4.3.3. Fire frequency and intensity in Comoé
National Park and Upper Aguima Catchment
In Upper Aguima Catchment, the fire frequency ranged from 1 to
3. In 1995, 1998 and 2001, the fire was used only during dry season but in
1998, three different fires were used consecutively (dry season, rain season
and at the end of rain season). In CNP, the fire frequency ranged from 1 to 2.
Most of them occurred during dry season when phytomass are abundant and dry.
The intensity of fire was assessed in CNP and five «high
fires date» were identified. These are originated from 1980, 1992, 1993,
1996 and 1997. The fire occurred during dry season when the combustible were
available.
4.3.4. Conclusion and discussion on events of fire in
savanna areas.
This study showed that the CNP needed more attention to become a
real biodiversity conservation area. The frequently use of fire caused a lost
of biodiversity.
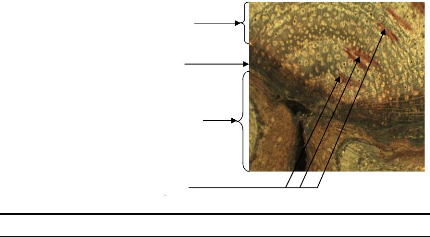
Compartment formed before bush fire
scar
Fire scar
Compartment formed after bush fire scar
Annual rings
Figure 17: Illustration of compartmentalisation
concept on D. microcarpum stem disc
Concerning trees, when the stem was injured, the tree develops
a dynamic defence process which forms structural and chemical boundaries in
order to resist the spread of pathogens. In short time, the tree forms
compartment and this positive reaction of the tree is named
compartmentalisation. The wood formed just after a fire injury showed an
anatomical wood which is different from the normal. Most of time, no vessel was
observed in this part of wood but a callous margin (edge of callous tissue
overgrowing a stem wound) was formed.
| 


