laki
[Accessed 13 Nov. 2016].
77
World Health Organisation, (2014). Global status report on
alcohol and health 2014. [online] WHO, pp.43-52. Available at:
http://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/global_alcohol_report/msb_gsr_2014_
1.pdf?ua=1 [Accessed 12 Dec. 2016].
WSTA. (2015). WSTA Market Overview London Wine Fair 2015
Edition. [online] Available at:
http://www.wsta.co.uk/images/Research/Market-Reports/LWFOverview2015.pdf
[Accessed 18 Sep. 2016].
Yan, S. (2016). The world is running low on old single malt
Scotch. [online] CNNMoney. Available at:
http://money.cnn.com/2016/03/04/luxury/global-single-malt-scotch-whisky-drought/
[Accessed 20 Oct. 2016].
| 


